在多晶体塑性变形的组织演变研究中经常用到Schmid因子(m = cosφ‧cosλ,其中,φ为外载荷与滑移面法线的夹角,λ为外载荷与滑移方向的夹角),通常在其他条件相同情况下,m越大,该取向就越容易启动滑移和孪晶[15]。根据Schmid定律τ = σ·m (其中,τ为分切应力,σ为拉伸应力),当作用在滑移面上沿着滑移方向的分切应力达到某一应力值时位错便开始滑移,这种宏观的Schmid因子也被用于判别启动孪晶时的孪晶变体选择[16~18]。在具体分析孪晶变体的选择问题时发现,仅使用m判断孪晶变体的选择是不准确的,Wang等[19]和Guan等[15]通过准原位实验并结合几何相容因子(m' = cosϕ‧cosк,其中,ϕ为相邻晶粒滑移面与孪生面法向的夹角,к为相邻晶粒滑移方向与孪生方向的夹角),分别确定纯Ti和镁合金塑性变形时的孪晶变体选择。
对于纯Ti塑性变形过程中的微观组织演变研究,变形孪晶形核及孪晶变体的选择是其中的主要内容,对变形后材料力学和化学性能有显著影响。在实际应用中发现,m'不能准确判断多晶纯Ti在塑性变形中的孪晶变体选择,因此本工作在上述研究基础上,提出了“取向相容因子ω”的概念,建立了一种更加适用于纯Ti的孪晶变体选择模型,通过此模型计算得到的孪晶变体与实验结果相吻合,对纯Ti的塑性变形机理提出了一种新的认识。
1 实验方法
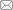
本工作所用材料为商用纯Ti (TA1),原始状态为棒状,直径为20 mm,具体化学成分(质量分数,%)为:N ≤ 0.01,C ≤ 0.01,H ≤ 0.03,Fe ≤ 0.02,O ≤ 0.06,Ti余量。从棒状材料上用线切割方式切取尺寸为5 mm × 10 mm × 30 mm的块状样品。实验采用DPD装置,DPD具有较高的应变速率(103 s-1)[13]。实验在液氮环境下进行,低温和高应变速率能够有效抑制位错运动,有利于变形孪晶的产生[6,16]。样品变形量为50% (应变ε = 0.7),图1为纯Ti取样的示意图,法向(ND)平行于压缩方向,观察面选择垂直轧向(RD)的面。样品经800、2000、5000和7000号砂纸打磨后,用酒精超声清洗并吹干,然后进行电解抛光,电抛液使用HClO4、CH3OH混合溶液(体积比1∶9),样品接恒流电源的阳极,电压17 V,温度-30℃,抛光时间60~90 s。为了观察孪晶类型及孪晶与原始晶体的取向关系,使用配有电子背散射衍射(EBSD)探头的Supra55场发射扫描电子显微镜(SEM)进行分析,工作电压20 kV、扫描步长0.1 μm。采集的数据使用Channel5数据处理软件进行分析。使用Tecnai G2 F20透射电镜(TEM)观察纯Ti的微观结构及变形孪晶,加速电压200 kV。TEM样品制备过程如下:在DPD样品上沿平行于轧向的方向线切割厚度0.5 mm样品,砂纸磨至50 μm后利用Tenupol-5减薄仪进行双喷减薄,双喷液与电抛液相同,温度-30℃,电压22 V。最后在GATAN695.C精密离子减薄仪上完成最终减薄,为避免温度影响,减薄在液氮环境中进行。
图1
图1
纯Ti样品取样示意图
Fig.1
Schematic of the seleced position of pure Ti sample (ND—normal direction, TD—transverse direction, RD—rolling direction)
2 实验结果与讨论
2.1 变形前后微观组织
图2
图2
动态塑性变形(DPD)前后纯Ti的微观组织与孪晶分布
Fig.2
EBSD images (a, b), (0001) pole figures (c, d), and image quality maps (e, f) of pure Ti before (a, c, e) and after (b, d, f) dynamic plastic deformation (DPD)
表1对变形后纯Ti中生成的孪晶界占总晶界的比例进行了统计,所有孪晶界占总晶界的比例约为21.24%。Xu等[9]对纯Ti进行了室温DPD研究,结果表明,其应变量最大为0.2,总孪晶占比为12.2%。Chun等[20]对纯Ti进行冷轧并观察其变形后的显微组织,研究发现,当变形量≤ 40%时,观察到{
表1 DPD后纯Ti中常见的6种孪晶占比
Table 1
| Type of twin | Misorientation angle and axis | Frequency of twin % |
|---|---|---|
| { | 85° < | 7.87 |
| { | 57.2° < | 0.02 |
| { | 35° < | 0.15 |
| { | 64.4° < | 11.50 |
| { | 86.8° < | 0.50 |
| { | 77° < | 1.20 |
| Total | - | 21.24 |
图3
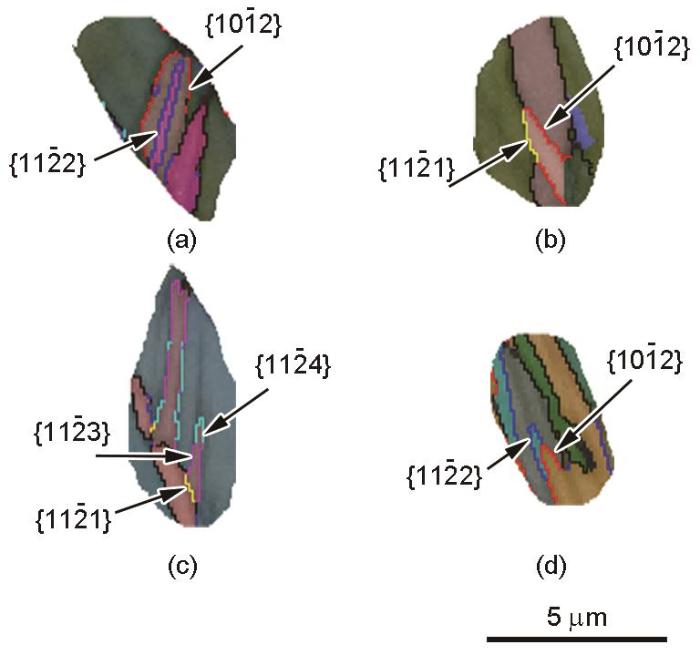
图3
液氮温度下DPD后纯Ti中不同类型孪晶的微观结构
Fig.3
Microstructures of typical areas in pure Ti after DPD at liquid nitrogen temperature
(a) secondary twin
(b, d) double twin
(c) tertiary twin
图4
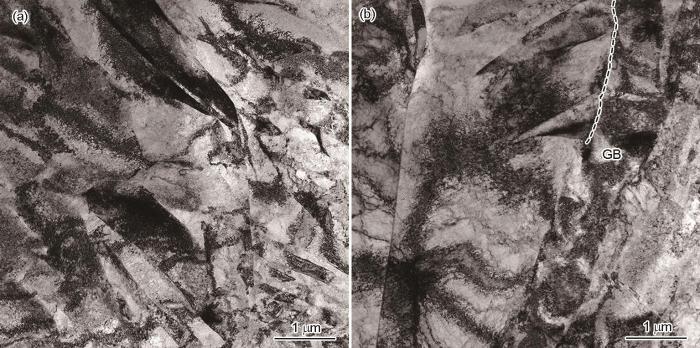
图4
液氮温度下DPD后纯Ti的TEM像
Fig.4
TEM images of rich twins (a) and twins nucleate at grain boundaries (b) in pure Ti after DPD at liquid nitrogen temperature (GB—grain boundary)
2.2 DPD对Schmid因子的影响
| Type of Burgers vector | Slip direction | Slip plane | Total number of slip system | Independent number of slip system |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basal <a> | < | {0002} | 3 | 2 |
| Prismatic <a> | < | { | 3 | 2 |
| Pyramidal <a> | < | { | 6 | 4 |
| Pyramidal <c + a> | < | { | 6 | 5 |
图5
图5
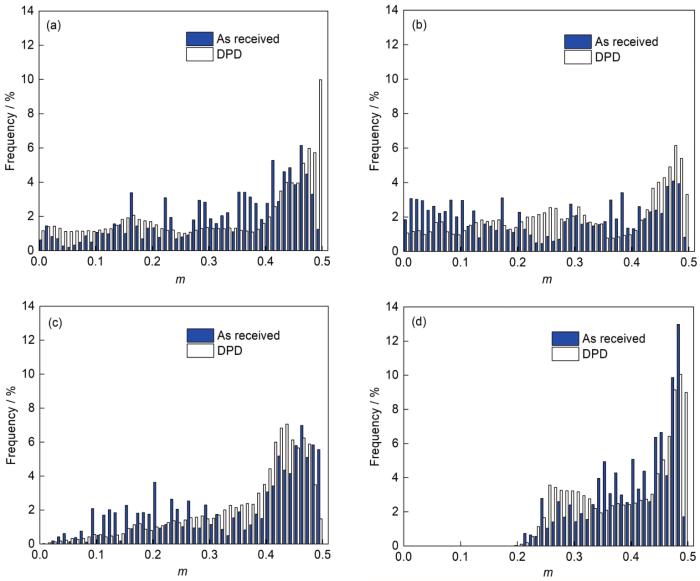
DPD前后纯Ti滑移系Schmid因子(m)图
Fig.5
Schmid factors (m) in basal slip (a, e), prismatic slip (b, f), pyramidal <a> slip (c, g), and pyramidal <c + a> slip (d, h) before (a-d) and after (e-h) DPD (σ—compression direction)
图6
图6
各晶粒滑移系在DPD启动前后的Schmid因子
Fig.6
m in basal slip (a), prismatic slip (b), pyramidal <a> slip (c), and pyramidal <c + a> slip (d) before and after DPD
2.3 滑移对孪晶变体选择的影响
位错与孪晶以及孪晶与孪晶之间的相互作用对于材料的性能具有重要影响,有研究[28]表明,位错在晶界的塞积和位错的反应能够促使变形孪晶的形核,而纯Ti中主要有6类变形孪晶,每一类孪晶都存在6种变体,相邻晶粒位错滑移对某一类变形孪晶形核时的孪晶变体选择有显著影响。Guan等[15]研究了镁合金中基面滑移对孪晶变体选择的影响,通过结合EBSD准原位实验进行了大量孪晶类型统计,同时计算得出了孪晶与相邻晶粒基面滑移的m',结果表明,m'决定了孪晶变体的选择,同时在滑移系中,基面滑移占据了主导地位,非基面滑移对孪晶的形成和变体的选择作用很小。Wang等[19]研究了纯Ti中相邻晶粒的位错滑移对孪晶变体选择的影响,发现在滑移系和孪晶系匹配较好的情况下,相邻软取向晶粒的位错滑移能够激发硬取向晶粒内的变形孪晶形核,孪晶变体选择同样由m'确定,这种机制激活的孪晶m'都比较大,而宏观m不起作用,一些m小的晶粒反而生成了孪晶。但在本工作的实际应用中发现,上述提到的m'不能准确判断多晶纯Ti在塑性变形中的孪晶变体选择,因此在上述研究基础上,提出了“取向相容因子ω”的概念,并尝试通过此参数建立一种更加适用于多晶纯Ti的孪晶变体选择模型。
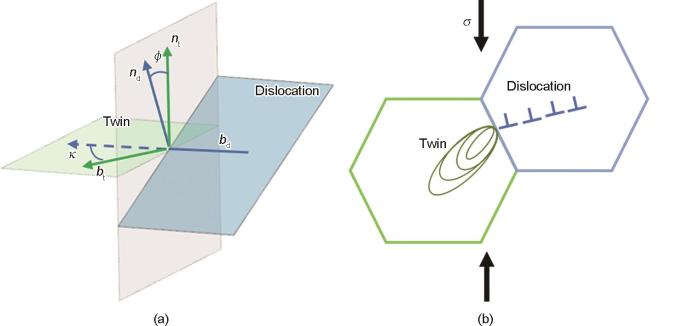
用m'来预测相邻晶粒间滑移的转移,根据m'的定义,相邻晶粒滑移系之间的几何相容因子可能在0~1之间变化。当m' = 1时,相邻晶粒间的滑移系完全相容,这种变形很容易穿过晶界。相反,m' = 0表示滑移系完全不相容,滑移方向或滑移面都是正交的,这不利于变形穿过晶界[29]。考虑孪晶与滑移的匹配关系,孪晶与滑移匹配关系越好,m'越大,但每个相邻晶粒的取向也分软取向和硬取向,其位错滑移的难易程度也不同,本工作在原有m'基础上引入相邻晶粒位错滑移对孪生的贡献这一参数ω。图7为ω的几何示意图,其中ω = m1·m' (其中,m1表示相邻晶粒的Schmid因子),ω表示相邻晶粒滑移对孪生晶粒变体选择的贡献。m1大,相邻晶粒的位错滑移容易启动,相邻晶粒滑移对孪晶变体的选择起到促进的作用;m'大,相邻晶粒的位错滑移和孪晶变体之间的匹配关系好,对孪晶变体的选择起到促进的作用。ω取值范围为0~0.5,ω越大该孪晶变体越容易启动。
图7
图7
取向相容因子(ω)原理示意图
Fig.7
Schematics of orientation compatibility factor (ω) (bd—slip direction of the dislocation, bt —twin direction, nd—normal direction of the slip plane of the dislocation, nt—normal direction of the twin plane, ϕ—included angle between the normal direction of the twin plane and the normal direction of the slip plane, κ—included angle between the twin direction and the slip direction)
(a) stereogram (b) planar graph
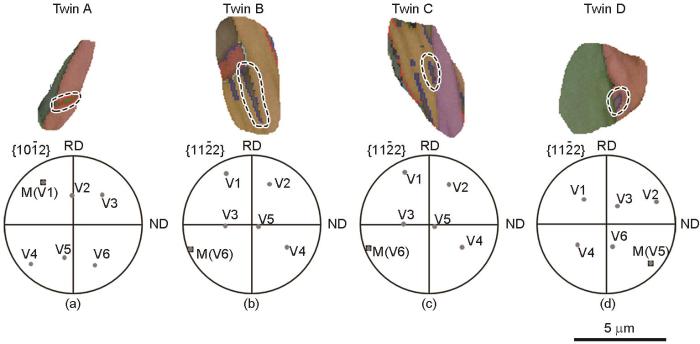
图8
图8
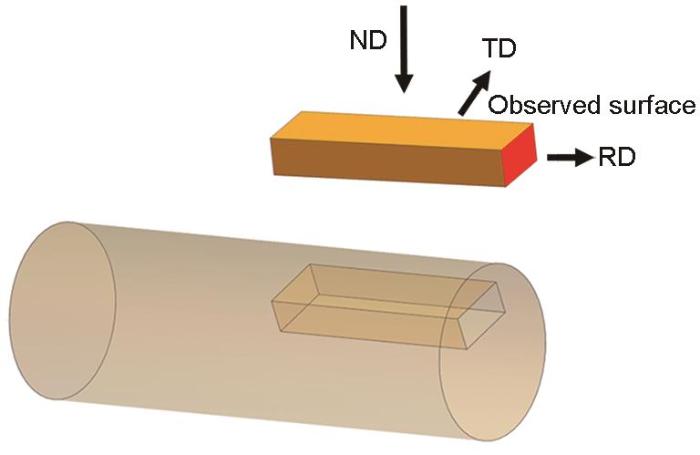
液氮温度下经过DPD变形后得到的纯Ti的4类孪晶EBSD图及其变体选择
Fig.8
EBSD maps of twins and the choose of twin variants (The dots represent the six possible twin variants (V), and the rectangles represent the actual twin variants initiated (M))
(a) twin A (b) twin B (c) twin C (d) twin D
表3为计算得到的4个孪晶变体的m、m'和ω。在孪晶A中,实际启动的孪晶变体是V1,其m是所有变体中的第二大数值,为0.431,与m最大的孪晶变体V4的值(0.446)相差不大,同时它的锥面<a>滑移的ω是0.285,也略小于第一大值(0.295);孪晶B实际启动的孪晶变体是V6,是m第二大的变体,但锥面<a>滑移的ω最大;在孪晶C中,实际选择的孪晶变体是V6,其m为0.299,是第二大的值,远低于第一大的0.486,但其锥面<a>滑移的ω最大;在孪晶D中,实际启动的孪晶变体是V5,其m和锥面<a>的ω都是最大的。上述分析表明,在纯Ti的实际孪晶变体的选择中,并没有遵循m最大,同时也没有遵循m'最大,计算结果表明,锥面<a>滑移的ω最大,这一计算结果与图7的EBSD分析结果相吻合,较好地预测了多晶纯Ti的孪晶变体选择。
表3 纯Ti孪晶变体的选择参数
Table 3
| Twin | Twin | m | m' | ω | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| variant | ||||||||||
| Basal | Prismatic | Pyramidal | Pyramidal | Basal | Prismatic | Pyramidal | Pyramidal | |||
| <a> | <a> | <a> | <a + c> | <a> | <a> | <a> | <c + a> | |||
| A | V1 | 0.431 | 0.582 | 0.497 | 0.716 | 0.624 | 0.148 | 0.205 | 0.285* | 0.170 |
| V2 | 0.013 | 0.121 | 0.453 | 0.456 | 0.833 | 0.031 | 0.051 | 0.075 | 0.101 | |
| V3 | 0.282 | 0.039 | 0.201 | 0.195 | 0.825 | 0.010 | 0.029 | 0.035 | 0.253 | |
| V4 | 0.446 | 0.355 | 0.651 | 0.741 | 0.789 | 0.067 | 0.218 | 0.182 | 0.387 | |
| V5 | 0.016 | 0.811 | 0.339 | 0.674 | 0.470 | 0.104 | 0.151 | 0.198 | 0.099 | |
| V6 | 0.270 | 0.975 | 0.190 | 0.633 | 0.340 | 0.150 | 0.085 | 0.295 | 0.068 | |
| B | V1 | 0.214 | 0.561 | 0.675 | 0.861 | 0.314 | 0.132 | 0.149 | 0.092 | 0.120 |
| V2 | 0.013 | 0.921 | 0.145 | 0.473 | 0.546 | 0.126 | 0.065 | 0.195 | 0.094 | |
| V3 | 0.120 | 0.231 | 0.720 | 0.742 | 0.611 | 0.053 | 0.319 | 0.260 | 0.163 | |
| V4 | 0.483 | 0.157 | 0.668 | 0.659 | 0.470 | 0.042 | 0.197 | 0.258 | 0.085 | |
| V5 | 0.063 | 0.430 | 0.224 | 0.296 | 0.969 | 0.058 | 0.089 | 0.116 | 0.203 | |
| V6 | 0.338 | 0.454 | 0.678 | 0.813 | 0.300 | 0.103 | 0.301 | 0.405* | 0.030 | |
| C | V1 | 0.215 | 0.406 | 0.644 | 0.760 | 0.626 | 0.082 | 0.158 | 0.116 | 0.208 |
| V2 | 0.006 | 0.824 | 0.285 | 0.645 | 0.501 | 0.227 | 0.086 | 0.099 | 0.076 | |
| V3 | 0.093 | 0.179 | 0.588 | 0.600 | 0.651 | 0.085 | 0.178 | 0.238 | 0.106 | |
| V4 | 0.486 | 0.033 | 0.448 | 0.409 | 0.721 | 0.009 | 0.110 | 0.128 | 0.177 | |
| V5 | 0.060 | 0.048 | 0.234 | 0.225 | 0.770 | 0.020 | 0.041 | 0.063 | 0.142 | |
| V6 | 0.299 | 0.783 | 0.478 | 0.795 | 0.523 | 0.228 | 0.145 | 0.316* | 0.089 | |
| D | V1 | 0.216 | 0.741 | 0.567 | 0.852 | 0.505 | 0.336 | 0.119 | 0.142 | 0.104 |
| V2 | 0.354 | 0.079 | 0.154 | 0.169 | 0.814 | 0.036 | 0.031 | 0.068 | 0.137 | |
| V3 | 0.018 | 0.108 | 0.631 | 0.606 | 0.604 | 0.049 | 0.132 | 0.202 | 0.124 | |
| V4 | 0.134 | 0.037 | 0.542 | 0.494 | 0.690 | 0.014 | 0.156 | 0.217 | 0.107 | |
| V5 | 0.479 | 0.855 | 0.194 | 0.580 | 0.420 | 0.388 | 0.041 | 0.233* | 0.076 | |
| V6 | 0.061 | 0.490 | 0.679 | 0.831 | 0.571 | 0.191 | 0.196 | 0.179 | 0.090 | |
本工作通过实际孪晶变体的标定验证了ω在预测孪晶变体选择中的可靠性,ω越大该孪晶变体越容易启动。ω这一参数从相邻晶粒的滑移对孪生晶粒变体选择的贡献角度出发,既考虑了晶粒间的匹配关系,也考虑到了周围的晶粒各个取向的影响。实验结果表明,相邻晶粒的锥面滑移<a>对孪晶晶粒的孪生变体选择起到主要贡献,这可能与较大应变的变形条件有关[15,19]。Guan等[15]研究表明,Mg和Ti都是hcp结构,Mg和Ti的轴比不同,在Mg中主要以基面滑移为主,但是在大应变条件下非基面滑移也会发生,而在Ti中以柱面滑移为主导,但是在大应变条件下非柱面滑移也会发生[19],这可能是本研究中所采用的低温、高应变速率、大变形的条件下,锥面滑移<a>成为促进孪晶变体形成的主要原因。
3 结论
(1) 在液氮温度下对纯Ti样品进行50%大变形量动态塑性变形,变形后试样中有大量孪晶产生,孪晶界占比高达21.24%,其中初级{
(2) 变形孪晶使原始晶粒Schmid因子发生了变化,当沿ND方向施加载荷,基面滑移系的Schmid因子在孪生后变大,其他滑移系的Schmid因子孪生前后变化不明显。
(3) 提出以取向相容因子ω作为多晶纯Ti孪晶变体选择的依据,ω越大该孪晶变体越容易启动,计算结果与实验结果相结合验证了参数ω的合理性,通过实际孪晶变体的分析,表明锥面<a>滑移对孪晶变体的选择起主要作用。
参考文献
Influence of phase volume fraction on the grain refining of a Ti-6Al-4V alloy by high-pressure torsion
[J].
Preparation of Ti(C x N1 - x ) thick films on titanium by plasma electrolytic carbonitriding
[J].
纯钛表面电解液微弧碳氮化制备碳氮化钛厚膜
[J].采用电解液微弧碳氮化技术(PECN), 在纯钛试样表面沉积出较厚且与基体结合牢固的多孔纳米Ti(CxN1-x)改性层, 研究了改性层结构和组成随PECN处理时间的演变规律. 结果表明: 随放电处理时间延长, PECN--Ti(CxN1-x)膜层厚度、膜层中C/N的原子比以及微孔直径皆增加. 处理150 min时, Ti(CxN1-x)膜层厚度可达15 um, 且膜层是由晶粒尺寸为40-60 nm的纳米晶粒组成. 处理过程中有氢渗入, 并在Ti(CxN1-x)层下面形成富含TiH2的过渡层. 后期的真空退火处理可以将氢除去使TiH2完全分解, 而不影响表面Ti(CxN1-x)膜的成分和形貌
The crystallography and deformation modes of hexagonal close-packed metals
[J].
Mechanik der plastischen formänderung von kristallen
[J].
Influences of temperature and strain rate on deformation twinning of polycrystalline titanium
[J].
温度和应变率对多晶纯钛孪晶变形的影响
[J].
The high-strain-rate response of alpha-titanium: Experiments, deformation mechanisms and modeling
[J].
Deformation twinning activity and twin structure development of pure titanium at cryogenic temperature
[J].
{11
Deformation behaviour of commercially pure titanium at extreme strain rates
[J].
Formation of nanostructures in commercial-purity titanium via cryorolling
[J].
Dynamic mechanical behavior of pure titanium
[J].
Dynamic plastic deformation (DPD): A novel technique for synthesizing bulk nanostructured metals
[J].
Effect of the Zener-Hollomon parameter on the microstructures and mechanical properties of Cu subjected to plastic deformation
[J].
Basal slip mediated tension twin variant selection in magnesium WE43 alloy
[J].
Deformation twinning
[A].
A self-consistent anisotropic approach for the simulation of plastic deformation and texture development of polycrystals: Application to zirconium alloys
[J].
Twinning, slip and catastrophic flow in niobium
[J].
Twin nucleation by slip transfer across grain boundaries in commercial purity titanium
[J].
Effect of deformation twinning on microstructure and texture evolution during cold rolling of CP-titanium
[J].
The role of strain rate and texture in the deformation of commercially pure titanium at cryogenic temperature
[J].
High strength and ductility of pure titanium via twin-structure control using cryogenic deformation
[J].
Deformation behaviour of commercially pure titanium during simple hot compression
[J].
Microstructural analysis and tensile properties of thick copper and nickel sputter deposits
[J].
Slip, twinning, and fracture in hexagonal close-packed metals
[J].
Initiation and accommodation of primary twins in high-purity titanium
[J].
Tensile and fatigue properties and deformation mechanisms of twinning-induced plasticity steels
[J].
孪生诱发塑性钢拉伸与疲劳性能及变形机制
[J].随着汽车工业的高速发展,以开发先进高强钢为重点的车辆轻量化设计已经成为各大汽车厂商的发展共识。本文基于国内外孪生诱发塑性(TWIP)钢强韧性和抗疲劳设计的成果以及本课题组多年来在该领域的研究工作,系统地总结了TWIP钢的研究现状及最新进展,探讨了影响TWIP钢拉伸性能与变形机制的影响因素,包括合金成分、组织状态、应变速率等。重点介绍TWIP钢的高、低周疲劳性能和微观损伤行为,并提出一种客观评价和预测低周疲劳寿命的方法。从TWIP钢的服役环境和实际应用角度出发,试图为新一代高性能TWIP钢的开发提供新的思路和实验证据。
Nonbasal deformation modes of HCP metals and alloys: Role of dislocation source and mobility
[J].
Compatibility of deformation in two-phase Ti Al alloys: Dependence on microstructure and orientation relationships
[J].