通常,这些钢板中含有Si、Mn、Al等合金元素,在浸入锌池前的退火过程中,这些可氧化的合金元素会扩散到钢板表面发生选择性氧化行为,形成SiO2、MnO、Al2O3等氧化物,从而影响可镀性。Miyata等[3]的研究表明,对于TRIP钢而言,当Si、Mn元素含量(质量分数)比在0.6左右时,界面组织由致密的Fe-Zn化合物组成,而Si、Mn比达到1左右时,表面会产生大量SiO2,导致可镀性下降;Blumenau等[4]在研究中指出,当Mn含量(质量分数,下同)高达20%以上时,钢中的Mn元素会消耗锌液中的大部分Al,反应生成MnAl6溶解到锌液中,造成Zn层中出现脆性ζ-FeZn13相,导致Zn层质量下降;而Bellhouse等 [5]的研究则发现,当Si元素含量提高到1.5%时,会造成剧烈铝热反应消耗锌液中的Al,使得Fe与锌液反应形成Fe-Zn化合物,从而影响Fe2Al5Zn0.4抑制层的形成,导致钢板的可镀性降低。由此可见,不同的Si和Mn含量及配比会形成不同的界面层组织,从而影响可镀性。
基于此,本工作采用搭载拉伸试验台的热场发射扫描电镜,原位分析3种先进高强钢,即Si-Mn系的DP钢和QP钢以及Mn-Al系轻质中锰钢的拉伸断裂行为,并结合界面组织实验分析和热力学计算,研究在相同热浸镀锌工艺条件下成分对界面组织的影响,阐明界面组织对高强钢力学行为的影响机理,从而为汽车用高强镀锌板的开发与应用提供理论参考。
1 实验方法
采用表1中3种980 MPa强度级别的汽车钢板作为实验用钢。No.1和No.2分别为宝钢生产的1.2 mm 厚的DP钢和QP钢冷轧板。No.3钢为轻质中锰钢,采用100 kg真空感应炉熔炼,经均匀化退火后热轧至3.5 mm,再经酸洗冷轧后,获得1.2 mm厚的实验用冷轧板。
表1 3种高强钢的化学成分 (mass fraction / %)
Table 1
| Steel No. | C | Mn | Si | Cr | Al | Ti | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.12 | 2.36 | 0.24 | 0.51 | 0.02 | 0.02 | Bal. |
| 2 | 0.22 | 2.34 | 1.59 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.02 | Bal. |
| 3 | 0.28 | 3.67 | - | - | 4.99 | - | Bal. |
采用Iwatani-Surtec热镀锌模拟实验装置对高强钢进行热浸镀锌处理,露点为+10 ℃,退火气氛为20%H2+80%N2 (体积分数),锌液成分为Zn-0.2%Al (质量分数),气刀N2量为200 L/min。100 mm×220 mm的矩形样品经丙酮与酒精清洗后置于镀锌模拟机内,以30 ℃/s速率加热至870 ℃保温240 s,以20 ℃/s速率冷却到460 ℃浸入锌池,3 s后取出,充N2快冷到室温。
采用搭载1.5 kN拉伸试验台的Apollo3000热场发射扫描电镜(SEM)对3种高强钢的拉伸断裂行为进行原位观察,加速电压为20 keV,拉伸速率为0.1 mm/min。样品尺寸如图1所示,样品厚度为1.2 mm。
图1
图1
原位分析时拉伸实验样品尺寸示意图
Fig.1
Schematic of tensile sample size for in situ analysis (unit: mm)
采用Helios600i双束型聚焦离子束(FIB)制备样品,并采用JEM-2100F场发射透射电镜(FE-TEM)分析界面层组织,加速电压为200 keV。在ETM504C电子万能试验机上开展室温静态拉伸实验,实验用钢板按照GB/T 228-2010加工成标距为30 mm的拉伸试样,其中,去Zn层实验用钢板需用20% (体积分数)的盐酸水溶液浸泡并用细砂纸轻磨。
2 热浸镀锌高强钢的界面组织及其热力学分析
2.1 界面组织
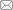
图2为3种高强钢经HCl、H2SO4腐蚀后的表面形貌及EDS分析。可以看出,3种高强钢经过相同热浸镀锌工艺处理后,表面均分布有颗粒状Fe-Al-Zn抑制层。其中,No.3钢表面颗粒粗大,No.1钢表面颗粒细小致密,而对No.2钢而言,其表面还存在致密的丝状Fe-Zn化合物。
图2
图2
3种高强钢经HCl、H2SO4腐蚀后的表面形貌及EDS分析
Fig.2
SEM images and EDS analyses of the inhibition layer in steels No.1 (a), No.2 (b) and No.3 (c) corroded by hydrochloric acid, and steel No.2 corroded by sulphuric acid (d)
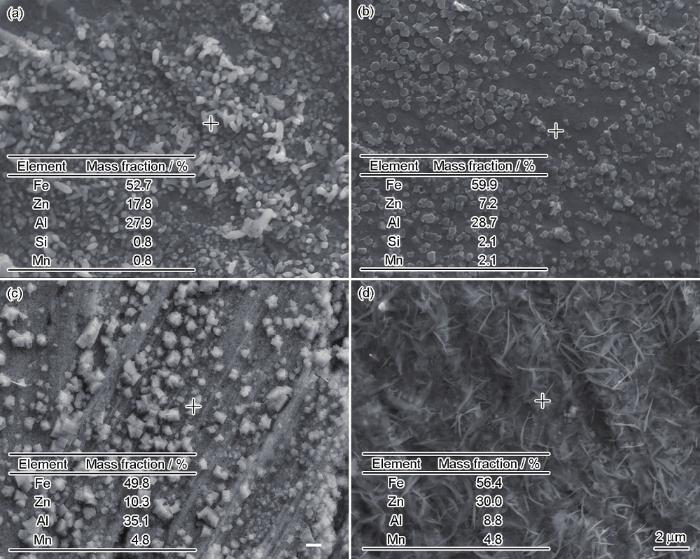
图3,4,5分别为No.1~No.3钢在退火温度为870 ℃、露点为+10 ℃热浸镀锌条件下基体/Zn层界面组织的TEM分析结果。结合图3a的界面形貌和EDS分析可以看出,No.1钢界面区域由上部Zn层、Fe-Al-Zn抑制层(虚线区)和Fe基体构成。结合图3b和c的结构分析可知,抑制层主要由Fe2Al5Zn0.4形成,其间分布少量MnO,基体为铁素体。由图4a可见,与No.1钢相比,No.2钢界面组织同样包括上部Zn层、Fe-Al-Zn抑制层和Fe基体,但Fe-Al-Zn抑制层分布不连续,在铁基体中存在Fe-Zn化合物和少量内氧化物。结合图4b和c对抑制层结构分析可知,抑制层存在Fe2Al5Zn0.4和Al2O3,根据图4d和e,铁素体基体中存在的Fe-Zn化合物是ζ-FeZn13相。而对于No.3钢,图5a显示,其Zn层和铁基体之间是一层连续的Mn-O化合物,经图5b的结构分析确定为MnO层,结合图5a和c,No.3钢上部Zn层中出现了Γ-Fe11Zn40相,而结合图5a、d和e可知,在铁素体基体中分布有Al2O3。
图3
图3
No.1钢在退火温度为870 ℃、露点为+10 ℃热浸镀锌条件下基体/Zn层界面组织的TEM分析
Fig.3
Cross-sectional TEM analyses of the steel/Zn coating interface of the galvanizing steel No.1 annealed at 870 ℃ in a gas atmosphere with a dew point of +10 ℃
Color online
(a) TEM image and EDS elemental distribution maps of interface
(b, c) dark field TEM images and corresponding SAED patterns (insets) of Fe2Al5Zn0.4 and MnO in inhibition layer, respectively
(d) dark field TEM image and corresponding SAED pattern (inset) of Fe substrate
图4
图4
No.2钢在退火温度为870 ℃、露点为+10 ℃热浸镀锌条件下基体/Zn层界面组织的TEM分析
Fig.4
Cross-sectional TEM analyses of the steel/Zn coating interface of the galvanizing steel No.2 annealed at 870 ℃ in a gas atmosphere with a dew point of +10 ℃(a) TEM image and EDS elemental distribution maps of interface(b, c) dark field TEM images and corresponding SAED patterns (insets) of Fe2Al5Zn0.4 and Al2O3 in inhibition layer, respectively (d, e) dark field TEM images and corresponding SAED patterns (insets) of ferrite and ζ-FeZn13 in Fe substrate, respectively
Color online
图5
图5
No.3钢在退火温度为870 ℃、露点为+10 ℃热浸镀锌条件下基体/Zn层界面组织的TEM分析
Fig.5
Cross-sectional TEM analyses of the steel/Zn coating interface of the galvanizing steel No.3 annealed at 870 ℃ in a gas atmosphere with a dew point of +10 ℃
Color online
(a) TEM image and EDS elemental distribution maps of interface
(b) dark field TEM image and corresponding SAED pattern (inset) of MnO layer
(c) dark field TEM image and corresponding SAED pattern (inset) of Γ-Fe11Zn40 in Zn coating
(d, e) dark field TEM images and corresponding SAED patterns (insets) of ferrite and Al2O3 in Fe substrate, respectively
2.2 高强钢表面氧化物形成的热力学分析
图6
图6
3种高强钢在不同O2分压下的表面氧化物含量
Fig.6
Contents of surface oxide on high-strength steels No.1 (a), No.2 (b) and No.3 (c) under different O2 partial pressures (
饱和水蒸气压与露点的关系:
计算出不同露点下对应的不同氧分压:
式中,
由图6计算结果可知,No.1钢表面形成的主要稳定相是Mn2SiO4与MnO,No.2钢表面形成的主要稳定相为Mn2SiO4和SiO2,而No.3钢表面形成的稳定相则由MnAl2O4与Al2FeO4组成。相比之下,No.3钢表面形成的稳定氧化物含量最高,No.2钢次之,而No.1钢表面氧化物含量最少。
2.3 高强钢界面组织形成的热力学分析
由图6中的热力学计算可见,No.3钢表面形成的稳定氧化物应为Al2FeO4和MnAl2O4,且形成量较高。不过,有研究[20,21]指出,在高露点下Al和O的结合力较强,当未达到热力学平衡状态时,MnO+Al2O3通常先于MnAl2O4形成,而FeO+Al2O3则先于Al2FeO4形成,即经高温退火4 min后,钢板表面可能存在MnO、Al2O3和FeO亚稳相。此时,MnO会发生
根据以上热力学分析可见,在相同热浸镀锌工艺条件下,由于3种不同高强钢成分体系不同,形成的表面氧化物不同,进而对其界面组织产生了不同的影响。
3 界面组织对拉伸断裂行为的影响
3.1 高强钢拉伸断裂行为的原位分析
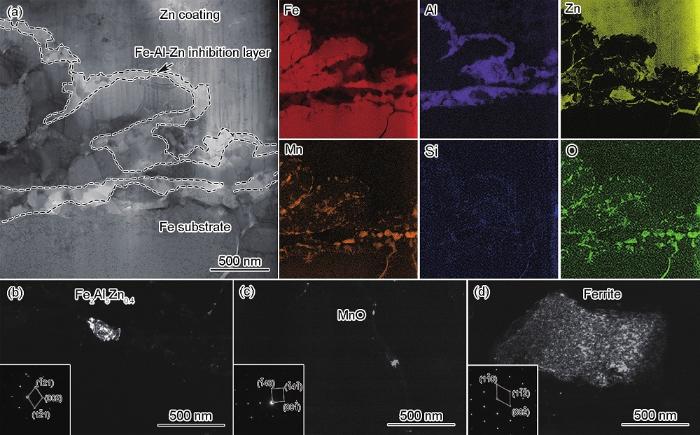
采用搭载有拉伸试验台的扫描电镜,对不同界面组织的3种高强钢的拉伸变形行为进行了分析,如图7,8,9所示。由图7a可以看出,No.1钢的界面区域不存在明显的化合物。当拉伸变形量达到6%时,界面位置产生裂纹(图7b),随着变形量的增大,裂纹进一步向Zn层扩展。当变形量为9%时,可以看到Zn层完全开裂,并且基体发生明显的变形(图7c)。当变形量达到12%时,试样发生断裂(图7d)。由图8a可以看出,No.2钢界面靠近铁基体区域存在Fe-Zn化合物;在拉伸至6%的变形量时,裂纹在Zn层/基体界面处形成(图8b);随着变形量的增大,在图8c中看到Fe-Zn相的位置出现粗大裂纹,这些裂纹向铁基体中扩展,直至变形量为14%时发生断裂(图8d)。值得指出的是,No.2钢中Zn层的开裂与基体失效断裂几乎同时发生。由图9a可以看出,No.3钢界面区域不存在明显的化合物,在拉伸至3%的变形量时,裂纹在Zn层中产生(图9b)。随着变形量的增大,裂纹增多并加深,在Zn层中扩展(图9c),至17%变形量时发生断裂(图9d)。
图7
图7
No.1钢拉伸至不同变形量时裂纹扩展的原位分析
Fig.7
In situ analyses of cracking of steel No.1 under different deformations
Color online
(a) EDS line scan analysis (along dash arrow, inset) of the steel/coating interface, respectively
(b, c) the cracking in coating under 6% and 9% deformations
(d) fracture zone under 12% deformation
图8
图8
No.2钢拉伸至不同变形量时裂纹扩展的原位分析
Fig.8
In situ analyses of cracking of steel No.2 under different deformations
Color online
(a) EDS line scan analysis (along dash arrow, inset) of the steel/coating interface
(b) the cracking in coating under 6% deformation
(c) EDS analysis of Fe-Zn compounds and the cracking in coating under 12% deformation
(d) fracture zone under 14% deformation
图9
图9
No.3钢拉伸至不同变形量时裂纹扩展的原位分析
Fig.9
In situ analyses of cracking of steel No.3 under different deformations
Color online
(a) EDS line scan analysis (along dash arrow, inset) of the steel/coating interface
(b, c) the cracking in coating under 3% and 9% deformations, respectively
(d) fracture zone under 17% deformation
3.2 高强钢室温拉伸性能研究
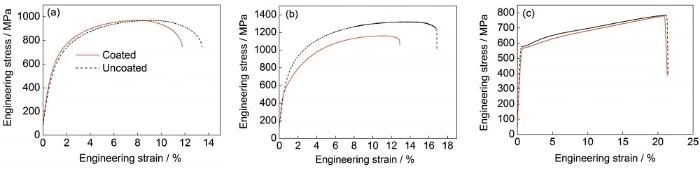
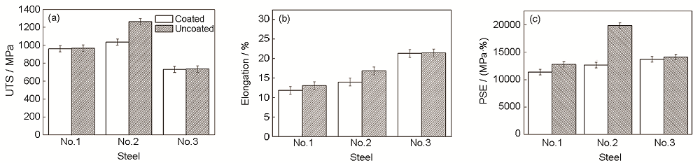
由以上原位分析可以看出,不同界面组织的3种热浸镀锌高强钢板在拉伸过程中的断裂行为明显不同:No.1钢在6%变形量时,拉伸裂纹在界面产生,向Zn层扩展,Zn层开裂后基体继续变形直至失效;No.2钢的拉伸裂纹同样在界面产生,向基体扩展直至试样断裂,而No.3钢在约3%变形量时Zn层出现裂纹,并在Zn层扩展,基体变形失效后试样断裂。本工作采用室温拉伸性能测试,进一步研究了这种断裂行为对高强钢力学性能的影响。图10为镀锌钢板(coated)与去除锌层钢板(uncoated)室温拉伸过程中的工程应力-工程应变曲线,图11是其抗拉强度、断裂延伸率以及强塑积的对比。可以看出,No.2钢去锌板的力学性能明显优于镀锌板,No.1钢去锌板的塑性略好于镀锌板,而No.3钢几乎没有变化。No.2钢镀锌板在拉伸过程中裂纹向基体扩展,是其力学性能较差的主要原因
图10
图10
3种高强镀锌板与去锌板的工程应力-工程应变曲线
Fig.10
Engineering stress-engineering strain curves of high-strength coated and uncoated steels No.1 (a), No.2 (b) and No.3 (c)
图11
图11
3种高强镀锌板与去锌板的力学性能
Fig.11
Ultimate tensile strength (UTS) (a), elongation (b) and product of strength and elongation (PSE) (c) of three high-strength coated and uncoated steels
3.3 界面组织对拉伸断裂行为的影响
图12
图12
3种高强钢界面组织对其拉伸断裂行为的影响示意图
Fig.12
Schematics of cracking mechanism at the coating and steel interface of high strength steels No.1 (a), No.2 (b) and No.3 (c)
综上所述,No.2钢界面组织会对其力学性能造成不利的影响,No.3钢Zn层中存在脆性化合物所以Zn层质量较差。通过调整成分和镀锌工艺参数(退火温度、气氛、露点等)以控制界面组织,有望改变镀锌产品的质量。
4 结论
(1) 在退火温度870 ℃,还原性气氛为20%H2+80%N2 (体积分数),以及露点为+10 ℃的热浸镀锌工艺条件下,No.2钢表面形成Mn2SiO4与SiO2热力学稳定相,由于发生铝热还原反应消耗了Al,阻碍了连续Fe2Al5Zn0.4抑制层的形成,存在ζ-FeZn13脆性相的界面层组织在拉伸应力作用下容易发生开裂,并向基体扩展造成力学性能下降。
(2) 在相同热浸镀锌工艺条件下,No.1钢表面形成少量Mn2SiO4与MnO热力学稳定相,界面层组织主要由连续的Fe2Al5Zn0.4抑制层组成,在拉伸应力作用下界面产生裂纹向Zn层扩展,基本不会影响力学性能。
(3) 在相同热浸镀锌工艺条件下,No.3钢表面形成MnO与FeO亚稳相,被Al还原出的Fe与锌液接触使得Zn层内部形成脆性Γ-Fe11Zn40相,在拉伸变形初期,Zn层即发生开裂,但主要由MnO组成的界面组织不会对力学性能产生明显影响。
参考文献
Development trend and challenge of advanced high strength automobile steels
[J].
先进高强度汽车钢的发展趋势与挑战
[J].
Development trend of substituting hot-biq galvanized sheet for electro-galvanized sheet
[J].This paper discusses the present status and trend of substituting hot-dip galvanized sheet for electro- galvanized steel sheet. The advantages and disadvantages ofhot-dip galvanized sheet and electro-galvanized sheet are described in the paper.
国内外热镀锌板取代电镀锌板的发展趋势
[J].探讨了国内外热镀锌板取代电镀锌板的现状及发展趋势,分别阐述了热镀锌板和电镀锌板的优势和劣势。
Effect of Si/Mn ratio on galvannealing behavior of Si-addied steel
[J].
Reactive wetting during hot-dip galvanizing of high manganese alloyed steel
[J].
Selective oxidation and reactive wetting of 1.0 pct Si-0.5 pct Al and 1.5 pct Si TRIP-assisted steels
[J].
Development of the surface structure of TRIP steels prior to hot-dip galvanizing
[J].
Microstructure and tensile behavior of duplex low-density steel containing 5 mass% aluminum
[J].
Formability of galvanized interstitial-free steel sheets
[J].
Characterization of hot-dip galvanized coating on dual phase steels
[J].
Influence of gas atmosphere dew point on the selective oxidation and the reactive wetting during hot dip galvanizing of CMnSi TRIP steel
[J].
Formation of surface and subsurface oxides during ferritic, intercritical and austenitic annealing of CMnSi TRIP steel
[J].
Effects of dew point on selective oxidation of TRIP steels containing Si, Mn, and B
[J].
Selective oxidation of dual phase steel after annealing at different dew points
[J].
Thermodynamic analysis of selective oxidation behavior of Si and Mn-added steel during recrystallization annealing
[J].
Numerical simulation of internal oxidation of steels during annealing treatments
[J].
Selective oxidation and reactive wetting during hot-dip galvanizing of a 1.0 pct Al-0.5 pct Si TRIP-assisted steel
[J].
Analysis of the Fe-Zn interface of galvanized high Al-low Si TRIP steels
[J].
Selective oxidation and reactive wetting during galvanizing of a CMnAl TRIP-assisted steel
[J].
Role of Al in Zn bath on the formation of the inhibition layer during hot-dip galvanizing for a 1.2Si-1.5Mn transformation-induced plasticity steel
[J].
Hot dip galvanizing behavior of advanced high strength steel
[J].
Selective oxidation of Al rich Fe-Mn-Al-C low density steels
[J].
Effect of alloying element segregation on the work of adhesion of metallic coating on metallic substrate: Application to zinc coatings on steel substrates
[J].
Compression deformability of Γ and ζ Fe-Zn intermetallics to mitigate detachment of brittle intermetallic coating of galvannealed steels
[J].
Relation between microstructure and adhesion of hot dip galvanized zinc coatings on dual phase steel
[J].