因此,本工作通过改变打印参数,制备了2种具有不同缺陷尺寸的SLM TC4合金,以定性探讨缺陷对于稳态阶段疲劳裂纹扩展的影响。同时,针对构件在实际服役过程中的载荷复杂多变,对SLM TC4合金进行了不同应力比(R = 0.1、0.3、0.5)的稳态阶段疲劳裂纹扩展速率研究,进行相关数据积累,以期为SLM TC4合金在航空航天等领域关键部位的广泛使用奠定基础。
1 实验方法
实验所用TC4粉末粒径为15~45 μm,其化学成分(质量分数,%)为:Al 6.22,V 4.21,Fe 0.032,C 0.01,N 0.0038,H 0.0095,O 0.10,Ti 余量,元素含量在标准范围内。利用BLT-S320型SLM设备打印TC4合金,使用不同的激光功率(P)和扫描速率(v)制备2种样品:P = 300 W,v = 1200 mm/s,记为SD;P = 250 W,v = 1400 mm/s,记为LD。样品打印完成后进行去应力退火。
利用电火花线切割(EDM)切取金相样品,依次使用400~2000号水磨砂纸研磨,随后使用粒度50 nm的SiO2悬浊液机械抛光至镜面,对未经腐蚀的金相样品采用GX71型光学显微镜(OM)观察缺陷分布。利用EDM切取标距长度25 mm,截面尺寸5 mm × 3 mm的矩形拉伸试样,试样长度方向垂直于打印方向,以1 × 10-3 s-1的应变速率在Instron 5982型试验机上进行室温拉伸实验。
利用EDM在样品上加工缺口,制备疲劳裂纹扩展速率实验所需的标准紧凑拉伸(CT)试样,切取方向和尺寸示意如图1所示。试样切割完成后进行机械抛光,以消除表面粗糙度可能对实验结果造成的影响。依据GB/T 6398—2017《金属材料疲劳试验疲劳裂纹扩展方法》,于室温、大气条件下,在Instron 8801疲劳试验机上预制疲劳裂纹,以消除缺口形状的影响。预制过程使用频率为20 Hz的正弦波,R = 0.1,初始载荷Pmax = 5 kN,随裂纹扩展逐级降载至Pmax = 3.2 kN,预制裂纹的目标长度为3 mm。
图1
图1
标准紧凑拉伸(CT)试样尺寸示意图
Fig.1
Schematic of the geometry of the standard compact tension (CT) specimen (unit: mm)
完成裂纹预制后,采用恒载增K试验程序,保持加载频率10 Hz,分别进行LD (R = 0.1)和SD (R = 0.1、0.3和0.5)样品的疲劳裂纹扩展实验,每组重复3个试样。通过夹式引伸计监测记录实验数据,并利用柔度法和七点递增多项式拟合计算应力强度因子范围(ΔK)与疲劳裂纹扩展速率(da / dN,其中,a为裂纹长度,N为应力循环周次)。疲劳裂纹扩展速率实验结束后,在JSM-6510扫描电子显微镜(SEM)上观察试样断口形貌。
2 实验结果与讨论
2.1 缺陷分布及拉伸性能
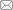
图2
图2
2种选区激光熔化(SLM) TC4合金的OM像
Fig.2
OM images of selective laser melting (SLM) TC4 alloy
(a) SD specimen (laser power is 300 W, scanning speed is 1200 mm/s)
(b) LD specimen (laser power is 250 W, scanning speed is 1400 mm/s)
表1 SLM TC4合金的拉伸性能
Table 1
| Specimen | σb / MPa | σs / MPa | δ / % |
|---|---|---|---|
| SD | 1212 ± 5 | 1105 ± 2 | 8.5 ± 0.1 |
| LD | 1270 ± 1 | 1152 ± 7 | 9.6 ± 0.1 |
Note:σb—tensile strength, σs—yield strength, δ—elongation
2.2 疲劳裂纹扩展速率
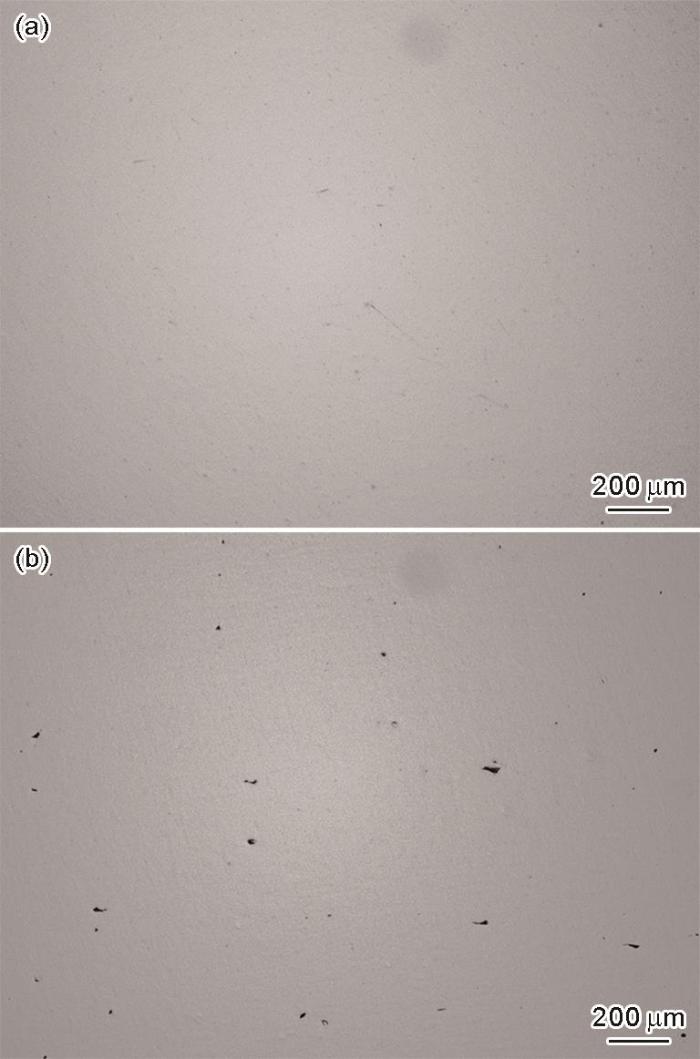
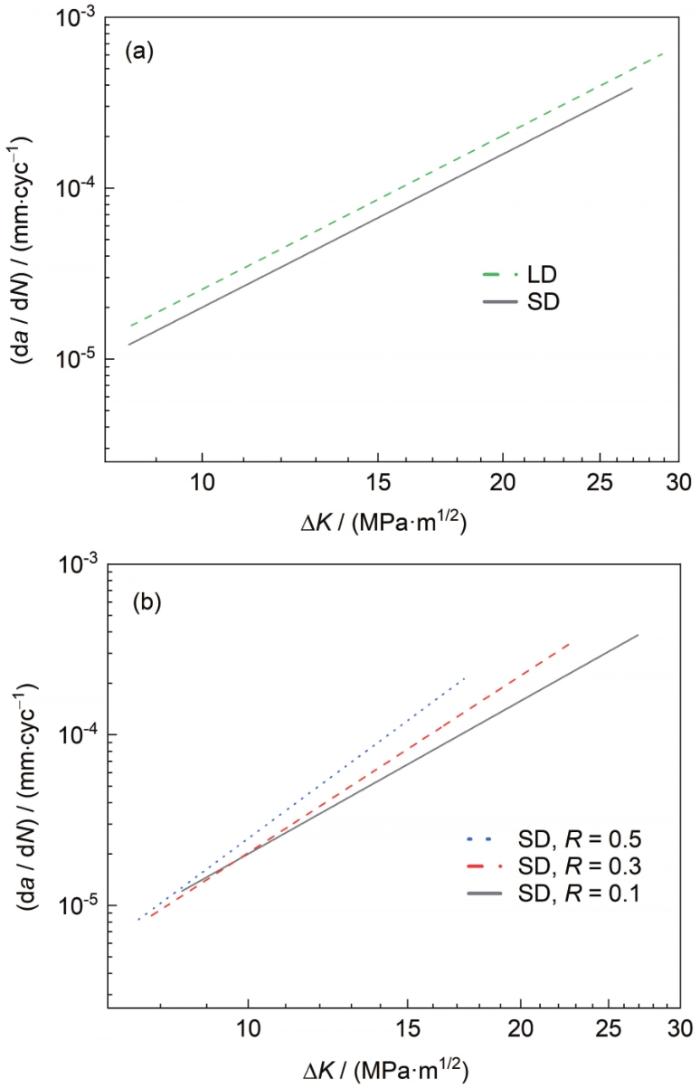
由于裂纹扩展第III阶段寿命极短,为了更直观地反映疲劳裂纹在稳态扩展阶段的规律,剔除了扩展速率急剧升高的瞬断区数据。在双对数坐标系中绘制了SD和LD 2种试样在R = 0.1时的da / dN-ΔK关系,如图3所示。可见,在相同的R下,SD和LD试样的ΔK大致相当。LD和 SD试样的数据近似平行,且LD数据位于SD数据的上方,即在相同ΔK下含较大尺寸缺陷试样的da / dN更高。经统计,LD和SD试样的平均失效寿命(Nf)分别为297140和362780 cyc,相比含小缺陷的试样,含较大缺陷试样的平均失效寿命降低了18.1%。
图3
图3
SD (激光功率300 W、扫描速率1200 mm/s)和LD (激光功率250 W、扫描速率1400 mm/s)试样在应力比R = 0.1时的疲劳裂纹扩展速率(da / dN)-应力强度因子范围(ΔK)关系
Fig.3
Relationships between da / dN and ΔK of LD and SD specimens at R = 0.1 (R—stress ratio; a—crack length; N—number of cycle; da / dN—fatigue crack growth rate; ΔK—stress intensity factor range; 1, 2, 3—specimen numbers)
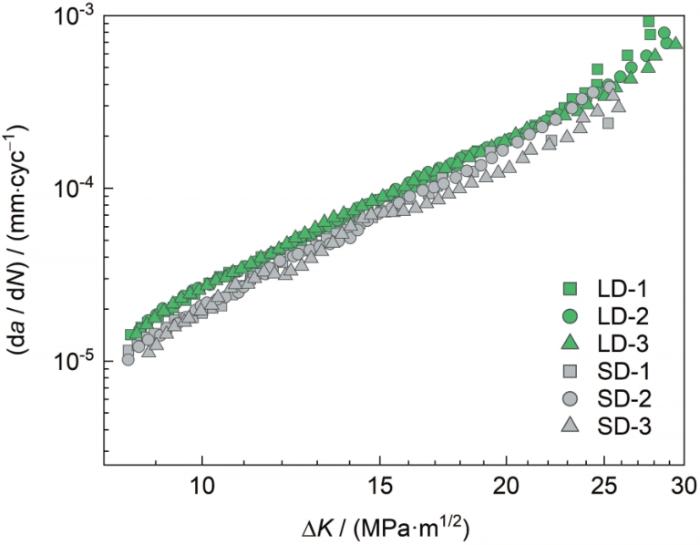
同时在双对数坐标系中绘制了SD试样不同R时的da / dN-ΔK关系如图4所示。可见,各组试样数据整体重复性较好,在双对数坐标下SLM TC4合金在稳态扩展阶段的da / dN和ΔK整体表现出良好的线性关系。图4中,R与ΔK的范围关系密切,R从0.1增加到0.3和0.5时,ΔK范围分别由8.5~26.9 MPa·m1/2减小至7.9~22.6 MPa·m1/2和7.7~17.3 MPa·m1/2。简言之,随着R的增大,对应的ΔK范围相应减小。这是因为在相同的ΔK下,较大的R对应着更大的最大应力强度因子(Kmax),因此材料会更早进入快速扩展阶段,从而发生断裂。即高R会降低稳态扩展时所需的ΔK,使失稳断裂提前发生。
图4
图4
SD试样在不同R下的da / dN-ΔK关系
Fig.4
Relationships between da / dN and ΔK of SD specimens at different R
此外,可以看出da / dN受R的影响也较大。在ΔK相同时,da / dN随着R增大而增大,R = 0.5对应的da /dN依次大于R = 0.3和0.1,尤其是在ΔK较大的区域。通常认为[20]R对da / dN的影响主要源于闭合效应:R较低时,裂纹面因压应力引起的闭合时间长,闭合效应明显;随着R增大,裂纹的张开位移变大,闭合效应减弱或消失,裂纹扩展速率加快。显然上述规律实际上是由外因导致的必然结果,不受成形工艺或材料组织类型的影响。同时,选取相同ΔK范围(10~16 MPa·m1/2),经统计,SD试样R = 0.1、0.3和0.5下的平均扩展周次分别为170160、163000和134000 cyc。相较于R = 0.1,R = 0.3和0.5时的扩展寿命分别降低了4.2%和21.3%,符合da / dN随R的增加逐渐增加的规律[21]。
2.3 稳态扩展阶段的Paris公式
尽管Paris公式只是da / dN和ΔK之间关系的经验公式,但形式简单且适用性强,在工程应用领域被广泛用来描述裂纹的稳态扩展行为,其形式为[22]:
式中,C和m是与材料相关的常数。分别对4组实验数据进行并置拟合,求得
对比
图5
图5
疲劳裂纹扩展速率的拟合结果
Fig.5
Fitting results of fatigue crack growth rate at different defect sizes (a) and stress ratios (b)
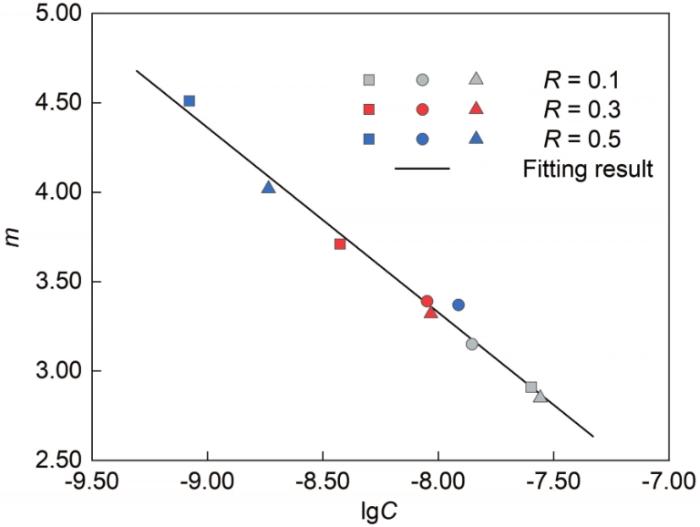
在上述缺陷尺寸与R对SLM TC4合金da / dN的影响中,大缺陷尺寸的不利影响较为直观。但SLM工艺一直致力于优化缺陷,以提高构件的质量和性能,且期望在材料使用过程中所含的缺陷越小越好,因而重点关注R对含小缺陷的试样的影响。对每个SD试样进行稳态扩展阶段的Paris公式拟合,分别计算m和C (以常用对数lgC表示),并作图6,可见2者之间保持很好的线性关系。
图6
图6
不同R下Paris公式中材料常数C和m的关系
Fig.6
Relationship between material constants C and m in different R
2.4 疲劳断口形貌
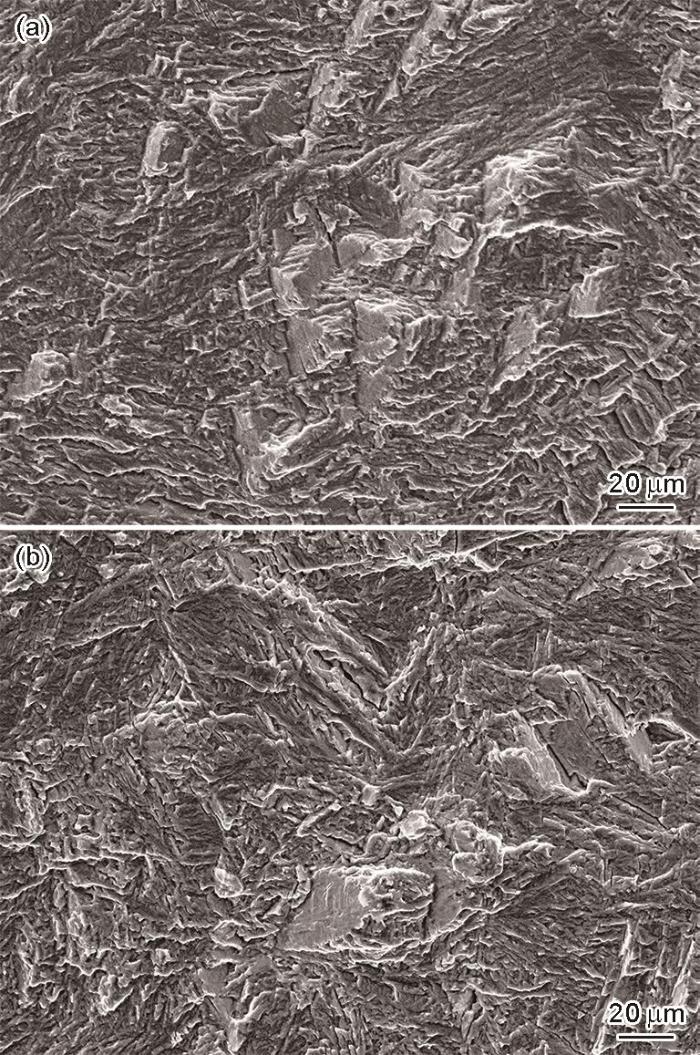
图7为SD和LD试样在R = 0.1和ΔK = 16 MPa·m1/2处疲劳断口的SEM像。图中并未观察到明显的缺陷痕迹,且2者的断口形貌无明显差异,均呈现出准解理特征。
图7
图7
SD和LD试样在R = 0.1和ΔK = 16 MPa·m1/2条件下疲劳断口的SEM像
Fig.7
SEM images of fractographies of SD (a) and LD (b) specimens at R = 0.1 and ΔK = 16 MPa·m1/2
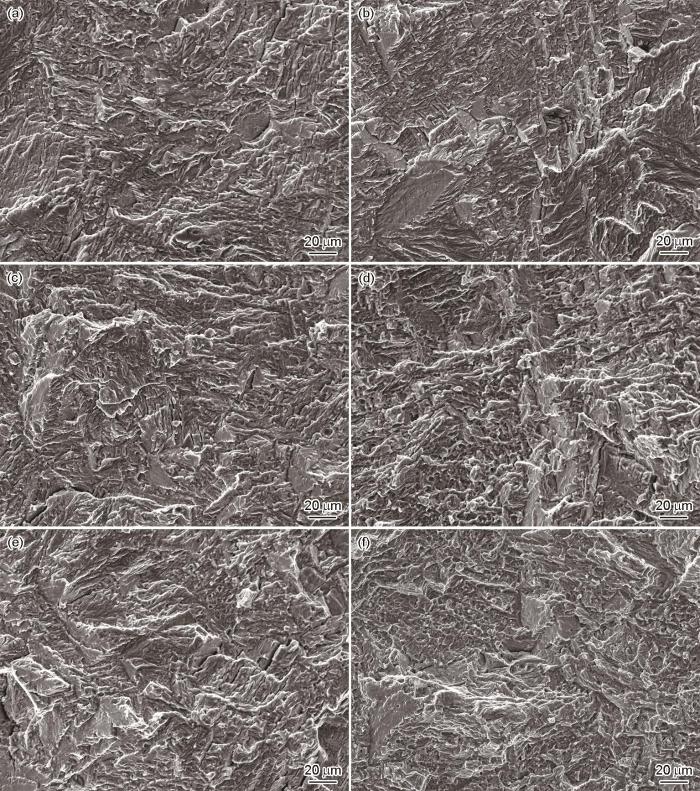
图8为不同R时SD试样疲劳断口的SEM像(ΔK分别为10和15 MPa·m1/2)。由图可见,在较低的ΔK时不同R试样的断口形貌极为相似,有着许多小解理平面与撕裂棱,呈现出准解理断裂的方式,还存在有大量垂直于扩展面分布的二次裂纹,且二次裂纹有着一定的深度(图8a、c和e)。随着裂纹扩展到高ΔK区,不同R的断口形貌之间产生了差异(图8b、d和f)。在R = 0.1时的断口仍保持着与低ΔK区相似的特征,但在更大应力比(0.3和0.5)下裂纹扩展的延性特征开始增多,撕裂棱的棱角逐渐圆滑,类似韧窝的结构明显增加,裂纹扩展过程发生了由准解理断裂向延性断裂的转变。同时二次裂纹的数量减少,至R = 0.5时二次裂纹不可见。
图8
图8
SD试样在R = 0.1、0.3和0.5时,ΔK = 10和15 MPa·m1/2处疲劳断口的SEM像
Fig.8
SEM images of fractographies of SD specimens at ΔK = 10 MPa·m1/2 (a, c, e) and 15 MPa·m1/2 (b, d, f) with R = 0.1 (a, b), 0.3 (c, d), and 0.5 (e, f)
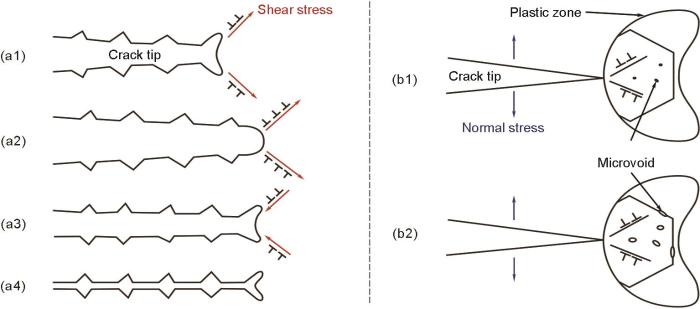
2.5 疲劳裂纹扩展机制
疲劳裂纹萌生后会沿着有最大切应力的滑移面方向扩展,当扩展至某一深度或遇到晶界后,滑移受到阻塞,裂纹开始沿着垂直于拉应力的方向扩展,即进入疲劳扩展第II阶段[25]。关于裂纹扩展机制主要存在滑移分离和累积损伤2种观点,前者通过裂纹尖端的钝化-复锐机制逐步扩展,后者通过微孔连接、聚集实现。从断口形貌可以得知,上述2种机制在裂纹扩展中并非独立存在而是共同作用,由钝化-复锐机制向微孔聚集机制转变。
图9
图9
2种疲劳裂纹扩展机制示意图
Fig.9
Schematics of blunting/re-sharpening (a1-a4) and microvoid coalescence (b1, b2) fatigue crack growth mechanisms
(a1) tensile load (a2) maximum tensile load (a3) compress load (a4) zero load
(b1) microvoid nucleation (b2) microvoid growth
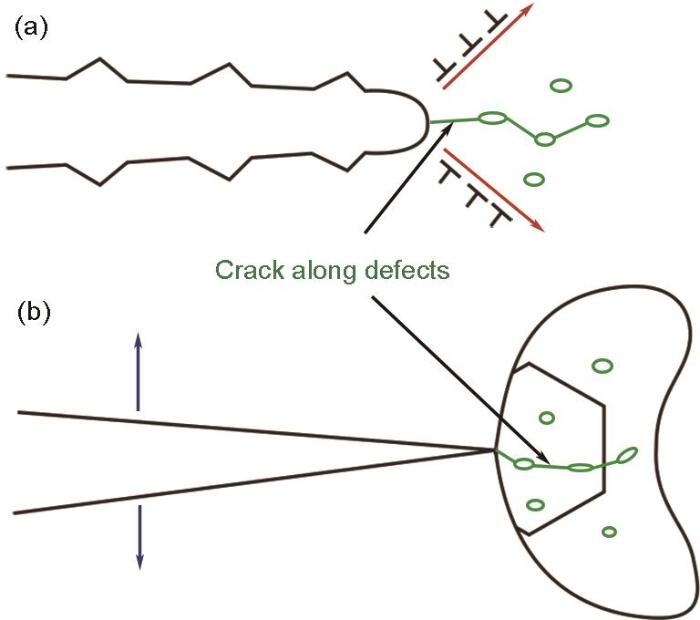
图10
图10
缺陷对裂纹尖端的影响示意图
Fig.10
Schematics of effects of defects on crack tips of blunting/re-sharpening (a) and microvoid coalescence (b) mechanisms
在疲劳裂纹扩展中,切应力的作用主要依靠循环载荷作用下的位错损伤累积,而正应力的影响则更倾向于静态拉伸引起的断裂形式。因此基于裂纹扩展机制的转变,可以借助临界平面法中临界平面上最大正应力和切应力幅的比值——临界平面应力比(ρ),来衡量正应力与切应力的关系,进而考虑2种应力对疲劳损伤的综合影响[27]。在单轴疲劳中切应力主要受应力幅的影响,而正应力主要受最大应力影响,可以计算临界平面上的切应力和正应力分量:
式中,τa为临界平面上的切应力幅,σa为正应力幅,σmax为最大正应力,σn, max为临界平面上的最大正应力。因此ρ可表示为:
通
由于正应力的存在会加速疲劳裂纹扩展,但在ΔK较小的某一点其作用尚未显现,疲劳损伤仍主要依靠切应力作用下位错的不断循环累积,此时不同R下的da / dN没有差别。随着裂纹扩展,正应力的加速作用逐渐凸显,同时较大的R对应较高的ρ。ρ增加,改变了正应力与切应力相对大小关系,进而提高了正应力在裂纹扩展过程中的加速效果,因此da / dN由大到小依次为R = 0.5、0.3、0.1。加之稳态扩展阶段的da / dN曲线呈双对数线性关系,导致不同R的拟合直线相交于同一点(即存在特定的旋转中心)。对
3 结论
(1) 缺陷尺寸增大,稳态阶段疲劳裂纹扩展速率增大,Paris公式中的系数m不变,C增大;应力比R增大,稳态阶段疲劳裂纹扩展速率增大,曲线在低应力强度因子时汇集,Paris公式中的材料系数m增大,C减小,m和lgC之间存在不受R影响的线性关系。
(2) SLM TC4合金的疲劳裂纹扩展过程由钝化-复锐机制向微孔聚集机制发生转变。随着R增大,正应力作用增加,断口中表现出延性断裂特征,二次裂纹数量明显减少,韧窝数量明显增加。
(3) 通过对循环变形过程中正、切应力对疲劳损伤的不同作用,结合疲劳断裂损伤机制,揭示了不同R下lgC与m呈线性关系的本质原因:ΔK较小时,正应力作用不明显,切应力作用不受应力比影响,导到da / dN-ΔK曲线汇聚在一点。
参考文献
Titanium alloy production technology, market prospects and industry development
[J].
Classification and applications of titanium and its alloys
[J].
Numerical simulation of stress evolution of thin-wall titanium parts fabricated by selective laser melting
[J].Selective laser melting (SLM) is a very promising additive manufacturing (AM) technology for fabrication of thin-walled parts due to its high forming accuracy with complex shape. The higher temperature gradient in rapid heating and cooling process is prone to produce larger thermal stress, which will induce warpage deformation of SLMed parts. However, most of the current SLM stress studies focus on the residual stress, and only a few reports on the transient stress in the thermal cycle during SLM. In this work, a thermal-mechanical coupled transient dynamic finite element model was established to study the effects of laser scan rate and layer thickness on stress evolution during SLM processing. The results show that under the action of thermal cycle, the internal stress evolution in SLM of titanium alloy thin-walled parts presents a thermal stress cycle. Under the relief annealing of the thermal stress cycle, the peak thermal stress increases first and then decreases in the heating stage, and stabilizes and approaches the value of residual stress in the cooling stage. The residual stress of SLMed thin-walled parts is less than the transient peak stress during heating. After several thermal cycles with stress relief annealing effect, the peak thermal stress of SLM thin-walled parts can be reduced by more than 30%.
钛合金薄壁件选区激光熔化应力演变的数值模拟
[J].建立了选区激光熔化(SLM)热-结构耦合瞬时动态有限元模型,探究了激光扫描速率和铺粉层厚度对SLM成形钛合金薄壁件应力演变的影响。结果表明,在热循环作用下,SLM成形钛合金薄壁件的应力演变呈周期性变化。在热应力循环去应力退火作用下,热应力极大值在加热阶段先增加后减小,最后在冷却阶段趋于稳定并接近残余应力。SLM成形薄壁件最终残余应力小于加热过程中的瞬时应力峰值。随沉积高度的增加,热循环作用减弱,应力极大值下降幅度逐渐减小。经过多次热循环去应力退火作用后,SLM成形薄壁件过程中的热应力极大值下降幅度可达30%以上。
Metal additive manufacturing: A review
[J].
Influence of mixing enthalpy on the microstructure of laser multilayer deposited Ti-6Al-4V alloy
[J].
混合焓对激光多层沉积Ti-6Al-4V合金凝固组织的影响
[J].分别以预合金粉末和混合元素粉末为原料进行激光多层沉积Ti-6A-4V合金, 采用XRD研究了预合金粉末、混合元素粉末和沉积试样的相组成,采用金相显微镜研究了沉积试样的凝固组织. 结果表明, 预合金法激光多层沉积Ti-6Al-4V合金的凝固组织由外延生长的柱状晶组成,且随激光功率的提高, 合金凝固组织倾向于由柱状晶转变为等轴晶; 随着激光功率由1600 W增加至2700 W, 混合元素法激光多层沉积Ti-6Al-4V合金的凝固组织则由粗大等轴晶逐渐转变为外延生长的柱状晶.扫描速率对合金凝固组织的影响较小. 对混合焓对合金凝固组织的影响进行了讨论.
Effects of defects and microstructures on tensile properties of selective laser melted Ti6Al4V alloys fabricated in the optimal process zone
[J].
Effect of laser 3D printing process on quality of titanium alloy
[J].
激光3D打印工艺对钛合金质量的影响
[J].为了解决传统锻造方法锻造TC4钛合金时容易造成的生产效率低且锻造形状简单等问题,对TC4钛合金进行了激光3D打印,并确定了最佳激光3D打印工艺参数.利用金相显微镜和扫描电子显微镜对TC4钛合金单道打印层的成形质量、显微组织与相组成进行了分析.利用显微维氏硬度计和万能拉伸试验机测量了打印层的硬度和拉伸力学性能.结果表明,在最佳工艺参数下TC4钛合金打印成形良好,其打印层组织主要由片层状α固溶体组成.打印层的Z向拉伸强度指标低于XY向,而Z向拉伸塑性指标高于XY向,且Z向强度和塑性指标均超越了TC4锻件国家标准(GB/T 25137-2010).同时Z向和XY向拉伸断口形貌均为塑性断口.
Additive manufacturing of strong and ductile Ti-6Al-4V by selective laser melting via in situ martensite decomposition
[J].
Effect of heat treatment on the phase transformation and mechanical properties of Ti6Al4V fabricated by selective laser melting
[J].
Heat treatment of Ti6Al4V produced by selective laser melting: Microstructure and mechanical properties
[J].
Defects in additive manufactured metals and their effect on fatigue performance: A state-of-the-art review
[J].
Defect induced fatigue behaviors of selective laser melted Ti-6Al-4V via synchrotron radiation X-ray tomography
[J].As a very promising additive manufacturing (AM) technique, selective laser melting (SLM) has gained considerable attentions due to the feasibility of producing light-weight metallic components directly from virtual design data. On the other hand, high strength, low density and high corrosion resistance Ti-6Al-4V alloy has been a preferred AM used material for the aviation and military industries. However, the fatigue damage behaviors of SLMed or AMed components usually suffer from interior defects such as incomplete fusion and gas pores due to unstable process or unsuitable processing parameters. Therefore, thorough investigations on process-induced and metallurgical defects and its influence on the fatigue behavior is required for robust designs and engineering applications of high performance SLM components. As an advanced characterization approach, synchrotron radiation micro computed X-ray tomography (SR-μCT) has been recently to investigate the fatigue damage behaviors of critical components with defects. Based on self-developed in situ fatigue testing rig fully compatible with the BL13W1 at Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility (SSRF), several AMed specimens were prepared for in situ fatigue SR-μCT. The Feret diameter and extreme values statistics were then adopted to characterize the defect size, morphology, population, location and the influence on fatigue life. Fatigue fractography was also examined to further identify the defect to really initiate a fatigue crack. Results show that two types of defects including gas pores and the lack of fusion can be clearly distinguished inside SLM Ti-6Al-4V alloys. Fatigue crack with a typical semi-ellipse usually initiates from the defects at the surface and near the surface. Besides, the defects less than 50 μm and sphericity of 0.4~0.65 dominate for the SLM Ti-6Al-4V alloys. It is also found that the larger the characteristic size of the defect, the lower the fatigue life. Current results can provide a theoretical basis and support to predict the fatigue performance of SLM Ti-6Al-4V alloys. Further investigations should be performed on the relationship between the critical defect and fatigue strength by introducing the Kitagawa-Takahashi diagram.
基于同步辐射X射线成像的选区激光熔化Ti-6Al-4V合金缺陷致疲劳行为
[J].基于自主研制的原位疲劳试验机和高分辨同步辐射X射线三维成像技术,采用Feret直径和极值统计方法定量表征选区激光熔化Ti-6Al-4V合金的缺陷特征尺寸、数量、位置及形貌,原位观测疲劳裂纹的萌生与扩展行为,通过辨识疲劳断口源区的缺陷特征,开展缺陷诱导的疲劳损伤评价研究,从而建立缺陷特征与疲劳寿命之间的关系。分析表明,缺陷主要为未熔合和气孔,等效直径小于50 μm的频率为90%,球度分布于0.4~0.65之间;在不考虑表面粗糙度的情况下,疲劳裂纹优先在试样表面或近表面缺陷处萌生,呈现出典型的半椭圆形貌;同时缺陷特征尺寸越大,疲劳寿命越低。研究结果为增材高性能部件的疲劳性能及寿命评估提供了重要的理论参考。
Selective laser melting of TC4 titanium alloy fatigue and fracture
[J].
激光选区熔化TC4钛合金疲劳与断裂
[J].
Crack propagation and fracture toughness of Ti6Al4V alloy produced by selective laser melting
[J].
Beyond the orthogonal: On the influence of build orientation on fatigue crack growth in SLM Ti-6Al-4V
[J].
Fatigue crack growth behavior of laser powder bed fusion additive manufactured Ti-6Al-4V: Roles of post heat treatment and build orientation
[J].
Experimental study of effect of post processing on fracture toughness and fatigue crack growth performance of selective laser melting Ti-6Al-4V
[J].
Microstructural optimization through heat treatment for enhancing the fracture toughness and fatigue crack growth resistance of selective laser melted Ti6Al4V alloy
[J].
Different effects of multiscale microstructure on fatigue crack growth path and rate in selective laser melted Ti6Al4V
[J].
An investigation of the effects of stress ratio and crack closure on the micromechanisms of fatigue crack growth in Ti-6Al-4V
[J].
An investigation of the effects of microstructure and stress ratio on fatigue crack growth in Ti-6Al-4V with colony α/β microstructures
[J].
A critical analysis of crack propagation laws
[J].The practice of attempting validation of crack-propagation laws (i.e., the laws of Head, Frost and Dugdale, McEvily and Illg, Liu, and Paris) with a small amount of data, such as a few single specimen test results, is questioned. It is shown that all the laws, though they are mutually contradictory, can be in agreement with the same small sample of data. It is suggested that agreement with a wide selection of data from many specimens and over many orders of magnitudes of crack-extension rates may be necessary to validate crack-propagation laws. For such a wide comparison of data a new simple empirical law is given which fits the broad trend of the data.
Effects of stress ratio on fatigue crack growth rate of TC4-DT alloy
[J].
应力比对TC4-DT钛合金疲劳裂纹扩展速率的影响
[J].
Pertinence of material constants in paris model for fatigue crack propagation rate of metallic materials
[J].
金属材料疲劳裂纹扩展速率Paris模型中材料常数的相关性
[J].
Mechanisms of fatigue crack growth—A critical digest of theoretical developments
[J].
Crack growth rate of TC18 alloy with different microstructure
[J].
显微组织对TC18合金裂纹扩展速率的影响
[J].