GH4586合金是我国自主开发的一种高合金化的镍基变形高温合金,该合金在-192~850 ℃范围内表现出优良的力学和物理性能,目前已用于制造多种型号的火箭发动机高温转动盘锻件[1~3]。如表1所示,GH4586合金的成分与René 41[4]和GH4738[5]合金成分相近,具有高Ti、低Al和高W、Mo的特点。目前,该合金采用双真空冶炼工艺(真空感应熔炼+真空自耗重熔)可实现直径460 mm以下锭型的稳定批量生产[6],但是扩大锭型至直径508 mm以上,当冶炼工艺不合理时会出现白斑冶金缺陷,并且遗传至盘锻件上,对发动机的安全服役带来了隐患。前期试制结果表明,采用双真空冶炼直径508 mm铸锭制备的GH4586合金盘锻件上易形成白斑缺陷,但白斑缺陷对该合金组织和性能的影响尚不明确。
表1 典型盘锻件用变形高温合金的名义成分 (mass fraction / %)
Table 1
| Alloy | C | Cr | Co | Ti | Al | W | Mo | Nb | Fe | Ni |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH4586 | 0.06 | 19.0 | 11.0 | 3.20 | 1.6 | 3.0 | 8.0 | - | - | Bal. |
| GH4141 | 0.06 | 15.0 | 11.0 | 3.10 | 1.5 | - | 9.5 | - | - | Bal. |
| GH4169 | 0.03 | 19.0 | - | 0.95 | 0.5 | - | 3.0 | 5.2 | Bal. | 52.5 |
| GH4738 | 0.03 | 19.5 | 13.5 | 3.10 | 1.4 | - | 4.3 | - | - | Bal. |
对于燃气涡轮式的航空航天发动机而言,高压压气机盘、高低压涡轮盘等变形高温合金盘类转动部件的冶金质量十分关键,尤其是白斑缺陷[7~9]。白斑缺陷区域的溶质元素贫化,在低倍腐蚀时因浅腐蚀而呈白色斑点,故称为白斑缺陷[10]。由于白斑缺陷在高温合金中的形成机制与来源较为复杂,其形成的关键冶炼参数判据尚未完全掌握,且采用现有无损检测方法较难识别,因而是当前国内外变形高温合金领域关注度最高的冶金缺陷之一[7,11~13]。根据白斑缺陷的形状、特点和形成原因,可分为分离(discrete)白斑、枝晶(dendritic)白斑和凝固(solidification)白斑[10]。分离白斑的特征为与基体有明显的边界,其成因是锭壳、锭冠和电极突出物落入熔池未完全熔化残留形成。当落入物洁净度较差时,分离白斑中可能形成氧化物、氮化物和/或碳化物团簇,即“脏(dirty)白斑”,对合金性能危害较大;枝晶白斑呈树枝晶形貌,其成因是电极缩孔导致电弧不稳造成枝晶团簇落入熔池,即“电极掉块”未完全熔化残留形成;凝固白斑呈线状、环状或钩状,其成因是在浅平的熔池条件下,熔速过低会造成一次枝晶臂不断粗化,粗化后的枝晶臂将枝晶间富溶质元素的熔体排出,进而形成贫溶质元素的浅腐蚀区[7,10,14]。
国外针对GH4169、GH4738等合金中的白斑缺陷开展了较多的研究[10,13~15]。GH4169合金为高Nb含量的Fe-Ni基变形高温合金(表1),易偏析元素Nb的贫化是该合金白斑的最主要特征。脏白斑是GH4169合金冶金质量控制的关键问题,严重时会导致盘体的非包容性破裂,已造成过严重的飞行事故[13]。GH4738合金为高Ti、低Al的镍基变形高温合金[16],与GH4586合金相比,其Mo含量较低且不含W,合金化程度相对较低。虽然国外基于对GH4169、GH4738等合金的研究,基本明确了变形高温合金中白斑的种类及其对应的形成机制,但是对于GH4586合金而言,高合金化的成分特点使其白斑缺陷表现出独有的组织特征,因此需要系统研究其对该合金组织和力学性能的影响。
值得注意的是,采用真空自耗作为最终重熔工艺制备的铸锭,从工艺上无法确保彻底消除分离白斑和枝晶白斑[17]。因此,系统掌握白斑缺陷对GH4586合金盘锻件组织和力学性能的影响,对评估合金零部件质量、寿命设计和可靠性,以及明确白斑缺陷的形成机制和控制方法均具有重要的意义。鉴于此,本工作以实际生产中发现的GH4586合金盘锻件上的白斑缺陷为研究对象,系统分析白斑缺陷的组织特征及其对力学性能的影响,为更深入地认识变形高温合金的白斑缺陷提供数据支撑。
1 实验方法
实验材料为前期试制中发现的带有白斑缺陷的GH4586合金盘锻件,名义成分见表1。实验用盘锻件的主要制备工艺为:采用真空感应熔炼制备直径430 mm感应锭,感应锭作为自耗电极经真空自耗重熔制备直径508 mm自耗锭,经高温均匀化处理(1190 ℃保温48 h)后利用快锻机开坯制备直径280 mm棒材,再利用锻压机模锻为直径600 mm的盘锻件,盘锻件经热处理(1080 ℃保温4 h+760 ℃保温16 h)后进行机加工。当盘锻件加工至半精加工尺寸时浸入酸槽内进行低倍腐蚀,确定白斑缺陷位置,根据白斑缺陷尺寸利用线切割取组织观察试样、硬度试样和拉伸性能试样。
显微组织分析采用GX71型光学显微镜(OM)、JXA-8530型电子探针(EPMA)、JSM-7800F型扫描电子显微镜(SEM)和Thermofisher Tecnai型透射电子显微镜(TEM),SEM和EPMA分别采用二次电子(SE)和背散射电子(BSE)模式观察,其中TEM样品采用Thermofisher G4 HX型聚焦离子束(FIB)提取,TEM样品薄区厚度约为50 nm,利用TEM进行选区电子衍射(SAED)和能谱(EDS)鉴定第二相种类。利用KB30SR-FA型Vickers硬度计分别测试正常区域和白斑缺陷区域的Vikers硬度,按照GB/T 4340.1-2009标准执行,测量5个点后取平均值(aver.)和标准偏差(stand. deviation)。拉伸性能试样标距段尺寸为直径3 mm×15 mm,取样时确保白斑缺陷位置在拉伸性能试样的标距段上,各测3个试样后取平均值和标准偏差,室温拉伸性能测试按照GB/T 228.1-2010标准执行。拉伸性能测试完成后,利用SEM对拉伸断口的断面和剖面进行形貌观察。
为了分析合金的第二相种类及其对应的化学组成,利用Jmatpro软件计算合金凝固相图(SPD)与热力学平衡相图(TPD)。为探究白斑缺陷的形成机制,利用Procast数值模拟软件仿真分析合金感应锭凝固过程中的温度、应力及缩孔情况,并对GH4586合金的感应锭进行解剖,分析枝晶组织、偏析和缩孔情况。
2 实验结果
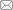
2.1 白斑缺陷的组织形貌
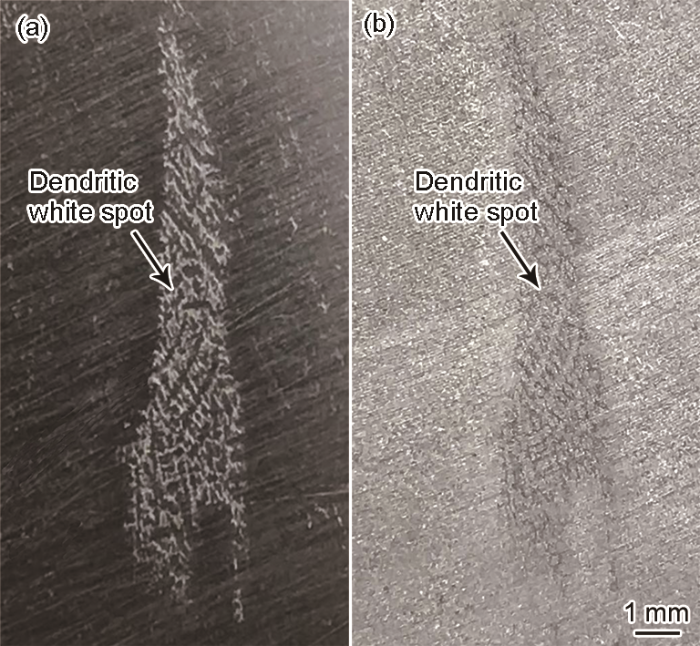
图1
图1
GH4586合金盘锻件上白斑缺陷的典型宏观形貌
Fig.1
Typical macro morphologies of white spot defects in the GH4586 alloy disk
(a) polished (b) etched
图2
图2
GH4586合金盘锻件中白斑缺陷的OM和SEM像
Fig.2
OM (a), SEM-BSE (b, c) and SEM-SE (d~f) images showing typical micro morphologies of white spot defects in the GH4586 alloy disk
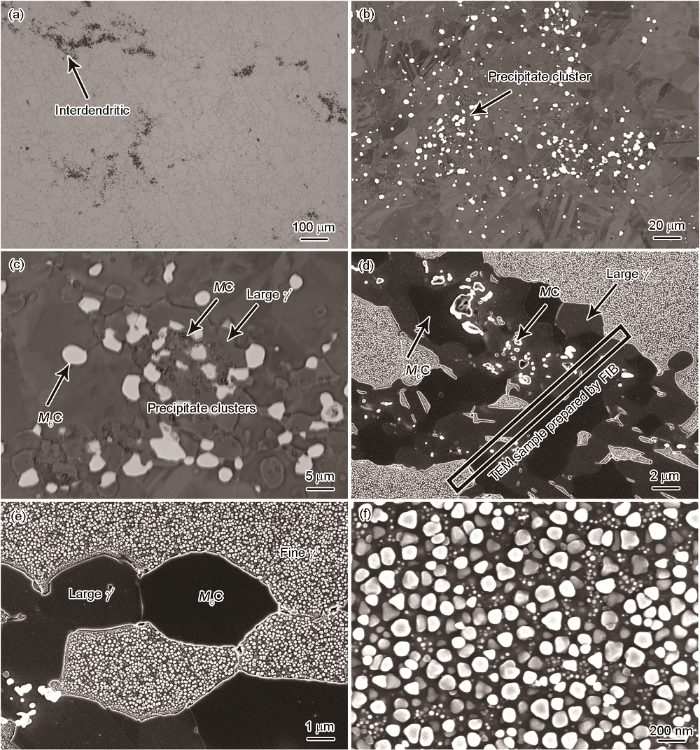
2.2 白斑缺陷中的第二相
图3
图3
对应图2a区域白斑缺陷的EPMA元素面扫描分布图
Fig.3
EPMA elemental maps of the white spot defect corresponding to Fig.2a
Color online
图4
图4
对应图2c区域白斑缺陷的EPMA元素面扫描分布图
Fig.4
EPMA elemental maps of white spot defect corresponding to Fig.2c
Color online
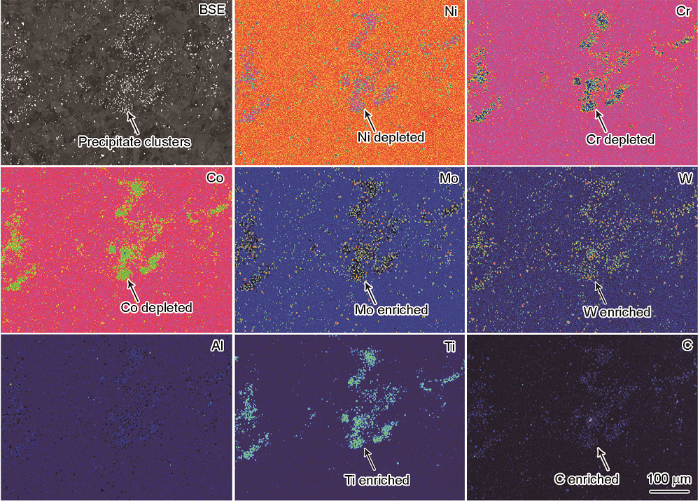
图5
图5
对应图2d框线位置的白斑缺陷中第二相团簇的TEM像和SAED花样
Fig.5
TEM image (a) and SAED patterns of positions P1 (b), P2 (c) and P3 (d) of the precipitate clusters in white spot defect shown in the Fig.2d with the wire frame
表2 图5a中P1、P2和P3位置的EDS分析结果 (atomic fraction / %)
Table 2
| Position | C | Al | Ti | Cr | Co | Ni | Mo | W |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 0.30±0.17 | 9.29±2.42 | 14.39±3.10 | 2.24±0.48 | 5.59±1.21 | 67.62±14.60 | 0.44±0.11 | 0.14±0.03 |
| P2 | 7.72±0.95 | 1.31±0.30 | 5.25±0.90 | 23.20±3.96 | 10.25±1.75 | 22.61±3.86 | 23.29±4.27 | 6.37±0.97 |
| P3 | 47.49±5.94 | 0.26±0.06 | 42.24±7.70 | 0.53±0.10 | 0.15±0.03 | 0.44±0.08 | 7.01±1.36 | 1.88±0.31 |
2.3 白斑缺陷对力学性能的影响
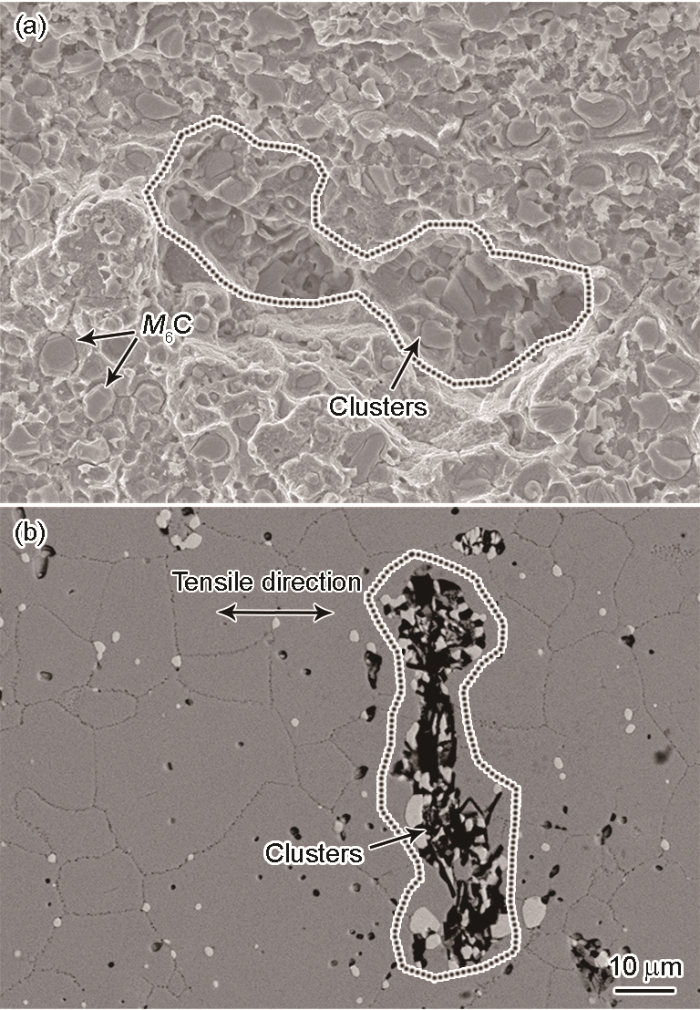
白斑缺陷和正常区域的硬度和室温拉伸性能测试结果见表3。白斑缺陷对GH4586合金的硬度和室温拉伸性能的影响较大。与正常区域相比,白斑缺陷区域的硬度提高18.61%,但室温抗拉强度和塑性显著降低,抗拉强度降低20.71%,屈服强度小幅降低1.72%,延伸率显著降低97.30%,面缩率大幅降低87.5%。对白斑缺陷部位的断口形貌和纵剖面进行观察分析,结果示于图6。由图6a可见,断口表面有较多块状M6C型碳化物;由图6b可见,近断口表面的第二相团簇沿垂直于拉伸方向出现明显开裂,且该断裂位置与图6a所示断口表面凹坑的尺寸和形状相一致。这表明,与基体组织相比,第二相团簇更易开裂,属于高硬度的脆性相,应为造成白斑缺陷区域拉伸性能大幅降低的主要原因。
表3 白斑缺陷区域与正常区域的Vikers硬度和室温拉伸性能
Table 3
Area | Hardness / HV | σb / MPa | σ0.2 / MPa | δ / % | ψ / % | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aver. | Stand. deviation | Aver. | Stand. deviation | Aver. | Stand. deviation | Aver. | Stand. deviation | Aver. | Stand. deviation | |
| Normal | 446 | 15.52 | 1487 | 38.21 | 1107 | 18.81 | 18.5 | 3.88 | 16.0 | 3.00 |
| Defect | 529 | 16.31 | 1179 | 7.41 | 1088 | 1.73 | 0.5 | 0.28 | 2.0 | 0.57 |
图6
图6
白斑缺陷拉伸试样断口形貌及纵剖面近断口处形貌
Fig.6
Typical fracture morphology (a) and the morphology of longitudinal section nearby the fracture (b) of the tensile sample with white spot defect
3 分析讨论
3.1 白斑缺陷对组织和力学性能的影响
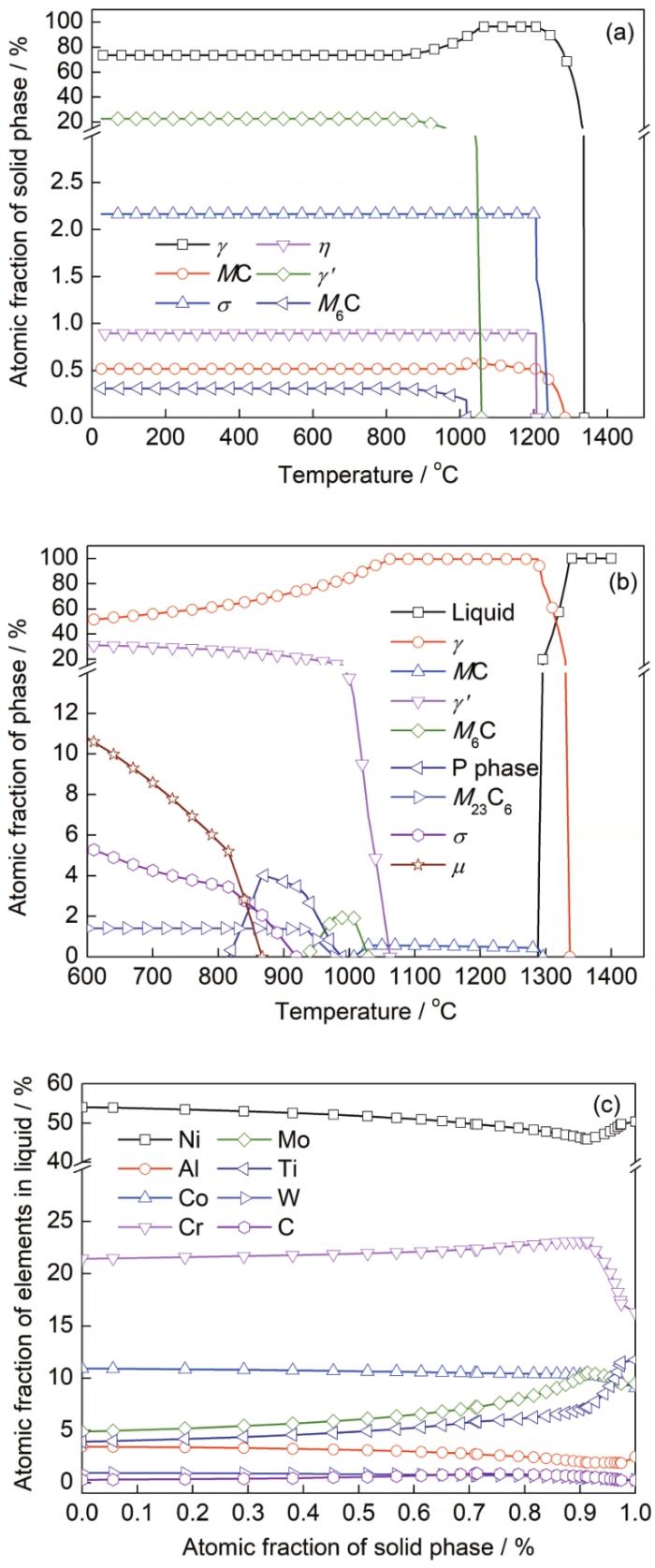
图7为GH4586合金凝固相图、热力学平衡相图和凝固过程液相中元素含量计算结果。从图7a和b可见,GH4586合金在凝固条件下和热力学平衡条件下可能析出的第二相种类不同,在凝固条件下可能会析出η相、MC型碳化物、M6C型碳化物、γ′相和σ相(图7b);在热力学平衡条件下,合金中可能会析出MC型碳化物、M6C型碳化物、M23C6型碳化物、γ′相、σ相、μ相和P相(图7b),上述各相的化学组成列于表4。从图7c可见,GH4586合金在凝固条件下,随着固相含量的增加,液相中溶质元素的含量相对富集或贫化。在固相含量超过95%条件下,液相中的Ti、Mo、Cr元素为正偏析,W、Al、Ni、Co元素为负偏析。
图7
图7
GH4586合金凝固相图、热力学平衡相图和凝固过程液相中元素含量计算结果
Fig.7
Solidification phase diagram (a), thermodynamic phase diagram (b) and element fraction of liquid during the solidification (c) of the GH4586 alloy calculated by Jmatpro
表4 基于Jmatpro软件计算得到的GH4586合金凝固相图和热力学平衡相图中各相的化学组成 (atomic fraction / %)
Table 4
| Phase | Method | Ni | Al | Co | Cr | Mo | Ti | W | C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MC | SPD | - | - | - | 0.20 | 0.37 | 52.25 | 0.62 | 46.56 |
| σ | SPD | 23.47 | 0.05 | 11.46 | 39.13 | 25.49 | - | 0.39 | - |
| η | SPD | 66.37 | 1.91 | 8.76 | 0.27 | - | 22.70 | - | - |
| MC | TPD | - | - | - | 0.35 | 0.33 | 48.70 | 2.67 | 47.95 |
| σ | TPD | 16.52 | 0.00 | 18.95 | 54.89 | 9.51 | - | 0.13 | - |
| γ′ | TPD | 71.95 | 10.23 | 3.15 | 1.80 | 0.09 | 12.39 | 0.40 | - |
| M6C | TPD | 26.60 | - | 2.84 | 20.19 | 32.89 | - | 3.19 | 14.29 |
| M23C6 | TPD | 3.02 | - | 1.28 | 64.96 | 10.00 | 0.00 | 0.04 | - |
| P | TPD | 27.34 | - | 7.74 | 30.76 | 25.01 | - | 9.15 | - |
| μ | TPD | 23.82 | - | 21.14 | 20.53 | 29.54 | - | 4.97 |
对比表2和4,可进一步确定图2中块状富Ni、Ti的第二相为大尺寸γ′相(P1),块状富W、Mo的碳化物为M6C型碳化物(P2),颗粒状的富Ti的碳化物为MC型碳化物(P3)。对比分析图7b与图3、4可知,GH4586合金中枝晶白斑缺陷的元素偏析与凝固过程中枝晶元素偏析的规律基本一致。值得指出,白斑缺陷中部分元素如Ni、W的偏析规律与凝固过程中枝晶元素偏析规律不一致,其原因与枝晶白斑中大量的第二相析出有关。对比可知,GH4586合金枝晶白斑中析出的第二相(图5和表2),基本符合合金凝固过程中的第二相析出规律(图7a和表4)。GH4586合金凝固过程中枝晶间富集Mo、Ti元素(图7c),故而形成了大量的M6C和MC型碳化物;在凝固过程中Ni元素为负偏析元素,而富Ni、Ti的大尺寸γ′相大量析出,使得枝晶白斑中出现了Ni元素的相对富集现象(图4)。
由上可知,由于GH4586合金较高的合金化程度,Ti、Mo元素易在枝晶间偏析,以枝晶白斑缺陷的形式遗传至盘锻件上,造成枝晶间区域形成了由MC型碳化物、M6C型碳化物和大尺寸非共格γ′相组成的第二相团簇。这种第二相团簇硬度高,有利于裂纹的萌生和扩展,是导致合金的抗拉强度和塑性显著降低的直接原因。GH4586合金中白斑缺陷对正常区域的共格γ′相无明显影响,因而对室温屈服强度的影响较小。
3.2 GH4586合金白斑缺陷的形成机制及控制方法
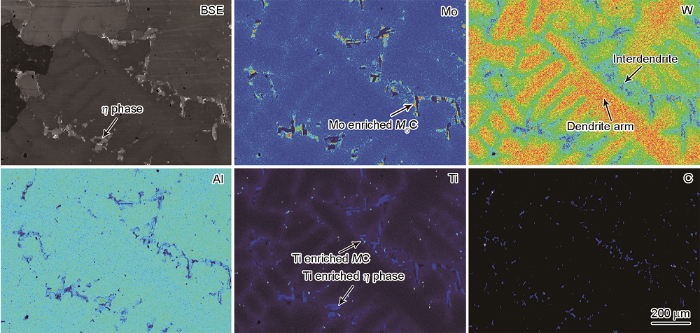
GH4586合金盘锻件的冶炼工艺采用直径430 mm的感应锭经真空自耗重熔后制备成直径508 mm的自耗锭。为了进一步明确GH4586合金中白斑缺陷的形成机制,解剖分析了GH4586合金的感应锭,即真空自耗重熔电极。图8为GH4586合金感应锭试样的EPMA元素面扫描分布图。可见,GH4586合金感应锭试样中存在明显的元素偏析,Mo、Ti为正偏析,W、Al为负偏析,该规律符合热力学计算结果(图7a);此外,感应锭上存在明显的枝晶花样,一次枝晶臂间距约为400 μm,二次枝晶臂间距约为150 μm,与图1所示白斑缺陷枝晶花样的尺寸相当;通过元素分布和热力学计算结果(表4)可初步判断感应锭试样的枝晶间析出了较多MC型碳化物、M6C型碳化物和η相。
图8
图8
GH4586合金感应锭试样的EPMA元素面扫描分布图
Fig.8
EPMA elemental maps of vacuum induction melting (VIM) ingot sample of GH4586 alloy
Color online
一次浇铸后的GH4586合金感应锭在Ar气中自然冷却凝固,由于铸锭熔池深、冷速慢,很容易在钢锭中心形成缩孔和孔洞等缺陷;而自耗锭依靠循环水和He气介质进行强冷却凝固,自耗锭的熔池浅、冷速快,所以自耗锭二次枝晶臂间距显著小于感应锭[22]。此外,经过高温均匀化处理后,GH4586合金自耗锭能够最大限度降低枝晶偏析程度[23],而图1b所示枝晶偏析仍遗传至盘锻件中,可能是由于其枝晶粗大、偏析程度大所致。由此推断,GH4586合金盘锻件中白斑缺陷的来源应是感应锭在自耗重熔过程中的掉块。与自耗锭相比[19],感应锭的枝晶更为粗大、元素偏析程度更高,在盘锻件制备过程中元素偏析未彻底消除,进而遗传至盘锻件中形成白斑缺陷。由于GH4586合金中的枝晶白斑缺陷是一种成分偏析较为严重的冶金缺陷,很难在均匀化处理、锻造和热处理等盘锻件的生产工艺环节彻底消除,因此必须优化冶炼工艺,实现白斑缺陷的有效控制。
GH4586合金在真空感应熔炼过程中,经合金熔化和精炼后的钢液在真空下浇注进铸铁的模腔内,钢液通过铸铁模具向真空室内散热,当钢液降温至固相线以下后完成凝固[9]。在凝固过程中,一方面模具向真空室的传热主要依靠热辐射,散热效率低,会造成钢锭中形成较大的温度梯度,进而形成较大的热应力;另一方面钢锭在凝固过程中会发生体积收缩,先凝固的部分会对未凝固部分产生一定的拉应力;此外,GH4586合金的合金化程度高,钢锭凝固过程中枝晶偏析倾向大,合金中的Ni3(Al, Ti)型γ′相析出速率极快[24],γ′相的不均匀析出还会进一步增大内应力。图9所示为GH4586合金感应锭凝固过程的数值模拟结果,包括钢锭浇铸1/4、钢锭浇铸完成、浇铸后3种不同冷却阶段(t1、t2、t3表示冷却时间逐渐延长)共5个状态下的温度、固相含量、内应力和缩孔分布图。可见,在浇铸阶段钢锭中的温度梯度、内应力和缩孔含量均较低;浇铸完成后随冷却时间延长,钢锭中形成了较大的温度梯度,至t3时间钢锭顶端发生明显补缩,钢锭底端形成较多缩孔,并在钢锭内部形成了较大的内应力。
图9
图9
GH4586合金真空感应锭凝固过程的数值模拟结果
Fig.9
Numerical simulations of the solidification process of GH4586 alloy VIM ingot for pouring by 1/4 (a1~d1), pouring end (a2~d2), cool for t1 (a3~d3), cool for t2 (a4~d4) and cool for t3 (a5~d5), which t1, t2 and t3 mean the cooling time increased
Color online
(a1~a5) temperature (b1~b5) mass fraction of solid phase (c1~c5) effective stress (d1~d5) total shrinkage porosity
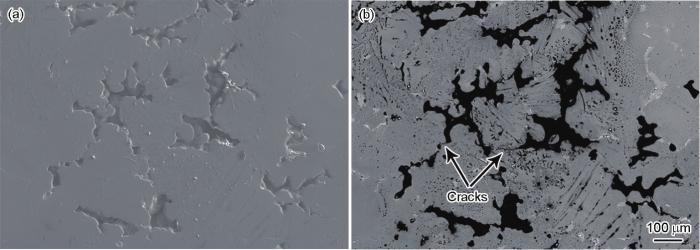
通过对GH4586合金感应锭进行解剖分析发现,钢锭中形成了较多的缩孔及其周围的裂纹,如图10所示。真空自耗重熔过程中,在电弧热的作用下感应锭端面局部熔化形成熔滴后落入熔池实现重熔精炼[9]。然而,电弧热的作用还会在感应锭中产生较高的温度梯度,由于电极中的缩孔周围存在裂纹或易于裂纹扩展,大量缩孔在应力的作用下易形成贯穿裂纹,造成电极掉块,从而形成图1所示的枝晶白斑。需要注意的是,缩孔并不会直接造成枝晶白斑形成,在内应力的作用下缩孔处裂纹萌生和扩展并造成电极掉块,才是造成枝晶白斑形成的直接原因。因此,为了有效控制GH4586合金中的枝晶白斑缺陷,提升电极致密度和降低电极内应力是重点关注的工艺优化方向。
图10
图10
GH4586合金真空感应锭中缩孔典型形貌SEM像
Fig.10
SEM-SE (a) and SEM-BSE (b) images showing typical morphologies of the shrinkage porosity in GH4586 alloy VIM ingot
综上所述,采用常规工艺生产大尺寸GH4586合金感应锭,作为自耗电极进行重熔,电极本身有较大的内应力和缩孔,在真空自耗重熔过程中,电极端部在电弧作用下瞬间熔化,会在电极中产生很大的温度梯度,促使内应力逐渐增大并导致电极开裂、掉块[25],大量缩孔的存在还会加速自耗电极中裂纹的萌生和扩展,进而增大白斑缺陷的形成几率。因此,为了控制GH4586合金中的白斑缺陷,一方面应优化感应锭的凝固工艺降低缩孔含量,并采取合理的去应力退火工艺降低内应力[26];另一方面应采用二次精炼的工艺措施,将感应锭利用真空自耗重熔或电渣重熔精炼后提高钢锭的冶金质量,改善自耗电极的致密度,再进行真空自耗重熔制备最终状态的铸锭[27]。因此,为了制备直径600 mm级的大尺寸GH4586合金盘锻件,提高自耗电极的冶金质量和优化自耗重熔工艺是控制GH4586合金盘锻件中白斑缺陷的工艺优化方向。
4 结论
(1) GH4586合金盘锻件中的白斑缺陷为枝晶白斑,宏观上表现为枝晶花样,微观组织为由MC型碳化物、M6C型碳化物和大尺寸非共格γ′相组成的第二相团簇。
(2) 由于枝晶白斑中析出了较多的高硬度、易开裂的第二相团簇,造成GH4586合金的室温抗拉强度和塑性显著降低,对GH4586合金盘锻件的力学性能影响较大。
(3) GH4586合金大尺寸真空感应锭凝固过程中会形成较大的内应力和较多的缩孔,用做电极进行自耗重熔易因缩孔开裂而发生电极掉块,落入熔池后则会成为白斑缺陷。提升自耗电极的质量和优化真空自耗工艺,是控制GH4586合金盘锻件中的白斑缺陷的工艺优化方向。
参考文献
Influence of hot working process on microstructures of superalloy GH4586
[J].The effects of temperature, strain rate and plastic strain on flowbehavior and microstructures of GH4586 wrought superalloy wereinvestigated by compressive deformation performed on MTS machine atdeformation temperatures of 950 to 1150℃ and strain ratesof 0.001 to 1 s-1. The results show that the flow stress increasesdrastically with the decrease of deformation temperature and the increaseof strain rate. Dynamic recrystallization process can be effectivelypromoted by increasing deformation temperature. When deformationtemperature is higher than 1100℃, completely recrystallizedmicrostructures can be obtained with engineering strain of 30%, whilewhen the temperature is lower than 1050℃, dynamic recrystallizationdoes not occur with engineering strain up to 40\%. Grain size of annealedmicrostructures increases with the increase of deformation temperature.Ideal plasticity and resultant microstructures can be achieved by effectivecontrol of deformation temperature.
热加工工艺对GH4586合金微观组织的影响
[J].在MTS热模拟实验机上采用热压缩实验的方法研究了在温度为950—1150℃、应变速率为0.001—1 s-1的实验条件范围内,GH4586合金高温塑性变形过程中变形温度、应变速率及变形量等工艺参数对流变应力和微观组织的影响。结果表明, 流变应力随着变形温度的降低和应变速率的提高而迅速增大。提高变形温度能够有效的促进动态再结晶过程, 在1100℃以上变形时, 在30%的工程应变量下即能够获得完全再结晶的锻态组织;当变形温度低于1050℃时, 工程应变超过60%仍未观察到动态再结晶。在变形量与热处理制度一定的条件下, 材料热处理后的晶粒度随变形温度的升高而增大。有效控制材料的变形温度是获得良好热加工塑性、降低变形抗力和获得均匀微观组织的关键措施。
Effects of precipitated phases on the crack propagation behaviour of a Ni-based superalloy
[J].
Effect of long-term aging on the fatigue crack growth rate of a nickel-based superalloy
[J].
Processing of nickel-base superalloys for turbine engine disc applications
[J].
Research progress of wrought superalloys in China
[J].etc. These products are widely used in aviation, aerospace, energy, petrochemical, nuclear power and other industrial fields. In this paper, domestic progress of wrought superalloys in recent ten years was reviewed, including advances in fabrication process, research in new alloys (GH4169G, GH4169D, GH4065 and GH4068 alloy et al.) and new techniques (deforming of FGH4096 alloy, nitriding of NGH5011 alloy and 3D printing of In718 alloy et al.).]]>
国内变形高温合金研制进展
[J].变形高温合金是指通过铸造-变形工艺生产的高温合金,包括盘、板、棒、丝、带、管等产品,该类产品广泛用于航空、航天、能源、石化、核电等工业领域。本文介绍了国内变形高温合金近10年的最新进展,分别从变形高温合金的制备工艺流程,GH4169G、GH4169D、GH4065、GH4068等新合金的研制,以及FGH4096的变形化、NGH5011的氮化、In718合金的3D打印等新技术3个方面展开论述。
Effect of cooling rate after solid solution on microstructure and tensile properties of GH4586 superalloy at 850 ℃
[J].
固溶冷却速度对GH4586合金组织及850 ℃拉伸性能的影响
[J].
Development of several important problems on producing technologies of wrought superalloy
[J].
变形高温合金生产工艺中几个重要问题的研究和进展
[J].
Investigation on the abnormal corrosion spots of GH4169G alloy parts
[J].
GH4169G合金零件异常腐蚀区缺陷分析
[J].
White spots in superalloys
[A].
Recent development of nickel-based disc alloys and corresponding cast-wrought processing techniques
[J].et al. These alloys can provide a promising solution of high reliability combined with low life cycle cost for military and commercial gas turbines. Nonetheless, in order to maximize the advantageous of cast-wrought disc alloys on reliability and cost-effective ratio, the comprehensive understanding about the prevention and identification of metallurgical defects, increase in the yield rate of materials during conversion, processing of fine-grained billets and dual-property disc forgings, is still needed.]]>
变形高温合金盘材及其制备技术研究进展
[J].近年来一系列新型的高性能变形高温合金盘材在航空发动机和燃气轮机上获得了重要应用,这些盘材合金在追求高承温能力的同时更加注重服役性能、工艺性能与全寿命成本之间的平衡。国内在三联熔铸直径508 mm自耗锭、多重循环热机械处理制备直径300 mm以上细晶棒材、盘件热模锻成型与组织性能控制等关键制备技术取得突破的基础上,成功研制了GH4065、GH4720、GH4175与GH4975等一系列高性能盘材合金及全尺寸锻件,为先进军用涡扇发动机、大涵道比商用发动机提供了高可靠性、低成本的盘件选材方案。为充分发扬变形盘材在可靠性与成本方面的特有优势,需要在高性能盘材的合金设计与成分优化、自耗锭冶金缺陷的预防与识别、自由锻开坯的效率与成材率提升、双组织双性能盘件制备等方面进一步开展深入的研究工作。
The influence of VAR processes and parameters on white spot formation in alloy 718
[A].
On the formation of white-spot defects in a superalloy VAR ingot
[J].
Integrated simulation of the forging process for GH4738 alloy turbine disk and its application
[J].In order to control the grain size of forged turbine disk of wrought superalloy like GH4738 more effectively, constitutive equations and grain structure evolution models of GH4738 alloy are used in Deform 3D (TM) for achieving integrated simulation of whole forging process of GH4738 alloy turbine disk (from preheating billet for upsetting to die forging). By using of integrated simulation, the variation of temperature, average grain size, etc., during the whole forging process has been explored, making it possible to control these parameters quantitatively. Comparing with traditional simple stage simulation, results of integrated simulation are more consistent with corresponding experimental results of forged turbine disk (300 mm in diameter). Therefore, the reliability of the integrated simulation is verified. Finally, with the application of integrated simulation, GH4738 alloy turbine disk with a diameter of 1450 mm has been successfully forged by 8x10(4)t forging press. This work provides a more practical simulation method for helping the process design of forging large turbine disk.
GH4738合金涡轮盘锻造过程的集成式模拟及应用
[J].TM软件对该合金涡轮盘从自由锻前预热直至模锻完成的整个锻造过程的集成式模拟. 借助集成式模拟实现了对锻件在整个锻造过程中温度、平均晶粒尺寸等参数的定量控制. 同时采用直径300 mm涡轮盘的实际锻造结果验证了所用模型和该模拟方法的可靠性. 最后, 把集成式模拟运用于直径1450 mm涡轮盘盘件的锻造过程模拟, 并根据模拟优化方案在8×104 t锻压机下成功锻制直径1450 mm涡轮盘盘件. 为大型变形高温合金涡轮盘的锻造成型提供了工艺优化的理论依据和研究方法.]]>
Characterizing solute-lean defects in superalloys
[J].
Study on freckle of a high-alloyed GH4065 nickel base wrought superalloy
[J].η-phases, block M3B2 borides and MC carbides are formed in the forged condition. It is confirmed by the thermodynamic calculations that the η-phases, M3B2 borides and MC carbides are much easier forming in the freckle than that in matrix. After heat treatment, compared with matrix, the lathy η-phases are still existed in the freckle; the size and quantity of primary γ′ phases increase significantly while the size and morphology of the secondary γ′ phase are basically identical, only with less quantity. It has been found that due to the high content of γ′ phase, the γ′ dissolution temperature in the freckle is higher than that in the matrix. This induces an impeded recrystallization process caused by the coarsened γ′ phases during forging process and the grain size of the freckle region is significantly smaller than that of matrix. Based on this study, the formation of freckle can be effectively controlled by meticulous controlling of the previous smelting process, releasing of electrode residual stress, suitably reducing VAR melting rate, and accelerating VAR cooling.]]>
高合金化GH4065镍基变形高温合金点状偏析研究
[J].η相、块状M3B2型硼化物与MC型碳化物。热力学相计算亦证实了点状偏析区较正常组织区域更容易生成η相、M3B2和MC。热处理后,与正常组织区域相比,点状偏析中仍存在板条状η相,一次γ′相的尺寸和数量明显增加,二次γ′相尺寸和形貌基本相同但数量减少。分析发现,由于点状偏析区的成分变化使得γ′相回溶温度升高,导致锻造中粗大γ′相阻碍再结晶长大,点状偏析区晶粒尺寸小于正常组织区域。采取前道次冶炼精细化控制、释放电极残余应力、适度降低真空自耗重熔熔化速率、加强真空自耗重熔冷却等措施,可以有效降低点状偏析的形成倾向。]]>
Thermodynamic simulation of precipitations in GH586 superalloy
[J].
GH586高温合金析出相的热力学模拟计算
[J].利用热力学计算软件Thermo-Calc与相应的Ni基高温合金数据库,从热力学角度通过计算最小吉布斯自由能,得到GH586合金可能析出的平衡相,并预测化学成分对析出相的影响,分析各相的析出规律,为挖掘合金组织潜力和改善合金使用性能提供理论依据.
The structural evolution of superalloy ingots during hot working
[J].
Advances in triple melting superalloys 718, 706, and 720 [A]. Superalloys 718, 625, 706 and Various Derivatives
[C].
Effect of extent of homogenization on the hot deformation recrystallization of superalloy ingot in cogging process
[J].The elimination of the segregation improves the thermo plasticity of superalloy ingot during the homogenization process, but coarser grain structure and high-temperature oxidation caused in further homogenization have an adverse impact on the thermo plasticity. The inheritance of coarse grain structure in the followed hot working process increases the tendency of cogging crack and makes the grain refining harder, leading to a lower yield of the final workpiece. The microstructure characteristics and their hot deformation behaviors of GH4740H, GH4738, GH3625 and 690 alloys under different homogenizations were investigated by means of microstructure analysis methods and crack propagation testing. The experimental results show that the reasonable homogenization processing needs to take into account the segregation elimination arising thermo plasticity addition, more to consider grain coarsing and severe oxidation leading to decrease plasticity. Based on the residue dendrites can provide more recrystalazation nucleation sites, the partial homogenization possessing probably exists rationality. This research work provides an exploratory study for the improvement of the homogenization-cogging process of superalloy.
高温合金铸锭均匀化程度对开坯热变形的再结晶影响
[J].利用OM, SEM和裂纹扩展速率测试等手段分析了GH4740H, GH4738, GH3625和690合金不同均匀化程度下的组织特征以及这些组织状态的热变形行为, 系统研究了合金均匀化工艺因素与再结晶的关联规律. 研究结果表明, 合金均匀化需要兼顾枝晶偏析消除带来的热塑性改善以及晶粒长大和氧化加剧所导致的后续热变形时的塑性下降; 合金未完全均匀化留下的残留枝晶间区域提供了再结晶形核位置, 提高再结晶形核率. 在相同热变形条件下, 有残留枝晶组织的试样再结晶程度明显高于完全均匀化、无枝晶组织的试样. 为此提出基于部分均匀化制度的高温合金均匀化开坯控制方法具有合理性.
Effects of grain-boundary carbides on high-temperature strength in the superalloy GH586
[J].
GH586合金的晶界碳化物高温强化
[J].
Reducing defects in remelting processes for high-performance alloys
[J].
Investigation of high performance disc alloy GH4065 and associated advanced processing techniques
[J].Much attention has been paid to the development of more advanced materials for high-pressure compressor and turbine discs of gas turbine engines. A high performance wrought superalloy GH4065 for disc applications has been recently developed based on the comprehensive evaluation of a series of model alloys with characteristic chemical composition, lattice parameter, particularly γ’ volume fraction. The concentration of major alloying elements of GH4065 is closely similar with René 88 DT and specifically optimized considering the demands of ingot metallurgy technologies. Therefore, GH4065 can be considered as an ingot metallurgy version of powder metallurgy René 88 DT. Large scale vacuum arc remelting (VAR) ingots of GH4065 alloy with diameter up to 508 mm have been produced via standard triple melting techniques. Micro-scale segregation of alloying elements on large VAR ingot has been effectively suppressed due both to optimized alloying elements concentration and to improved melting techniques. Ultra-low carbon content (less than 0.02% in mass fraction) significantly decreases the dendritic segregation tendency of certain alloying elements and promotes the uniformity of microstructures. VAR ingot of GH4065 exhibits extraordinary hot plasticity, ingot conversion can be accomplished using conventional open die forging procedure. Fine and uniform γ+γ’ duplex structures can be obtained on billets and disc forgings via a newly developed multi-cycle thermomechanical processing method. The flow stress data show that the formation of γ+γ’ microduplex results in a significant decrease of flow stress in comparison with γ’ dispersion structures under exactly the same deformation conditions. The distribution of strain rate sensitivity m in relationship with temperature and strain rate accurately identifies a specific domain within which γ+γ’ microduplex exhibits superplasticity. Full-scale turbine discs of GH4065 alloy with diameter of 630 mm achieve an optimal combination of creep resistance, fatigue lifetime and ductility. GH4065 discs exhibit extraordinary microstructural and property stability during prolonged thermal exposure, which means that dendritic segregation has been successfully restricted to an acceptable level. The results reveal that highly alloyed disc alloys produced via ingot metallurgy techniques exhibit lower costs and higher productivity, and can still meet the ever increasing demand of high performance gas turbine engines.
高性能涡轮盘材料GH4065及其先进制备技术研究
[J].在对一系列高合金化模型合金进行系统比选研究的基础上, 发展了新型的GH4065变形高温合金, 该合金化学成分与René 88 DT合金类似, 并针对铸锻制备工艺的要求进一步实施了优化. 研制结果表明, 应用三联低偏析熔铸和多重循环热机械处理等新型技术生产的GH4065合金, 适用于制备先进航空发动机关键热端转动部件, 综合性能完全满足高压压气机盘和低压涡轮盘的工况要求, 必要时可以作为高压涡轮盘的高可靠性、低成本解决方案. 随着变形高温合金材料和制备工艺的发展, 应用铸锻工艺制备的高性能涡轮盘材料能够满足先进航空发动机的技术要求.
Effect of ingot size on microstructure and properties of the new advanced AD730TM superalloy
[A].