高温合金是指能在600℃以上的高温及一定应力作用环境下长期工作的材料[1]。由于具有良好的抗氧化性能和抗热腐蚀性能、优异的高温强度,良好的疲劳性能和断裂韧性等综合性能[2],高温合金广泛应用在国防、能源、海事、航空以及其他需要稳定可靠材料的关键领域[3,4]。随着对合金承温能力日益增高的需求,近些年新的合金材料和制备工艺的开发也在不断发展[5]。高温合金优异的高温性能受多方面因素的影响,其中最主要的因素是与基体共格的Ni3Al型析出相(γ'相),γ'相的含量、数量、尺寸和分布等组织特征影响材料的力学性能[6~9]。根据γ'相在制备和热处理过程不同时段的析出,将其分为一次γ'相(通常直径大于500 nm)、二次γ'相(通常直径50~500 nm)和三次γ'相(通常直径小于50 nm)。在对高温合金的承温能力水平不断增加的背景下[10],出现了很多对材料的改进[11]、工艺的改进和创新[12]等相关方面的研究和报道,研究人员对合金中γ'相的形成[13~16]、成分[17~19]及其对高温力学性能的影响[20,21]等方面也做了大量研究,近年来很多材料基因组思路和新方法也应用到了高温合金的表征里[22,23]。采用现有的手段,无法获取高温合金中一次、二次和三次γ'相有代表性的定量数据,因而γ'相的定量统计表征目前尚是个未解的难题。
通常用来表征纳米级颗粒的方法[24,25]主要包括7类,其中适合用于表征高温合金中γ'相的尺寸分布的方法主要是图像表征法(原子力显微镜(AFM)、扫描电镜(SEM)和透射电镜(TEM))、X射线衍射(XRD)法以及提取技术(物理化学相分析&小角X射线散射(SAXS))。其中AFM适合测量单个粒子的表面形貌等细节特征,不适合测量粒子的整体统计特征[24,25];传统SEM和TEM可直接观察形貌和测定粒径,但限于视场只能对局部区域进行观察,结果有一定的偶然性且存在统计误差[26~28];XRD适用于晶态粒子晶粒度的测定,当测定粒子的粒径很小时,由于表面张力带来的畸变,会使得测量值不准确[29];物理化学相分析& SAXS的优点是能够测定颗粒的原始尺寸,且可在一次测试中获取高统计量的颗粒尺寸分布信息[30~34],缺点是化学提取步骤多造成颗粒损失而影响粒径测定,并且无法直接观察测定位置处的形貌而缺乏直观性。因而,要获取高温合金中一次、二次和三次γ'相有代表性的定量数据,需要建立一种新的表征研究方法。
目前全球范围内高通量SEM有2个技术路线,分别为我国的聚束科技(北京)有限公司掌握的单束场发射高通量电镜技术(Navigator-100系列)和以蔡司公司为首的技术团队推进的由61个电子束组成的多并行束电镜技术(MultiSEM 505、MultiSEM 506),本工作所用高通量SEM为前者。
Navigator-OPA高通量场发射SEM拥有全新设计的浸没摇摆透镜成像系统,采用多通道直接电子探测技术代替传统的光电倍增管,使该系统可实现100 MB/s级二次电子(secondary electron,SE)和背散射电子(backscatter electron,BSE)的超高速同步成像,成像速率在同等条件下是同类机型的10倍以上。可采集的图像大小范围为512 × 512~24K × 24K (即24576 × 24576)像素尺寸。保持超低图像畸变和1‰计量级的高线性度,通过矩阵式扫描模式可对超大区域(直径100 mm)进行无遗漏采集并形成atlas地图集分布文件,综合成像能力最大可达4 TB/d,使之具备了跨尺度高通量信息融合能力。目前Navigator-100系列已经成功应用在生物组织超微结构、材料基因工程研究、芯片检测/IP保护、薄膜制备工艺、锂电池制备工艺等领域。Wang等[23]在Navigator-100系列基础上结合原位统计分布分析思想,全面解析了整块镍基单晶高温合金中γ'相尺寸的分布,跨尺度地展现了纳米级γ'相在毫米级枝晶干和枝晶间的分布规律。Ju等[35]在Navigator-100系列电镜的基础上结合机器学习,通过大尺寸和多尺度的分析对第二代单晶高温合金中的碳化物在蠕变测试时的演变行为进行了研究,提供了样品量级的统计数据并以一种空前的方式阐释了高温合金中碳化物的影响。本工作利用原位高通量场发射SEM,结合MIPAR软件[36]建立合适的γ'相分割和识别策略,确立获取γ'相定量表征数据所需要的最小区域,以此建立一种可以对一次、二次和三次γ'相识别的定量统计表征方法。
1 实验方法
1.1 试样和准备
采用1080℃、4 h制度进行固溶热处理,随后经5种不同的速率冷却至室温,最后经760℃、4 h时效热处理。5种不同冷速下得到的挡板材料分别命名为CR-1~CR-5。其中,CR-1~CR-3冷却方式有所区别但冷却速率接近,CR-4冷速最慢,CR-5冷速最快。通过固溶处理和时效处理等热处理制度可以调控γ'相的析出和长大,进而得到所需要的材料性能[42]。
用于SEM表征的样品为挡板环件正中心处线切割得到的10 mm × 10 mm × 10 mm的立方体形样品。5种工艺下总共获取7个样品,其中,CR-2~CR-5 4种试样在环切面中心位置处各取了1块样品;CR-1在环件3个不同位置处,环切面中心各取一个样品,总共3块样品。
1.2 主要仪器及实验过程
用于原位高通量场发射SEM表征的样品,经过机械研磨、抛光后,在30 V电压下于H2SO4、CH3OH混合溶液中进行电解抛光,随后在3.8 V电压下在CrO3、H3PO4、H2SO4混合溶液中进行电解腐蚀。通过高通量场发射SEM的SE模式获取试样γ'相的形貌像,电镜采集图像的参数是:电压4 kV,像素尺寸为2.5 nm的57000倍图像,视场大小为5.12 μm × 5.12 μm,重叠区10%。
每个10 mm × 10 mm × 10 mm样品采集5张3000倍放大的2048 × 2048像素尺寸的图像,用于低倍下一次γ'相面积分数的统计。
为了能清晰观察二次和三次γ'相,选用了放大倍数为57000倍的SE像用于分析。对每个10 mm × 10 mm × 10 mm的样品采集2048 × 2048像素尺寸的图像,并通过高通量连续采集能力获得22 × 22张的图像阵列并最终完成拼接,得到一个高倍的可对一次、二次和三次γ'相进行观察的大视场。这个视场比实际表征所需区域要大,用于研究所需的最小表征区域尺寸,以实现高效获取所有γ'相的定量统计数据。
采用MIPAR软件,基于大量的SEM图像建立γ'相的分割和识别流程,并以此来对样品的γ'相图像分析,建立γ'相的定量统计表征方法。
2 测试方法建立
2.1 基于MIPAR软件建立γ'相分割和识别流程
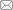
2.1.1 对低倍数SEM图像中一次γ'相的分割和识别流程
将5个试样的3000倍SEM像分别导入MIPAR软件中,依据一次γ'相的灰度、尺寸等基本信息,通过前处理、二值化等步骤建立图像分割和识别流程Recipe-1,对图像中黑色的一次γ'相进行分割和识别处理,如图1所示。低倍数下,一次γ'相的边缘不够清晰,但衬度差别明显,总体上可以得到较好的分割识别效果。此外,3000倍时视场较大,包含的一次γ'相数量多,更具统计意义。
图1
图1
对3000倍SEM像中一次γ'相建立识别Recipe-1的主要步骤
Fig.1
Main procedures on building the Recipe-1 for characterizing primary γ' precipitates in SEM images with magnification of 3000
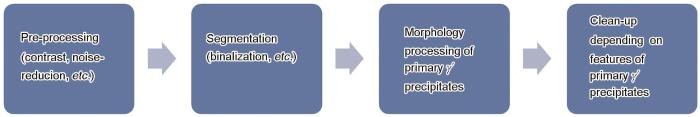
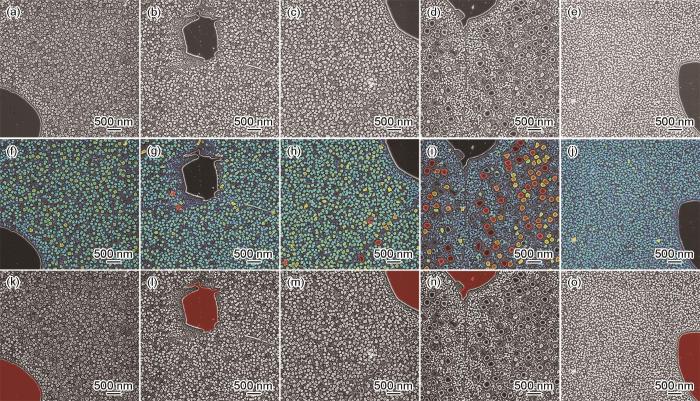
图2
图2
CR-1样品SEM像和采用Recipe-1识别一次γ'相后的伪彩色图像
Fig.2
Original SEM images with a magnification of 3000, in which the black particles were primary γ' precipitates (a-c) and corresponding pseudo-colorized images by Recipe-1 according to the diameter of primary γ' precipitates (d-f) in sample CR-1
表1 CR-1~CR-5 5个样品5张3000倍伪彩色图像中一次γ'相的统计面积分数 (%)
Table 1
| Sample | Number of SEM image | Average area fraction | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| CR-1 | 12.2256 | 11.4022 | 11.9496 | 11.0040 | 12.8140 | 11.8791 |
| CR-2 | 11.4778 | 11.9671 | 12.0973 | 11.8957 | 11.8351 | 11.8546 |
| CR-3 | 14.4065 | 14.4875 | 12.1480 | 12.8234 | 13.1789 | 13.4089 |
| CR-4 | 14.4171 | 14.4254 | 15.6861 | 13.9458 | 12.9404 | 14.2830 |
| CR-5 | 11.5034 | 11.1639 | 12.3995 | 12.7150 | 11.9160 | 11.9396 |
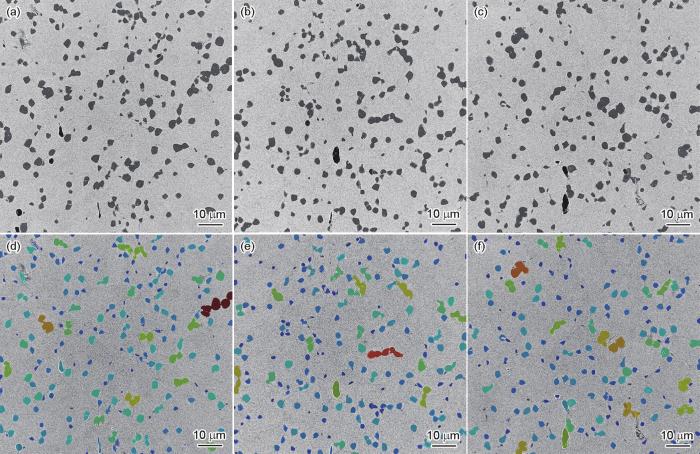
2.1.2 对高倍数SEM像中一次、二次和三次γ'相的分割和识别流程
5个样品的γ'相差别较大,将5个样品57000倍的SEM像分别导入MIPAR软件中建立分割和识别流程Recipe-2,主要步骤如图3所示。相较于3000倍图像中只能看见一次γ'相,57000倍图像里同时存在尺寸和灰度差异均较大的一次、二次和三次γ'相,需要分别进行分割和识别。因此,Recipe-2中将其分成两层分别识别,但应用批处理后生成所有γ'相的定量统计数据。
图3
图3
对57000倍SEM像中一次、二次和三次γ'相建立识别Recipe-2的几个主要步骤
Fig.3
Main procedures on building the Recipe-2 for characterizing primary, secondary, and tertiary γ' precipitates in SEM images with magnification of 57000
图4
图4
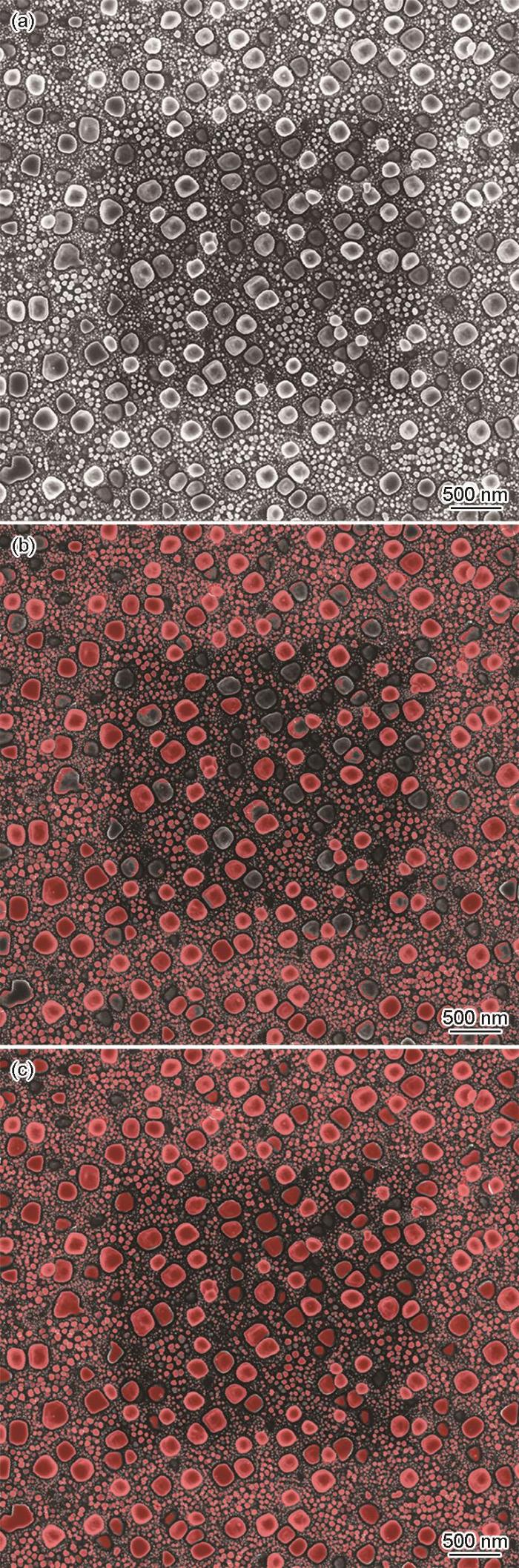
CR-1~CR-5 5个样品57000倍SEM像以及采用Recipe-2识别后的伪彩色像
Fig.4
Original SEM images with a magnification of 57000 (a-e) and corresponding pseudo-colorized images by Recipe-2 according to the diameter of secondary and tertiary γ' precipitates (f-j) and primary γ' precipitates (k-o) for samples CR-1 (a, f, k), CR-2 (b, g, l), CR-3 (c, h, m), CR-4 (d, i, n), and CR-5 (e, j, o)
二次和三次γ'相按尺寸着色后,聚集和分布的趋势明显。一次γ'相边缘存在细小的锯齿状小毛边且大部分处于晶界上,二次γ'相在晶粒内分布弥散,三次γ'相则主要聚集在晶界和一次γ'相周围,晶粒内也弥散分布。
2.2 表征区域最小尺寸的确立
2.2.1 表征区域最小尺寸确立的意义
对于一次、二次和三次γ'相这一类颗粒的识别统计,参考现有标准[43]需要对大量的颗粒进行分析,以认识统计客体的本质特征和数量规律,即达到对统计客体的理性认识,使得对γ'相表征结果的各种平均性指标与材料实际指标接近。
高温合金中的一次γ'相尺寸较大,数千倍放大倍数(如图2)就可以对一次γ'相进行识别表征。且低倍数下表征视场比较大,视场内的一次γ'相数量较多,单张低倍数图像中所表征的一次γ'相面积分数更接近样品中的实际值。但数千倍放大倍数时看不清二次和三次γ'相形貌,无法得到其定量数据。57000倍放大倍数时,可以同时看清楚一次、二次和三次γ'相,但单张高倍图像的视场有限,代表性较差。
高通量SEM的高通量采集能力,能够完成多张图像的高速采集和拼接,实现高倍图像的大视场分析。但需要研究这个大视场至少需要多少张高倍图像。因此,建立一种可以对一次、二次和三次γ'相识别的定量统计表征方法,首先需要确定一个最小尺寸的区域,使得在这个区域内得到的一次、二次和三次γ'相的数据与材料的实际值接近。
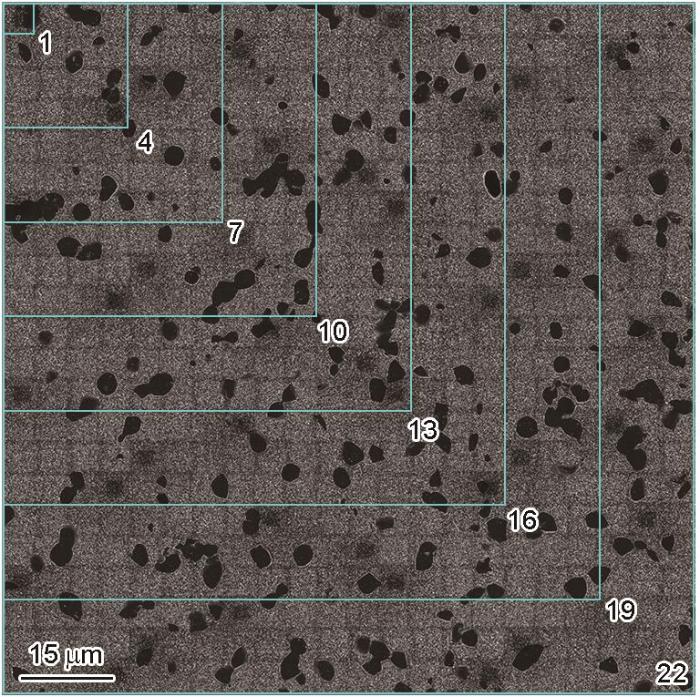
图5为CR-1样品484张57000倍图像拼接得到的拼接图,将其按照图像数量为1 × 1、4 × 4、7 × 7、…、22 × 22分成8组。采用Recipe-2分别对每组图像的一次、二次和三次γ'相进行识别和统计,分别通过57000倍和3000倍图像中一次γ'相面积分数以及二次和三次γ'相的数量比、二次和三次γ'相的面积分数来确定一个合适的γ'相表征区域尺寸。
图5
图5
CR-1样品484张57000倍SEM像的拼接图(拼接矩阵22 × 22)
Fig.5
Stitched image by 484 original SEM images with magnification of 57000 of sample CR-1 (The scanning matrix of images was 22 × 22)
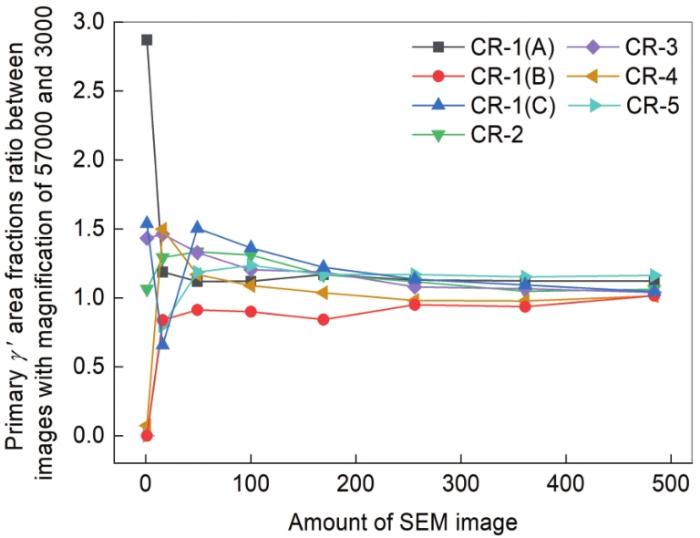
2.2.2 通过一次γ'相面积分数进行表征区域确定
表2所示为各样品采用Recipe-2得到不同张数57000倍图像中一次γ'相的面积分数。可以看出,当图像数量只有一张时,一次γ'相的面积分数波动比较大,可能恰好与样品实际值相近,也可能远高于实际值(如CR-1(A))或者面积分数为0 (如CR-1(B)和CR-5)。随着图像数量增多,一次γ'相的面积分数发生变化,趋近于某一数值。当图像数量为13 × 13张或者更多时,所有样品的一次γ'相面积分数都趋近于相应样品的某一特定数值,有几个样品(比如CR-1(A))在7 × 7时一次γ'相面积分数就已稳定。
表2 CR-1~CR-5样品不同张数57000倍伪彩色图像中一次γ'相的统计面积分数 (%)
Table 2
| Sample | MS | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 × 1 | 4 × 4 | 7 × 7 | 10 × 10 | 13 × 13 | 16 × 16 | 19 × 19 | 22 × 22 | |
| CR-1(A) | 34.1182 | 14.1041 | 13.2905 | 13.2980 | 13.8856 | 13.4047 | 13.3321 | 13.3222 |
| CR-1(B) | 0 | 9.9570 | 10.8282 | 10.6772 | 10.0037 | 11.2758 | 11.1122 | 12.0587 |
| CR-1(C) | 18.2661 | 7.8074 | 17.8653 | 16.1729 | 14.5078 | 13.4821 | 12.9862 | 12.3973 |
| CR-2 | 12.5951 | 15.3236 | 15.8086 | 15.5322 | 13.8407 | 13.2423 | 12.4115 | 12.5834 |
| CR-3 | 19.1938 | 19.5960 | 17.8005 | 16.1286 | 15.9201 | 14.4578 | 14.2913 | 13.9391 |
| CR-4 | 1.0355 | 21.3840 | 16.6870 | 15.5377 | 14.7993 | 13.9999 | 13.9489 | 14.4741 |
| CR-5 | 0 | 9.5127 | 14.1524 | 14.7422 | 13.9434 | 13.9481 | 13.7549 | 13.8762 |
图6
图6
各个样品57000倍和3000倍图像中一次γ'相面积分数之比随图像张数的变化
Fig.6
Tendency of primary γ' precipitates area fractions ratio between images with magnification of 57000 and 3000 in all samples varied with the amount of image
由此可见,对于建立一种可以对一次、二次和三次γ'相识别的定量统计表征方法,要准确定量表征这个区域内的一次γ'相面积分数,使结果与样品实际数值相近,所需要的2048 × 2048像素尺寸的图像数量至少为13 × 13张。
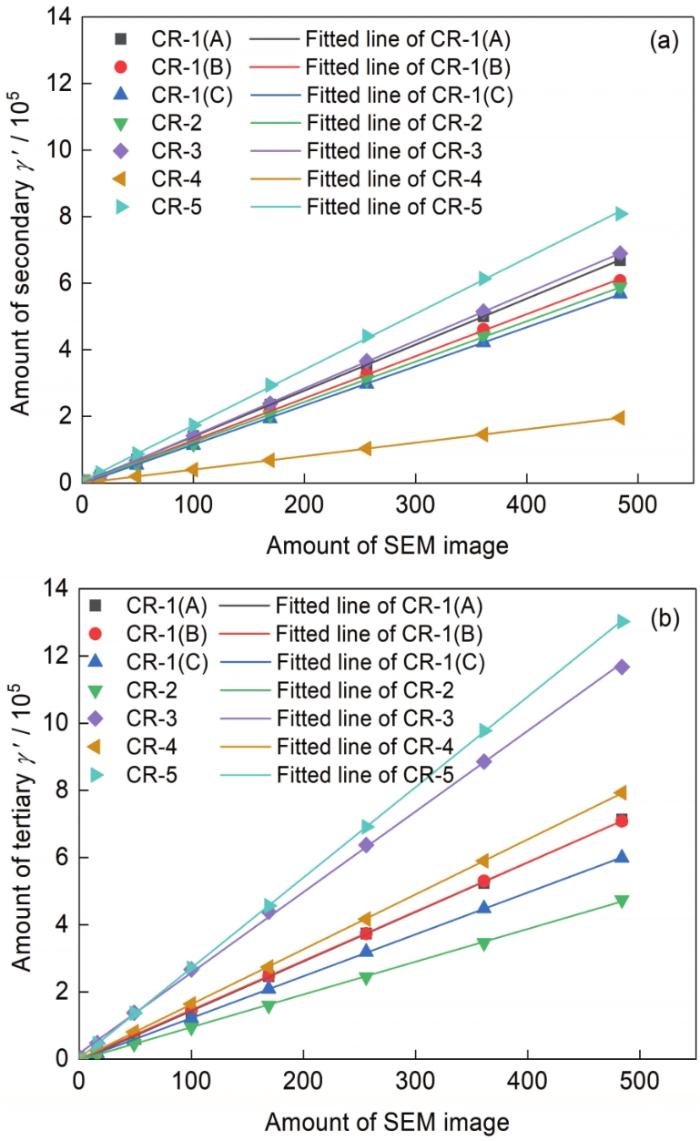
2.2.3 通过二次和三次γ'相的数量比进行表征区域确定
三次γ'相通常聚集于一次γ'相周围和晶界上(图4),一次γ'相的存在将对二次和三次γ'相的分布产生影响。因而在表征二次和三次γ'相定量信息时,需要考虑一次γ'相的存在,所以二次和三次γ'相数量的比值能够作为确定最小表征区域的一个指标。
图7
图7
CR-1~CR-5样品57000倍图像中二次和三次γ'相数量随图像张数的变化
Fig.7
Tendencies of the amount of secondary (a) and tertiary (b) γ' precipitates with magnification of 57000 in samples CR-1-CR-5 varied with the amount of image
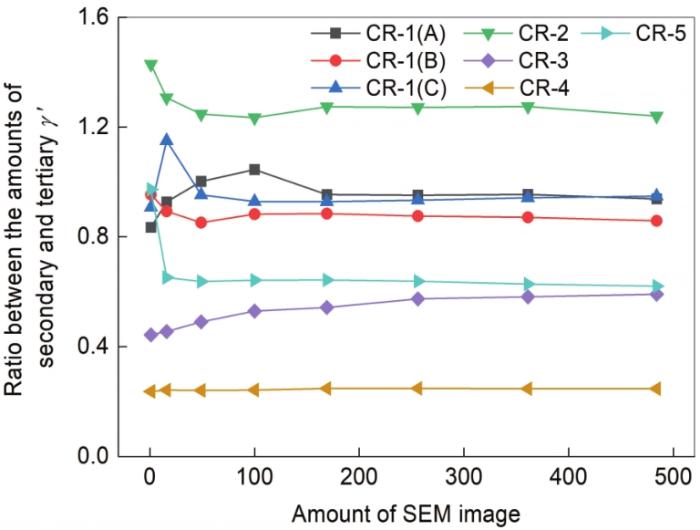
图8所示为各个样品不同数量57000图像中二次和三次γ'相的数量之比随图像张数的变化。可见,所有样品的二次和三次γ'相数量之比在13 × 13图像数量矩阵以后,比值开始趋于某一特定数值。CR-1样品中3次平行测试的结果差别较小,而不同冷却速率的样品差别较大。
图8
图8
各样品57000倍图像中二次和三次γ'相的数量之比随图像张数的变化
Fig.8
Tendencies of the ratio between the amounts of secondary and tertiary γ' precipitates with magnification of 57000 in all samples varied with the investigated amount of image
其中CR-1样品中二次和三次γ'相的数量最接近,其比值接近于1。冷却速率最慢的CR-4,包含了大量的三次γ'相而二次γ'相数量相对较少。随着图像数量的增多,所测得的数据结果代表性增强,因而所有样品所测小区域中的二次和三次γ'相的数量比值逐渐趋近于某一定值。整体来看,当所测试的区域为至少13 × 13矩阵图像时,5个样品中7个区域的二次和三次γ'相数量比值开始稳定。因此,通过二次和三次γ'相比值随图像张数的变化趋势,所确定的最小表征区域为13 × 13张图像。
表3 CR-1~CR-5样品不同张数57000倍伪彩色图像中二次γ'相的统计面积分数 (%)
Table 3
| Sample | MS | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 × 1 | 4 × 4 | 7 × 7 | 10 × 10 | 13 × 13 | 16 × 16 | 19 × 19 | 22 × 22 | |
| CR-1(A) | 21.6772 | 35.7952 | 36.6602 | 36.6367 | 36.3409 | 36.3452 | 36.3276 | 36.1951 |
| CR-1(B) | 29.4490 | 31.6903 | 32.4940 | 33.0152 | 33.0311 | 32.4605 | 32.3384 | 31.6845 |
| CR-1(C) | 18.7779 | 30.1542 | 27.0086 | 27.6534 | 28.4279 | 29.0237 | 29.3381 | 29.4686 |
| CR-2 | 28.7983 | 28.5878 | 28.9518 | 29.0544 | 29.5716 | 29.7345 | 29.9578 | 29.8297 |
| CR-3 | 31.2861 | 36.7546 | 37.4507 | 38.3250 | 38.0414 | 38.6012 | 38.6170 | 38.4221 |
| CR-4 | 25.6591 | 21.5179 | 23.8237 | 24.3587 | 24.8052 | 25.2127 | 25.2579 | 25.1590 |
| CR-5 | 40.0036 | 37.3287 | 35.6865 | 34.6941 | 34.7349 | 34.4413 | 33.9881 | 33.3435 |
表4 CR-1~CR-5样品不同张数57000倍伪彩色图像中三次γ'相的统计面积分数 (%)
Table 4
| Sample | MS | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 × 1 | 4 × 4 | 7 × 7 | 10 × 10 | 13 × 13 | 16 × 16 | 19 × 19 | 22 × 22 | |
| CR-1(A) | 4.3629 | 4.1475 | 3.9640 | 3.8927 | 4.0602 | 4.0986 | 4.1069 | 4.1726 |
| CR-1(B) | 4.1379 | 4.1596 | 4.1818 | 4.1152 | 4.1462 | 4.1376 | 4.1558 | 4.1437 |
| CR-1(C) | 3.4290 | 3.4859 | 3.7842 | 3.9601 | 3.9300 | 3.9189 | 3.8840 | 3.8672 |
| CR-2 | 3.7788 | 3.5975 | 3.7266 | 3.6885 | 3.7277 | 3.7315 | 3.7312 | 3.7543 |
| CR-3 | 5.9871 | 5.5649 | 5.3424 | 5.2784 | 5.2847 | 5.1110 | 5.0829 | 5.0549 |
| CR-4 | 5.3514 | 5.9551 | 5.8162 | 5.7008 | 5.6556 | 5.6393 | 5.5932 | 5.5939 |
| CR-5 | 8.5552 | 9.3975 | 9.2119 | 9.2089 | 9.2462 | 9.3367 | 9.4190 | 9.4513 |
建立一种可以对一次、二次和三次γ'相识别的定量统计表征方法,获取有代表性的二次和三次γ'相的定量数据,综合二次和三次γ'相数量、数量比值以及面积分数随图像张数的变化来看,视场内最少需要13 × 13张2048 × 2048像素尺寸的图像。
2.3 表征区域最小尺寸的确立
由于一定数量的统计才能更加理性地认识和反映客体与实际情况的本质特征和规律,并且一次、二次和三次γ'相在尺寸上存在较大的跨度,而一次γ'相的存在会对其他γ'相的析出和长大产生影响,因此选取的表征区域尺寸越大,越能反映材料的真实状况。但过多的图像将造成采集时间延长,数据分析压力增大,因而需要确立一个能反映材料实际情况的最小表征视场。
根据前文,一次γ'相面积分数,二次和三次γ'相数量、数量比值以及面积分数随图像张数变化综合结果,建立一种可以对GH4096高温合金中一次、二次和三次γ'相识别的定量统计表征方法,表征视场内最少需要13 × 13张2048 × 2048像素尺寸的图像。当被统计的图像张数大于等于13 × 13张时,一次γ'相的面积分数不再随图像张数增多而变化,且与低倍数下测得的结果接近;二次和三次γ'相的数量随被统计的图像张数增多而呈线性变化,且二次和三次γ'相的数量比值接近某一个数值。
3 准确性讨论
3.1 误差分析
图9
图9
样品CR-4中的二次和三次γ'相SEM像及其识别效果
Fig.9
Original SEM image of CR-4 (a) and corresponding pseudo-colored recognitions only colored by Recipe-2 (b), and colored by Recipe-2 and manual work (c)
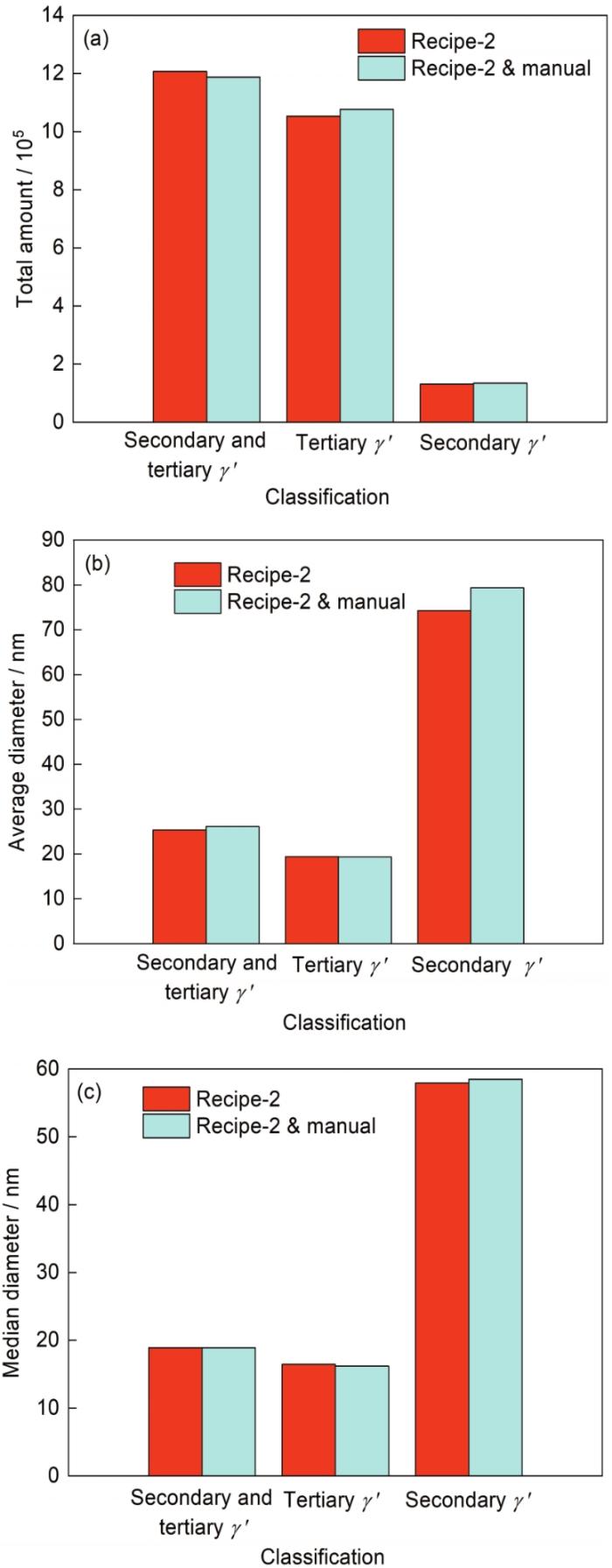
结合前文中确定的最小表征区域,通过上述的2种方法对CR-4样品169张57000倍图像中的二次、三次γ'相数量、平均尺寸、尺寸中位值对比结果如图10所示。可见,采用Recipe-2 +人工修正的方式下γ'相的总数减少了20583个,相较于仅采用Recipe-2的结果(1200000个左右)降低了1.71%,数量差别较小。较大尺寸的二次γ'相经修正得到正确识别以后,整体γ'相的平均尺寸略微增大,由25.34 nm增至26.10 nm,尺寸增大约3.00%。2种方法下整体的γ'相中位值是一样的。在经Recipe-2辅以人工修正处理后,三次γ'相的平均尺寸和尺寸中位值差别不大,二次γ'相的尺寸中位值也差别不大,但由于填补上了较大的二次γ'相其平均尺寸增大了5.09 nm,相较Recipe-2结果增大了6.85%。
图10
图10
Recipe-2和Recipe-2 +人工修正2种方式对CR-4样品169张57000倍图像中二次和三次γ'相的数量、平均尺寸、尺寸中位值的统计结果对比
Fig.10
Comparisons of total amount (a), average diameter (b), and the median diameter (c) of secondary and tertiary γ' precipitates in 169 images with magnification of 57000 in samples CR-4 between Recipe-2 and Recipe-2 & manual, two ways to recognized γ' precipitates
Recipe-2 +人工修正的方式需要耗费大量的人力和时间,无法做到样品的快速检测和分析。所建立的Recipe-2方式则无需再介入人力,对本工作中识别效果最差样品的结果,其误差范围也在可接受范围内。综合识别效果以及所需要的人力和时间,本工作以Recipe-2这一分割识别流程来建立方法并进行后续研究。
3.2 与相分析的结果进行对比
以基于169张2048 × 2048分辨率SEM像为基础,建立了γ'相定量统计表征方法,其结果可靠性仍需要与目前存在的方法进行比对。调研和对比了现有的γ'相分析手段,结合本文作者先前的一些工作,选择了物理化学相分析提取γ'相并采用SAXS进行γ'相尺寸表征分析,在一次SAXS测试中得到高统计量的γ'相尺寸分布信息。并将SAXS法得到的分布趋势与本工作结果进行对比验证,说明本工作方法的可行性。
SAXS法获得的是γ'相在各个尺寸段中的质量分数,且SAXS法只能测试尺寸为0~300 nm的颗粒;而本工作的图像统计法所获取的为各个尺寸段γ'相在二维图像中的面积分数,并且获取了尺寸为0~500 nm范围内所有颗粒的尺寸数据。由于表征手段的不同,所得的表征项目存在些许差异。但这些差异里,尺寸为300~500 nm范围的γ'相数量较少且可进行定量化,面积和质量间可进行关联性换算[44]且2者变化趋势一致。因而可以通过SAXS法得到的γ'相结果与本工作结果进行对比。
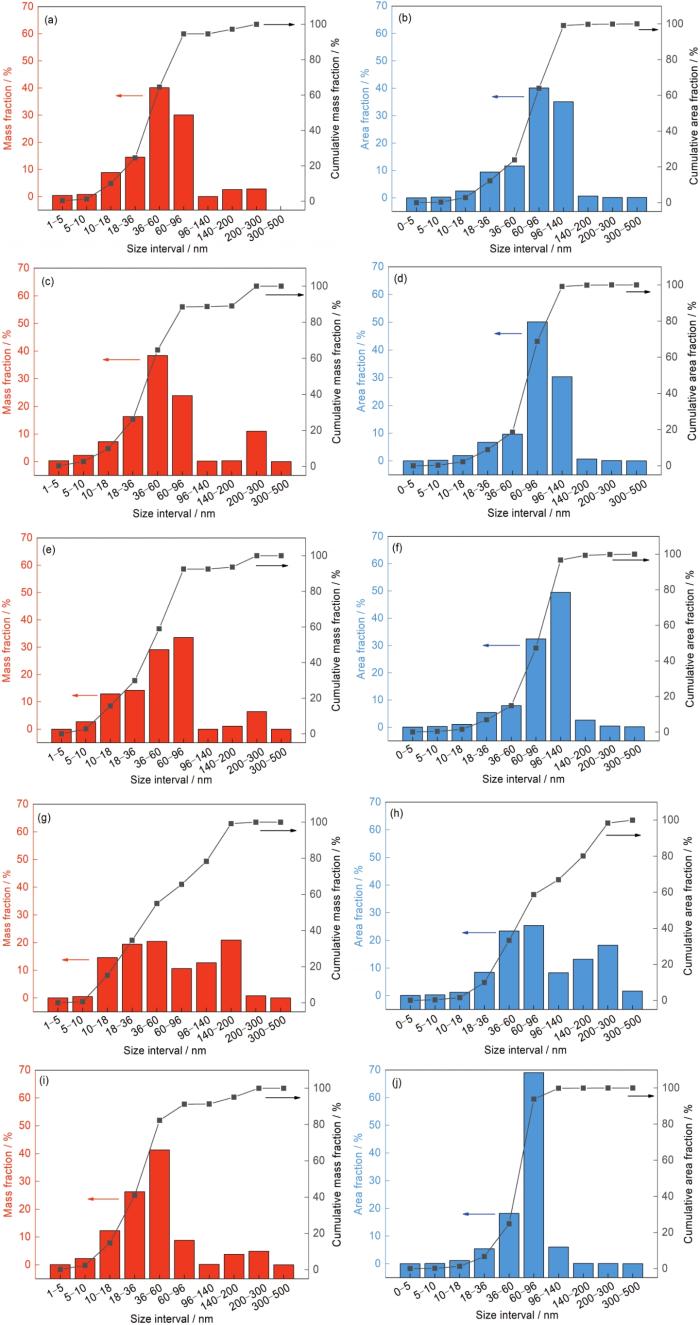
5个样品采用物理化学相分析和SAXS法测量的γ'相质量分数和本工作方法得到的γ'相面积分数结果如图11所示。
图11
图11
物理化学相分析和小角X射线散射(SAXS)法获得的γ'相质量分数以及本工作方法获得的γ'相面积分数的结果比较
Fig.11
Comparisons of mass fraction of γ' precipitates by using electrochemical extraction method & small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) (a, c, e, g, i) and area fraction of γ' precipitates by using the way in this work (b, d, f, h, j) in samples CR-1 (a, b), CR-2 (c, d), CR-3 (e, f), CR-4 (g, h), and CR-5 (i, j)
此外,常规SEM法受限于图像数量和数据多少,往往忽略一次γ'相对二次和三次γ'相的影响,而单方面测试二次和三次γ'相的数据,其结果不够全面;而SAXS法测定γ'相时需要先进行γ'相的提取,存在步骤多、时间长、可能丢失颗粒γ'相等缺点。本工作方法在兼具直观性的同时,综合考虑一次、二次和三次γ'相,确定了具有代表性的最小表征视场,基于统计性和全面性的基础去获取γ'相定量数据结果。
4 冷却速率、 γ' 相分布及性能间相关性
从γ'相数量上来看,冷速最快的CR-5样品二次γ'相数量最多,而冷速最慢的CR-4样品二次γ'相数量最少。从形貌上来看,CR-4样品由于冷却速率慢而存在一些明显较大的二次γ'相,而冷速最快的CR-5样品中的二次γ'相尺寸相近且分布相对平均。根据经典的形核长大机制,较慢的冷却速率造成材料的过冷程度降低,有利于材料中析出相的形核和长大,因此二次γ'相数量较少;同时根据Ostwald Ripening机制,较大尺寸γ'相的长大过程依赖于吸收周围较小尺寸的γ'相,因而在冷速较小的样品中会出现显著较大的二次γ'相。到冷却后期,由于温度较低,合金中大量析出较小尺寸的γ'相,因而CR-4样品中较小尺寸的三次γ'相数量也很多。而与之相应的,CR-5样品冷却速率快,过冷程度升高,较大尺寸析出相的长大受到抑制而形核能力增强且较小尺寸析出相能一定程度长大,因而二次γ'相的数量最多,且尺寸接近;同时三次γ'相的尺寸也较大,且数量较多。
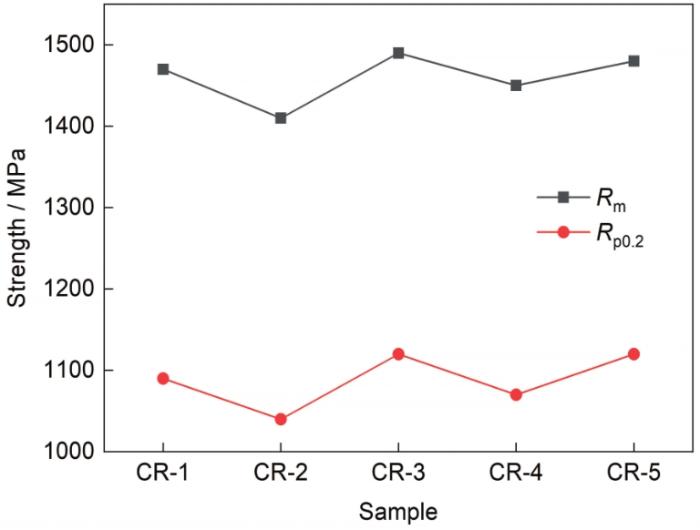
γ'相的析出情况和数量、尺寸等受到冷却速率的明显影响,强度与γ'相的数量和面积分数存在相关性。对5个样品进行400℃拉伸实验,测得5个样品塑性相当,相应的抗拉强度(Rm)和屈服强度(Rp0.2)如图12所示。
图12
图12
5个样品400℃拉伸的力学性能
Fig.12
Mechanical properties of samples CR-1-CR-5 tensiled at 400oC (Rm—tensile strength, Rp0.2—yield strength (plastic deformation at 0.2%))
5 结论
(1) 利用MIPAR软件建立了分割和识别流程,实现GH4096合金中一次、二次和三次γ'相的准确识别,获取到γ'相的定量数据。对最差视场进行误差分析,本工作方法测定的结果误差较小;将采用本工作方法得到的γ'相分布趋势与标准化的SAXS法得到的结果进行对比验证,2者结果一致。
(2) 通过57000倍和3000倍图像中一次γ'相面积分数比值、二次和三次γ'相数量比值、二次和三次γ'相面积分数等随图像张数的变化,得到了能代表性表征γ'相的最小视场——13 × 13张2048 × 2048像素尺寸的57000倍图像的表征区域。
(3) 结合冷却速率对本工作方法获取的γ'相定量数据以及图像中的形貌进行讨论,实验结果与经典的形核和长大机制和Ostwald Ripening机制的理论结果相符。不同冷却速率样品的400℃拉伸强度不同,但与γ'相定量结果存在相关性:强度高的样品,冷速相对较快,二次γ'相数量较多,γ'相面积分数总和也较高。
(4) 对具有一次、二次和三次γ'相的GH4096高温合金找到最小区域并建立统计表征方法,获取统计代表性定量数据,可用于探讨GH4096高温合金的工艺优化和性能预测。
参考文献
Annealing treatment methods and mechanisms for refining mixed and coarse grains in a solution treatment nickel-based superalloy
[J].
The current situation of application and development of superalloys in the fields of energy industry
[J].
高温合金在能源工业领域中的应用现状与发展
[J].高温合金在能源领域中有着广泛的应用. 煤电用高参数超超临界发电锅炉中, 过热器和再过热器必须使用抗蠕变性能良好, 在蒸汽侧抗氧化性能和在烟气侧抗腐蚀性能优异的高温合金管材; 在气电用燃气轮机中, 涡轮叶片和导向叶片需要使用抗高温腐蚀性能优良和长期组织稳定的抗热腐蚀高温合金; 在核电领域中, 蒸汽发生器传热管必须选用抗溶液腐蚀性能良好的高温合金; 在煤的气化和节能减排领域, 广泛采用抗高温热腐蚀和抗高温磨蚀性能优异的高温合金; 在石油和天然气开采, 特别是深井开采中, 钻具处于4-150 ℃的酸性环境中, 加之CO<sub>2</sub>, H<sub>2</sub>S和泥沙等的存在, 必须采用耐蚀耐磨高温合金. 本文简要介绍了国内外高温合金在上述领域中应用的现状与发展.
Present research situation and prospect of hot working of cast & wrought superalloys for aero-engine turbine disk in China
[J].In recent years, the demand for high-performance aero-engines has become crucial in China, and the service environment of turbine disk alloy becomes increasingly severe. A series of high resistant cast & wrought superalloys for turbine disks, such as GH4065, GH4720Li, GH4068, and GH4151, with working temperatures > 700°C, have been studied, produced, and applied widely. The current studies on cast & wrought alloys for turbine disks in China were summarized under the categories of homogenization treatment, cogging, disk forging, and microstructure and property regulation to promote the development of these superalloys and improve their comprehensive properties. The difficulties encountered during the research and preparation of these hard-to-deform superalloys and explored the alloys' potential development trend were outlined. The review would improve the production stability of the disk superalloys and promote their development.
国内航空发动机涡轮盘用铸锻难变形高温合金热加工研究现状与展望
[J].
Microstructure and hardness evolution in Haynes 282 nickel-based superalloy during multi-variant aging heat treatment
[J].In this paper, the effect of applied multi-variant heat treatment on microstructure, phase composition and mechanical response of Haynes 282 nickel-based superalloy was investigated. For this reason, temperatures of both stages of standard two-stage aging treatment (i.e., 1010 degrees C/2 h + 780 degrees C/8 h) were extended to 900-1100 degrees C/2 h and 680-880 degrees C/8 h ranges, respectively. Consequently, 30 different variants of heat treatment were applied. The microstructural features of heat-treated samples were investigated by means of light microscopy and SEM/EDS methods, while mechanical properties were examined via microhardness measurements. It was found that by using various combinations of temperatures of the first and second stage of aging, the room temperature hardness of Haynes 282 alloy can be decreased by similar to 100 HV units or increased by up to 25 HV units as compared to that of the alloy subjected to the standard heat treatment schedule. The mechanical response of the alloy is determined by a complex structural evolution involving the secondary precipitation of gamma', M23C6 and M6C phases, as well as their interaction with the fcc gamma matrix.
A study of solution cooling rate on γ′ precipitate and hardness of a polycrystalline Ni-based superalloy using a high-throughput methodology
[J].
Cooling precipitation and strengthening study in powder metallurgy superalloy U720LI
[J].
Effect of volume fraction and size of fine γ′ on creep strength of a DS nickel-base superalloy
[J].
细小γ′粒子的数量和尺寸对提高定向凝固高强度镍基高温合金蠕变强度的作用
[J].本文研究了定向凝固K3镍基高温合金的蠕变强度与细小γ′粒子的数置和尺寸的关系。实验结果证明,随着固溶温度升高,铸态粗大γ′逐步溶解并在随后冷却过程重新析出均匀细小正方形的γ′粒子。细小γ′体积分数(v_f)和尺寸(α)都随固溶温度的升高而增大,当固溶温度从1100℃升至1230℃,v_f从0.25增至0.63,α从0.10μm增至0.32μm。随着固溶温度的升高,第二阶段蠕变速率降低,持久寿命延长,大幅度提高合金的蠕变性能。适当的高温固溶加时效处理(如1210—1230℃,4h+900℃,32h)可提高定向凝固合金的中温(760℃,73.8kgf/mm~2)持久寿命10倍左右。 合金的中温蠕变性能取决于细小γ′的体积分数(v_f),尺寸(α)及其间距(λ),在固定温度和应力下,第二阶段蠕变速率((?))与它们之间符合以下关系。 (?)∝ λ~2/α或(?)∝ α/v_f~(2/3)(1-v_f~(1/3))~2 用透射电镜观察了合金三个蠕变阶段位错亚结构的变化,据此提出蠕变的位错模型和合金的强化机制,并导出第二阶段蠕变速率与γ′体积分数、尺寸和间距之间的关系式,与实验结果完全符合。
Requirements and forecast of turbine disk materials
[J].
对涡轮盘材料的需求及展望
[J].
Recent developments of powder metallurgy superalloy in Russia
[J].
俄罗斯粉末冶金高温合金研制新进展
[J].
Development and innovation of superalloy in China
[J].
我国高温合金的发展与创新
[J].本文描述了我国高温合金的发展历程, 近期的科技进步与创新和今后需进行的工作.
An investigation of diffusion-mediated cyclic coarsening and reversal coarsening in an advanced Ni-based superalloy
[J].
Influence of cooling rate on the development of multiple generations of γ′ precipitates in a commercial nickel base superalloy
[J].
Review progress in Ostwald ripening theories and their applications to nickel-base superalloys Part I: Ostwald ripening theories
[J].
Activation energy for growth in single size distribution and the dissolution features of γ′ precipitates in the superalloy IN738LC
[J].
Nanoscale characterization of elemental partitioning between gamma and gamma prime phases in René 88 DT nickel-base superalloy
[J].
Compositional variations between different generations of γ′ precipitates forming during continuous cooling of a commercial nickel-base superalloy
[J].
Compositional variations for small-scale gamma prime (γ′) precipitates formed at different cooling rates in an advanced Ni-based superalloy
[J].
Cooling precipitation and strengthening study in powder metallurgy superalloy Rene88DT
[J].
The influence of thermal exposure on the γ' precipitates characteristics and tensile behavior of superalloy IN-738LC
[J].
Progress in high-throughput materials synthesis and characterization
[J].
材料的高通量制备与表征技术
[J].
State-of-the-art review of high-throughput statistical spatial-mapping characterization technology and its application
[J].
Nanosensors and other techniques for detecting nanoparticles in the environment
[A].
Basic properties and measuring methods of nanoparticles
[A].
A quantifiable and automated volume fraction characterization technique for secondary and tertiary γ' precipitates in Ni-based superalloys
[J].
The research progress of methods for characterizing nanoparticles
[J].
纳米颗粒粒度测量方法进展
[J].
Characterization of nanoscale precipitates in superalloy 718 using high resolution SEM imaging
[J].At present, obtaining accurate volume fraction and size measurements of gamma '', gamma', and delta precipitates in Superalloy 718 has been challenging due to their size, crystal structures, low volume fractions, and similar chemistries. These measurements are necessary to validate precipitation models that in turn enhance selective laser melting fabrication. Superalloy 718 is a promising candidate for selective laser melting fabrication due to a combination of excellent mechanical properties and workability. A new technique, combining high resolution distortion corrected SEM imaging and with high resolution x-ray energy dispersive spectroscopy, has been developed to accurately and independently measure the size, volume fraction, and number densities of these three precipitates. A specimen of selective laser melted superalloy 718 was obtained and underwent a conventional heat treatment for superalloy 718 where it was solutionized at 1010 degrees C for one hour, gas quenched and followed by a two-step age (718 degrees C/11 h -> 621 degrees C/6 h) in order to produce a microstructure with all three precipitate types present. These results were further validated using x-ray diffraction and phase extraction methods.
Comparison of three methods of measuring nano-particles size
[J].
三种纳米颗粒粒径测量方法的比较
[J].
Comparison of nanometric particle size distributions as determined by SAXS, TEM and analytical ultracentrifuge
[J].
Verification for particle size distribution of ultrafine powders by the SAXS method
[J].
Physicochemical phase analysis of a directionally solidified Ni-based cast superalloy
[J].
一种定向凝固镍基铸造高温合金的物理化学相分析
[J].
Physicochemical phase analysis of iron-nickel based high temperature alloy with high chromium
[J].
一种高铬的铁镍基高温合金物理化学相分析
[J].
A macro-nano-atomic-scale high-throughput approach for material research
[J].A multiscale high-throughput approach helps to study the carbides in a nickel-base single-crystal superalloy.
Development and application of MIPAR™: A novel software package for two- and three-dimensional microstructural characterization
[J].Three-dimensional microscopy has become an increasingly popular materials characterization technique. This has resulted in a standardized processing scheme for most datasets. Such a scheme has motivated the development of a robust software package capable of performing each stage of post-acquisition processing and analysis. This software has been termed Materials Image Processing and Automated Reconstruction (MIPAR™). Developed in MATLAB™, but deployable as a standalone cross-platform executable, MIPAR™ leverages the power of MATLAB’s matrix processing algorithms and offers a comprehensive graphical software solution to the multitude of 3D characterization problems. MIPAR™ consists of five modules, three of which (Image Processor, Batch Processor, and 3D Toolbox) are required for full 3D characterization. Each module is dedicated to different stages of 3D data processing: alignment, pre-processing, segmentation, visualization, and quantification.
Research of ESR-CDS technology
[J].
电渣重熔连续定向凝固技术研究
[J].
Structure and hot deformation behavior of ESR-CDS René88DT
[J].
电渣重熔连续定向凝固René88DT合金的组织与热变形行为
[J].
Calculation on technological parameters of electroslag remelting continuous-directionally solidified René88DT nickel alloy ingot
[J].

The electrode of René88DT nickel allov ( % : 0.02 ~ 0.05C. 15.5 ~ 16.5Cr, 3.8 ~4.2Mo, ≤0.20Ta, 12.5 ~13.5Co,0.6~1.0Nb, 0.025 ~0.050Zr, 3.5~3.9Ti, 2.0〜2.4AI, 0.006〜0.015B, 3.8〜4.2W, 0.005 ~ 0.010Ce) is melted by a 200 kg vacuum induction furnace and the Φ160 mm x 220 mm René88DT alloy ingot is melted by a 500 kg shielding atmosphere drawing-out ingot electroslag remelting furnace with continuously directional solidification process according to requirement of solidified structure to determine the melting speed during remelting by controlling secondary dendrite area space in ingot solidification, metal bath shape and depth and to get relative remelting parameters by thermal equilibrium calculation. Results show that the relative error between calculated total remelting time and real remelting time is only 4.5%, the bath is hallow lo get fine solidified structure with whole 〈100〉 direction columnar structure and secondary dendrite area space- 60 〜80 μm
电渣重熔连续定向凝固René88DT镍基合金锭工艺参数的计算
[J].
Recent development of solidified structure controlling of superalloy during ESR process
[J].
电渣重熔高温合金凝固组织控制的研究进展
[J].
Hot deformation characteristics of Ni-base wrought superalloy CDS&W FGH96
[J].
镍基变形高温合金CDS&W FGH96热变形行为研究
[J].
Several development priorities of heat treatment technology in our country
[J].
我国热处理技术发展的几个重点
[J].
An investigation of high-temperature precipitation in powder-metallurgy, gamma/gamma-prime nickel-base superalloys
[J].