钴基高温合金通常应用于复杂恶劣的高温环境。为此,在合金的设计上,需要赋予其良好的高温力学性能和高温抗腐蚀性能。众所周知,钴基合金的抗高温氧化性能有赖于其表面是否能生成稳定、连续、缓慢生长且黏附性良好的氧化膜,如Al2O3和Cr2O3[1~5]。合金能生成保护性Al2O3膜的前提是其所含Al的浓度必须超过一定的临界值,这将会对合金的力学性能产生不利影响[5]。而Cr和Al的同时存在可以通过第三元素效应(TEE)[1,5]降低形成Al2O3膜所需的临界Al含量,从而使合金兼具良好的力学性能与抗高温氧化性能。研究人员已对三元Co-Cr-Al[6~11]和Ni-Cr-Al[11~22]合金的高温氧化行为进行了大量研究。
Weiser等[23,24]、Gao等[25]和Zenk等[26]研究发现,钴基合金中添加Ni元素能够提高其抗氧化性能,这一结果可能与Co和Ni 2种氧化物的生成自由能[1]和生长速率之间的差异以及O在2种金属中的溶解度和扩散率的差异有关[1,27]。到目前为止,关于Cr、Al元素对Co-Ni合金高温氧化行为影响的研究仍然较少。Seraffon等[28,29]研究了磁控溅射四元Co-Ni-Cr-Al涂层在900和950℃的空气中的高温氧化性能,并绘制了近似氧化图以分析M-Cr-Al型(M = Co、Ni)伪三元相图中外Al2O3膜生成的稳定区域。然而,由于沉积的涂层较薄且存在成分不均匀等缺陷,其高温氧化性能仍然有别于Co-Ni-Cr-Al合金。因此,有必要深入研究四元Co-Ni-Cr-Al合金的抗高温氧化性能。
本工作研究了2种Co-20Ni-8Cr-xAl (x = 3、5,质量分数,%,下同)合金在800、900、1000和1100℃下1.013 × 105 Pa O2中的等温氧化行为,探讨温度和Al含量对其抗氧化性和所生成氧化膜结构的影响。
1 实验方法
表1 Co-20Ni-8Cr-3Al和Co-20Ni-8Cr-5Al合金的设计成分和实际成分
Table 1
| Nominal (mass fraction / %) | Nominal (atomic fraction / %) | Actual (mass fraction / %) |
|---|---|---|
| Co-20Ni-8Cr-3Al | Co-19.27Ni-8.65Cr-6.23Al | Co-20.1Ni-7.99Cr-3.02Al |
| Co-20Ni-8Cr-5Al | Co-18.94Ni-8.38Cr-10.26Al | Co-20.2Ni-7.92Cr-5.03Al |
将退火后的合金铸锭经线切割成约10 mm × 8 mm × 1.5 mm的样品,并在边缘处切一个直径1 mm的孔便于悬挂。所有的样品均通过砂纸机械打磨至2000号,然后经丙酮、酒精超声清洗,吹干备用。
在氧压为1.013 × 105 Pa、流速为100 mL/min的O2中进行高温氧化实验。用Pt丝将样品悬挂在热天平中,随炉加热至实验温度,在800和900℃时持续24 h,1000和1100℃时持续20 h。实验结束时,样品在炉内冷却至室温。
采用配备X-MAX能谱仪(EDS)的INSPECTF 50扫描电镜(SEM)和Panalytical X'pert PRO X射线衍射仪(XRD)对样品进行表征,观察氧化膜截面形貌,确定氧化膜的成分、元素分布及相组成等。
2 实验结果
2.1 氧化动力学
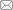
图1为Co-20Ni-8Cr-3Al和Co-20Ni-8Cr-5Al合金在800~1100℃的纯O2气氛中恒温氧化20 h的动力学曲线。在800℃时,Co-20Ni-8Cr-3Al合金在经过大约30 min的初始阶段后是抛物线速率常数(kp)为2.16 × 10-11 g2/(cm4·s)的抛物线阶段,直至实验结束。Co-20Ni-8Cr-5Al与Co-20Ni-8Cr-3Al合金的氧化增重曲线几乎重合,但在16 h后氧化速率略有下降,因此在经过30 min的初始阶段后显示为2个抛物线阶段,第1个阶段从0.5 h持续至16 h,kp = 2.09 × 10-11 g2/(cm4·s),随后是第2阶段,kp约为1.57 × 10-11 g2/(cm4·s)。
图1
图1
Co-20Ni-8Cr-3Al和Co-20Ni-8Cr-5Al合金在800、900、1000和1100℃下1.013 × 105 Pa O2中氧化20 h的动力学曲线
Fig.1
Kinetic curves for the oxidation of the Co-20Ni-8Cr-3Al and Co-20Ni-8Cr-5Al alloys in 1.013 × 105 Pa O2 at 800oC (a, b), 900oC (c, d), 1000oC (e, f), and 1100oC (g, h) for 20 h (t—time; kp, kp1, and kp2—rate constants)
(a, c, e, g) linear plots (b, d, f, h) parabolic plots
Co-20Ni-8Cr-3Al在900℃的行为与800℃类似,在经过大约30 min的初始阶段之后,为抛物线阶段,kp = 1.89 × 10-9 g2/(cm4·s)。Co-20Ni-8Cr-5Al在900℃时的初始抛物线阶段大约从15 min开始一直持续到9 h, kp = 8.71 × 10-10 g2/(cm4·s);随后第2阶段的氧化速率逐渐减小,最终kp = 4.94 × 10-10 g2/(cm4·s)。
1000℃时,Co-20Ni-8Cr-3Al的氧化显示为2个抛物线阶段,初始抛物线阶段从约25 min开始持续至7 h,kp = 8.56 × 10-9 g2/(cm4·s);随后是氧化速率有所下降的第2阶段,kp降为4.07 × 10-9 g2/(cm4·s)。Co-20Ni-8Cr-5Al合金也表现出类似行为,从初始kp = 9.64 × 10-11 g2/(cm4·s)降至最终kp = 9.50 × 10-12 g2/(cm4·s)。
在1100℃时,Co-20Ni-8Cr-3Al在前5 h呈现初始抛物线阶段,kp = 2.40 × 10-8 g2/(cm4·s),然后从5 h至20 h氧化速率随时间显著降低,kp约为6.77 × 10-10 g2/(cm4·s)。而Co-20Ni-8Cr-5Al在经历约1 h的快速增重后,呈现一个非常缓慢的近似抛物线的阶段,kp = 1.50 × 10-12 g2/(cm4·s)。
对比合金在各温度下的抛物线速率常数可知,在800℃氧化时,Al含量增加对合金的增重影响较小,而随着温度升高至900、1000和1100℃,因Al含量从3%增加到5%而导致合金氧化增重显著降低。
图2为4个氧化温度下2种合金的动力学曲线,以更清晰地显示温度变化对其氧化行为的影响。随着温度升高,Co-20Ni-8Cr-3Al增重逐渐增加,但1100℃时的曲线最终斜率明显小于1000℃时的曲线,即1100℃时的氧化速率最终低于1000℃。Co-20Ni-8Cr-5Al在900℃下的增重远大于其他氧化温度,而1000和1100℃的曲线在约7 h后相交。综上,温度从800℃升到900℃对2种合金的抗氧化性有消极影响,导致氧化速率显著提高;当温度升高到1000℃,Co-20Ni-8Cr-3Al的氧化速率继续增加,而Co-20Ni-8Cr-5Al则明显下降;温度从1000℃升高到1100℃ 2种合金的氧化速率均降低。
图2
图2
Co-20Ni-8Cr-3Al和Co-20Ni-8Cr-5Al合金在800、900、1000和1100℃下1.013 × 105 Pa O2中氧化20 h的动力学曲线
Fig.2
Kinetic curves for oxidation of the Co-20Ni-8Cr-3Al (a) and Co-20Ni-8Cr-5Al (b) alloys in 1.013 × 105 Pa O2 at 800, 900, 1000, and 1100oC for 20 h
2.2 氧化膜的形态和结构
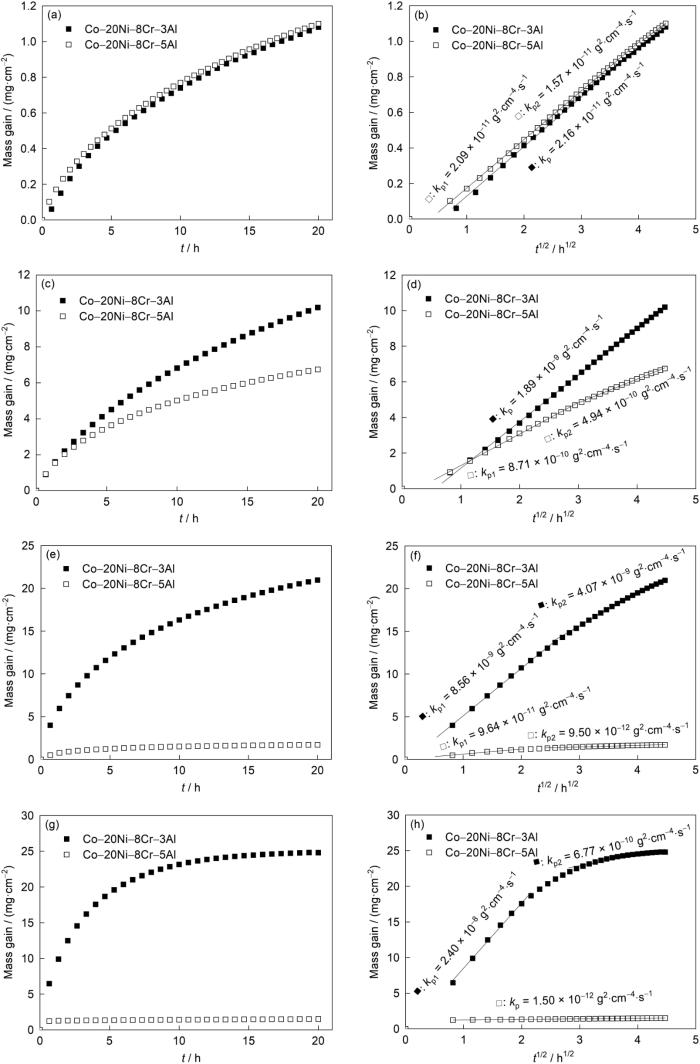
图3
图3
Co-20Ni-8Cr-3Al合金在800℃、1.013 × 105 Pa O2中氧化24 h的截面形貌和相应的元素分布
Fig.3
Cross-sectional morphologies (a, b) and element distributions (c) of Co-20Ni-8Cr-3Al alloy oxidized in 1.013 × 105 Pa O2 at 800oC for 24 h (Fig.3b is the enlarged view of selected area in Fig.3a; IOZ—internal oxidation zone)
图4
图4
Co-20Ni-8Cr-3Al合金在900℃、1.013 × 105 Pa O2中氧化24 h的截面形貌
Fig.4
Cross-sectional morphologies of Co-20Ni-8Cr-3Al alloy oxidized in 1.013 × 105 Pa O2 at 900oC for 24 h
(a) general view (b) view of a different region
图5
图5
Co-20Ni-8Cr-3Al合金在1000和1100℃下1.013 × 105 Pa O2中氧化20 h的截面形貌
Fig.5
Cross-sectional morphologies of Co-20Ni-8Cr-3Al alloy oxidized in 1.013 × 105 Pa O2 at 1000oC (a1, a2) and 1100oC (b1, b2) for 20 h (Figs.5a2 and b2 are the enlarged views of selected areas in Fig.5a1 and b1, respectively)
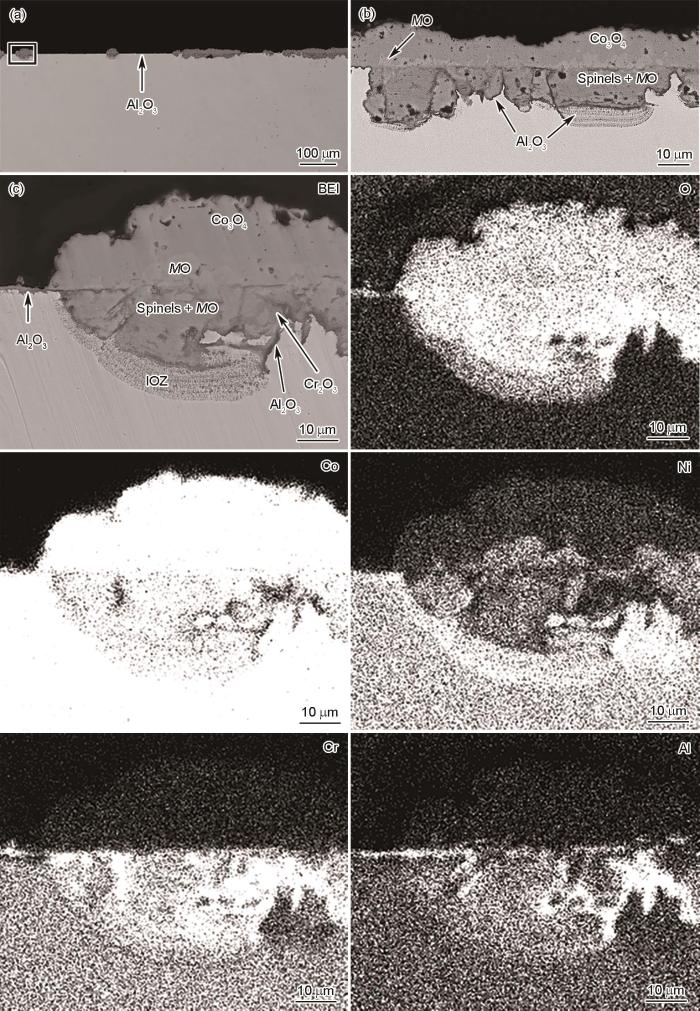
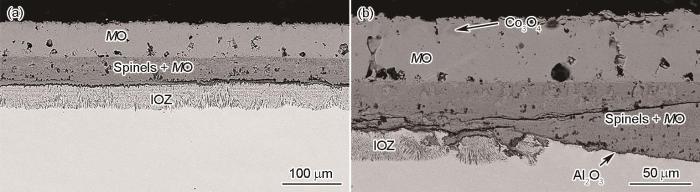
图6
图6
Co-20Ni-8Cr-5Al合金在800和900℃下1.013 × 105 Pa O2中氧化24 h的截面形貌
Fig.6
Cross-sectional morphologies of Co-20Ni-8Cr-5Al alloy oxidized in 1.013 × 105 Pa O2 at 800oC (a1, a2) and 900oC (b1, b2) for 24 h (Figs.6a2 and b2 are the enlarged views of selected areas in Figs.6a1 and b1, respectively)
图7
图7
Co-20Ni-8Cr-5Al合金在1000和1100℃下1.013 × 105 Pa O2中氧化20 h的截面形貌
Fig.7
Cross-sectional morphologies of Co-20Ni-8Cr-5Al alloy oxidized in 1.013 × 105 Pa O2 at 1000oC (a1, a2) and 1100oC (b1, b2) for 20 h (Figs.7a2 and b2 are the enlarged views of selected areas in Figs.7a1 and b1, respectively)
图8
图8
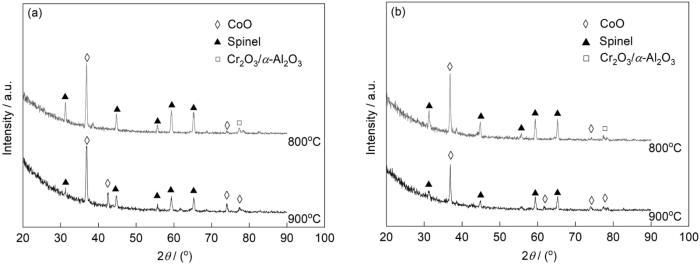
Co-20Ni-8Cr-3Al和Co-20Ni-8Cr-5Al合金在800和900℃下1.013 × 105 Pa O2中氧化24 h后的XRD谱
Fig.8
XRD spectra of Co-20Ni-8Cr-3Al (a) and Co-20Ni-8Cr-5Al (b) alloys oxidized in 1.013 × 105 Pa O2 at 800 and 900oC for 24 h
图9
图9
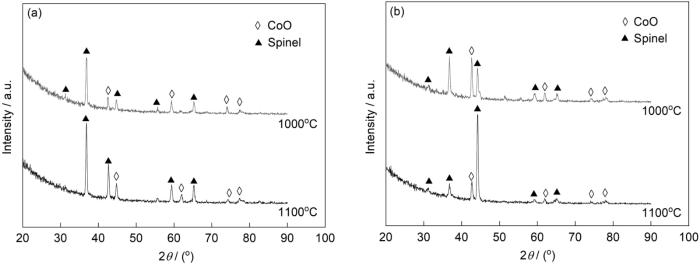
Co-20Ni-8Cr-3Al和Co-20Ni-8Cr-5Al合金在1000和1100℃ 1.013 × 105 Pa O2中氧化20 h后的XRD谱
Fig.9
XRD spectra of Co-20Ni-8Cr-3Al (a) and Co-20Ni-8Cr-5Al (b) alloys oxidized in 1.013 × 105 Pa O2 at 1000 and 1100oC for 20 h
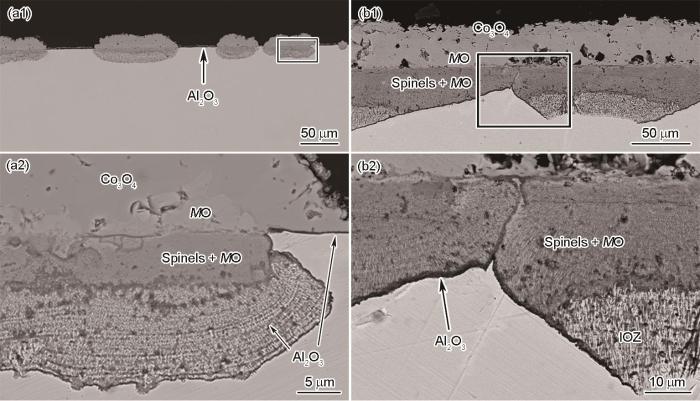
Co-20Ni-8Cr-3Al合金在800℃下氧化24 h的截面形貌如图3所示。大部分合金表面生成了连续的具有2层结构的外氧化膜,外层由Co3O4 (较暗)构成,包含CoO和NiO的固溶体(较亮,下文简单地表示为MO),在合金消耗区为MO和通式为MR2O4 (其中M = Co、Ni和R = Cr、Al,以下简称为尖晶石)的混合物的内层。Al的内氧化区(IOZ)仅存在于外氧化层下方的某些位置(图3b)。部分合金表面被一层薄薄的Al2O3膜覆盖,抑制了合金的内氧化(图3a)。合金表面结核状的氧化膜部分呈现出与图3b所示的连续氧化膜相似的结构。在900℃下氧化后(图4),Co-20Ni-8Cr-3Al表面的外氧化膜与800℃相似,但更厚且更规则(图4a)。氧化膜外层主要由MO组成,包含部分Co3O4颗粒,内层同样由MO和尖晶石组成。Al的内氧化通常也存在于氧化膜/合金界面下方(图4a),而在少数区域,在氧化膜/合金界面处形成连续的Al2O3薄层,防止了合金发生内氧化(图4b)。
Co-20Ni-8Cr-3Al在1000和1100℃的1.013 × 105 Pa O2中氧化20 h后的截面形貌如图5所示。在2种温度下,合金表面均生成了双层氧化膜,其外层主要由CoO与少量NiO (MO)组成,内层则为MO与尖晶石以及Cr2O3的混合物。在1000℃氧化后的合金外氧化膜下存在Al的内氧化区,但在少数位置,在外氧化膜/合金界面形成一层连续的氧化膜,阻止了合金的内氧化。而在1100℃氧化后的Co-20Ni-8Cr-3Al合金(图5b),Al的内氧化区显著少于1000℃,且内层尖晶石和Cr2O3的数量有所增加。由于外部CoO层的快速生长(在2种温度下约占总氧化膜厚度的50%),该合金在1000和1100℃下均未表现出良好的抗高温氧化性能。
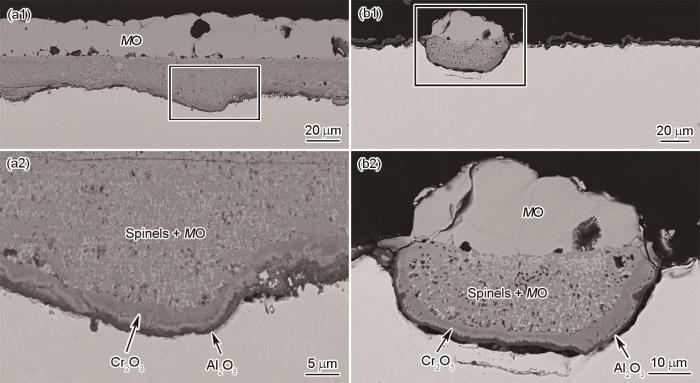
图6a为Co-20Ni-8Cr-5Al在800℃氧化24 h的截面形貌。与Co-20Ni-8Cr-3Al在800℃生成的氧化膜结构类似,外氧化膜呈双层结构,通常以孤立结节的形式形成于合金表面(面积占比约30%),厚度不均匀,且氧化膜/合金界面不规则,部分区域发生了Al的内氧化。样品表面的剩余部分被连续Al2O3层覆盖,有效阻止了合金的氧化。在900℃氧化24 h后,Co-20Ni-8Cr-5Al上生长的氧化膜(图6b1)与在相同温度下氧化后的Co-20Ni-8Cr-3Al非常相似,只是外氧化膜的厚度减小(约减小40%)。此外,内层的厚度非常不规则,并且部分区域出现Al的内氧化区,而部分区域由于氧化膜/合金界面处生成了薄Al2O3层,未发生内氧化(图6b2)。
结合XRD谱和EDS分析,大多数合金表面观察到连续或结节状的双层外氧化膜,其外层由CoO和NiO的固溶体(MO)构成,内层包含MO和尖晶石的混合物,部分还含有Cr2O3。在外氧化膜下通常存在Al的内氧化区,氧化膜/合金界面不规则。氧化膜外层结构因氧化温度存在差异,对于在800℃下氧化的样品,该层外部区域由连续的Co3O4构成,而内部区域由MO构成。900℃时,外部区域基本由MO组成,Co3O4仅以岛状形式分布在MO的内部,而在1000和1100℃下合金氧化膜中不存在Co3O4。
3 分析讨论
借助Wallwork和Hed[6]提出的Co-Cr-Al三元合金氧化膜结构的分类依据,可将四元Co-20Ni-8Cr-3Al和Co-20Ni-8Cr-5Al合金的氧化膜分为4种类型,如表2所示。其中,I型氧化膜为双层结构,外层为厚且致密的CoO层,内层产物薄且多孔,主要由CoO与Al2O3、Cr2O3以及Co(Cr, Al)2O4尖晶石混合而成;随着Al和Cr含量的增加,生成II型氧化膜:其组成与I型的成分相似,但外层CoO层的相对厚度减小。在以上这2种情况下,合金都会发生Al的内氧化;III型氧化类型涉及Cr的外氧化和Al的内氧化,而Co的氧化受到抑制;IV型氧化膜为保护性的Al2O3膜,无任何内氧化,Co和Cr的氧化都被抑制。对于含有Cr和Al的四元Co-20Ni基合金,CoO被CoO和NiO的固溶体(MO)所取代,而尖晶石通常包含二价(Co, Ni)和三价(Cr, Al)金属离子氧化产物的组合。此外,在实验温度下Co还能够形成更高价态的氧化物Co3O4。
表2 Co-20Ni-8Cr-3Al和Co-20Ni-8Cr-5Al合金4种类型氧化膜的氧化产物
Table 2
| Type of scale | Oxidation product |
|---|---|
| I | MO (thick), Al2O3, Cr2O3, spinel |
| II | MO (thin), Al2O3, Cr2O3, spinel |
| III | Al2O3, Cr2O3, spinel |
| IV | Al2O3 |
事实上,很多情况下同一样品表面不同部位的氧化膜结构不同,所涉局域面积的相对占比取决于合金成分和反应温度。因此,往往能在同一个样品表面观察到多种氧化膜结构。表3列举了2种合金在4种温度下氧化后生成的氧化膜结构对应的氧化膜类型。Co-20Ni-8Cr-3Al合金在800℃下氧化时生成II型和IV型混合氧化膜,而在其他3个温度下生成的基本是II型氧化膜。对于Co-20Ni-8Cr-5Al合金,4种温度下氧化后均生成II型氧化膜,而在800和1100℃下还有IV型氧化膜生成。
表3 Co-20Ni-8Cr-3Al和Co-20Ni-8Cr-5Al合金在800、900、1000和1100℃下产生的氧化膜结构类型
Table 3
| Temperature / oC | Co-20Ni-8Cr-3Al | Co-20Ni-8Cr-5Al |
|---|---|---|
| 800 | Type II + type IV | Type II + type IV |
| 900 | Type II | Type II |
| 1000 | Type II | Type II |
| 1100 | Type II | Type II + type IV |
结合Nijdam等[15~18]提出的钴基合金高温氧化模型,分析本工作中合金氧化生成的氧化膜结构的形成过程。在高温氧化初期,Al含量最低的合金Co-20Ni-8Cr-3Al会同时发生Co和Ni的氧化,形成含有Cr的氧化物的混合氧化物,Al则发生内氧化。因此,形成了由CoO外层与尖晶石和Cr2O3的混合物内层组成的双层氧化膜。在第2阶段,氧化速率几乎呈抛物线形,氧化主要由金属组元通过混合氧化层的扩散控制,氧化速率取决于Cr2O3和尖晶石的空间分布和互连程度。在900、1000和1100℃,Co-20Ni-8Cr-5Al的氧化速率显著低于Co-20Ni-8Cr-3Al,这是由于尽管合金的Cr、Al含量仍不足以避免Al元素发生内氧化,但Al含量增加使得内氧化区颗粒状的Al2O3倾向于连续,抑制了双层氧化膜的生成,使其通常以结节的形式出现,在一定程度上限制了合金的氧化。
2种合金在800和900℃下生长的氧化膜外部区域均存在Co3O4,但形式不同,这主要归因于在900℃时,CoO/Co3O4的平衡压力为0.143 × 105 Pa,小于本实验中采用的O2压力1.013 × 105 Pa;而在800℃时,该压力为0.004 × 105 Pa,远低于1.013 × 105 Pa,且溶解在CoO中的Ni可能会进一步降低此压力[1]。因此,在800℃下形成了连续的Co3O4产物层,而900℃下则为岛状结构。
图10
图10
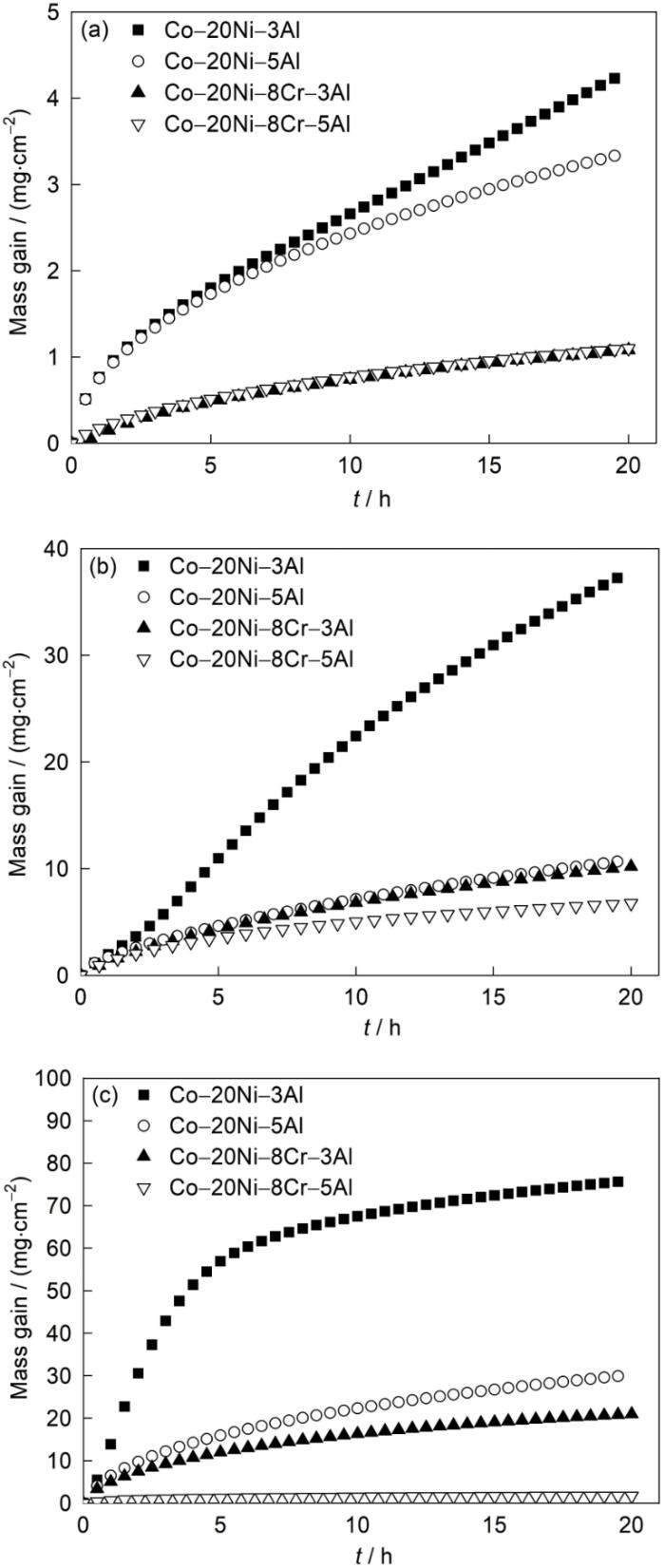
Co-20Ni-8Cr-xAl四元合金与Co-20Ni-xAl三元合金[31]在800、900和1000℃下1.013 × 105 Pa O2中氧化20 h的动力学曲线的比较
Fig.10
Comparisons of the kinetic curves for the oxi-dation in 1.013 × 105 Pa O2 at 800oC (a), 900oC (b), and 1000oC (c) for 20 h of the quaternary Co-20Ni-8Cr-xAl alloys with the corresponding data for the ternary Co-20Ni-xAl[31] alloys
4 结论
(1) Co-20Ni-8Cr-3Al和Co-20Ni-8Cr-5Al合金在800、900、1000和1100℃ 4种温度、1.013 × 105 Pa O2气氛中均发生了显著的氧化。在所有的温度下,各合金表面都生成了双层外氧化膜,其最外层主要为CoO和NiO固溶体(MO),而内层则为MO与尖晶石的混合物,在外氧化膜下方通常存在Al的内氧化区。
(2) 温度从800℃升到900℃,2种合金的氧化速率显著增加。温度升高到1000℃,Co-20Ni-8Cr-3Al的氧化速率提高,而Co-20Ni-8Cr-5Al氧化速率下降。温度从1000℃升高到1100℃时,2种合金的氧化速率均下降。
(3) Al含量由3%增加到5%导致Co-Ni-Cr-Al合金的氧化速率降低,一定程度上抑制了合金的氧化。但在实验条件下,5%的Al含量仍不足以形成保护性的外氧化膜。与相同Al含量的Co-Ni-Al三元合金相比,Cr和Al的同时存在有利于降低四元Co-Ni-Cr-Al合金的氧化速率。
参考文献
High-Temperature Corrosion and Materials Applications
[M].
Cyclic oxidation behavior of a cobalt-base superalloy
[J].
钴基高温合金的循环氧化行为研究
[J].

研究了钴基高温合金K40S在950℃和1000℃的循环氧化行 为.发现合金在950℃ 400 h以内的抗循环氧化性能较好.合金在1000℃氧化50 h以后因为 表面氧化膜剥落开始出现失重现象.在1000℃循环氧化初期的产物主要为Cr2O3,其次 为CoCr2O4和少量的CoO,400 h以后,Cr2O3基本剥落,合金表面由于Cr的损耗又生 成Cr2WO6、NiCr2O4以及挥发性的WO3氧化产物.添加Si和Mn元素使K40S合金抗循 环氧化性能明显地比不含Si和Mn元素的DZ40M钴基高温合金优越.
Impurity effects on alumina scale growth
[J].
The influence of alloying elements on the development and maintenance of protective scales
[J].
Mapping of the oxidation products in the ternary Co-Cr-Al system
[J].
Selection of an alloy composition in the ternary Co-Cr-Al system for oxidation resistance
[J].
The influence of aluminum additions on the oxidation of Co-Cr alloys at 1000 and 1200oC
[J].
The oxidation behavior of Co-Cr-Al alloys at 1000oC
[J].
The oxidation behavior of CoCrAl systems containing active element additions
[J].
A comparison of the oxidation behavior of Fe-Cr-Al, Ni-Cr-Al, and Co-Cr-Al alloys
[J].
The mechanism of oxidation of Ni-Cr-Al alloys at 1000oC-1200oC
[J].
Oxidation of Ni-Cr-Al alloys between 1000℃ and 1200℃
[J].
The oxidation behavior of some Ni-Cr-Al alloys at high temperatures
[J].
Effect of partial oxygen pressure on the initial stages of high-temperature oxidation of γ-NiCrAl alloys
[J].
Modelling the thermal oxidation of ternary alloys—Compositional changes in the alloy and the development of oxide phases
[J].
Promoting exclusive α-Al2O3 growth upon high-temperature oxidation of NiCrAl alloys: Experiment versus model predictions
[J].
Oxide phase development upon high temperature oxidation of γ-NiCrAl alloys
[J].
Effect of pre-oxidation temperature on high-temperature cyclic oxidation resistance of Ni-15Cr-5Al-5Si alloy
[J].Ni-15Cr-5Al-5Si (mass fraction/%) alloy was prepared by powder metallurgy method. After pre-oxidation at different temperatures (500,700,900,1 100℃), cyclic oxidation tests were carried out on the alloy at 1 100℃. The effect of pre-oxidation temperature on the high temperature (1 100℃) cyclic oxidation resistance of the alloy was studied and compared with that of Ni-15Cr-5Al alloy without silicon addition. The results show that the high-temperature cyclic oxidation resistance of the Ni-15Cr-5Al-5Si alloy was higher than that of the Ni-15Cr-5Al alloy. Pre-oxidation improved the high-temperature oxidation resistance of the alloy. With increasing pre-oxidation temperature, the high-temperature cyclic oxidation resistance increased, but the increase effect was not obvious.
预氧化温度对Ni-15Cr-5Al-5Si合金抗高温循环氧化性能的影响
[J].采用粉末冶金方法制备Ni-15Cr-5Al-5Si (质量分数/%)合金,经不同温度(500,700,900,1 100℃)预氧化处理后,在1 100℃进行了循环氧化试验,研究了预氧化温度对该合金抗高温(1 100℃)循环氧化性能的影响,并与未添加硅的Ni-15Cr-5Al合金进行了对比。结果表明:Ni-15Cr-5Al-5Si合金的抗高温循环氧化性能显著优于Ni-15Cr-5Al合金的;预氧化处理可以提高合金的抗高温循环氧化性能,随预氧化温度的升高,抗高温循环氧化性能提高,但提高效果不明显。
The third-element effect in the oxidation of Ni-xCr-7Al (x=0, 5, 10, 15 at.%) alloys in 1 atm O2 at 900-1000oC
[J].
The effect of Cr on the oxidation of Ni-10 at% Al in 1 atm O2 at 900-1000oC
[J].
Fundamental factors determining the mode of scaling of heat-resistant alloys
[J].
Growth mechanisms of oxide scales on two-phase Co/Ni-base model alloys between 800oC and 900oC
[J].
Influence of Co to Ni ratio in γ′-strengthened model alloys on oxidation resistance and the efficacy of the halogen effect at 900oC
[J].
High temperature oxidation behaviour of γ′-strengthened Co-based superalloys with different Ni addition
[J].High temperature oxidation behaviours of gamma'-strengthened Co-based superalloys with various Ni additions were investigated at both 800 degrees C and 900 degrees C. The results show that the superalloys show excellent oxidation resistance due to the formation of compact spinel oxide scales. With the increasing of Ni addition, the concentration of Cr in scale/alloy interface will be increased but that of Co will be decreased. And the growth of Cr2O3 will be promoted, while CoO nucleation will be hindered. Therefore, increasing Ni addition helps the formation of protective spinel oxide scales and delays nodular oxidation, which favours to be better oxidation resistance.
Intermediate Co/Ni-base model superalloys—Thermophysical properties, creep and oxidation
[J].
Diffusion-controlled growth of solid solution scales on nickel-cobalt alloys
[J].
The development of new bond coat compositions for thermal barrier coating systems operating under industrial gas turbine conditions
[J].
Oxidation behaviour of NiCrAl and NiCoCrAl bond coatings under industrial gas turbine conditions
[J].
Scaling behavior of four Co-20Ni-xCr-yAl (x = 8, 15 wt.%; y = 3, 5 wt.%) alloys exposed to 1 atm O2 at 1000oC and 1100oC
[J].
Oxidation behavior of ternary alloys Co-20Ni-3Al and Co-20Ni-5Al in 105 Pa O2 atmosphere at 800-1000oC
[J].
三元Co-Ni-Al合金在800~1000℃纯氧中的氧化行为研究
[J].研究了三元Co-20Ni-xAl (x=3,5,质量分数,%) 合金在纯氧中800~1000 ℃下20 h的氧化行为。氧化后,两种合金表面均生成了双层结构外氧化膜,外层膜主要由CoO与少量NiO组成,而内层膜则为CoO与尖晶石的混合物,外氧化膜下为铝的内氧化区。合金的氧化速率随氧化温度的升高而增大;合金中Al含量由3%增加到5%,Co-20Ni-Al合金的氧化速率随之下降,但5%Al仍不足以使合金表面生成保护性的单一氧化铝膜。