新型25Cr-20Ni系奥氏体耐热钢C-HRA-5[1,2]和Sanicro 25 (UNS S31035)[3]主要应用于630~700℃先进超超临界燃煤机组蒸汽管道。C-HRA-5 (简称C-5)钢管最终供货态通常经高温固溶处理,组织中含有大量的ΣCSL (coincident site lattice,重位点阵)晶界,以Σ3型孪晶界(twin boundaries,TBs)为主[4]。Σ ≤ 29称为低ΣCSL[5],其中Σ3、Σ9和Σ27比例达95%以上。影响奥氏体不锈钢中低ΣCSL晶界种类和分数的主要因素有时效温度及时间[4,6]、形变量[7,8]、退火温度及时间[9,10]和原始晶粒尺寸[7,10]等。据文献[6,11]报道,一般孪晶带两侧平行界面为共格孪晶界(coherent twin boundaries,CTBs),非共格孪晶界(incoherent twin boundaries,ITBs)通常位于孪晶生长的末端或者共格晶界的台阶。大量TBs可细化晶粒,减小位错滑移的距离,提高位错增殖能力,会对钢的拉伸性能产生影响[12]。低ΣCSL晶界还能提高奥氏体钢疲劳性能和抗腐蚀性能。如,709 (UNS S31025)[13]奥氏体耐热钢中超过50%的CSL晶界是Σ3型CTBs,能够抗蠕变孔隙形成和延缓疲劳裂纹扩展。304[14]和316L[15]不锈钢中,抗裂性最高的是Σ3和Σ9型晶界。在奥氏体不锈钢[5,7~9]及其他fcc金属[16~18]中大幅度增加低ΣCSL晶界可显著提高材料的抗晶间腐蚀性能,这主要源于CSL晶界网络抑制随机晶界上M23C6相的析出。
上述结果表明,奥氏体耐热钢中大量低ΣCSL晶界对性能有益。Li等[19]观察到Sanicro 25钢在700℃低周疲劳下退孪生现象显著;Sarkar等[20]研究发现,316钢在650℃低周疲劳和蠕变-疲劳交互作用下孪晶数量也大量减少,并认为退孪生的机制源于位错-TBs交互作用,与fcc结构金属Cu中的情况相同。通常认为,CTBs是高度抗迁移的[21]。Wang等[22]提出CTBs的迁移可以通过很高的剪应力来实现,他们在Cu薄膜中观察到ITBs上孪生位错沿TBs滑移导致退孪生现象。白敬胜等[23]对纳米孪晶Cu的研究也发现,退孪生带的形成机制与局部剪切应变相关,退孪生可协调局部剪切应变。Li等[24]通过对纳米孪晶Cu进行原位拉伸高分辨透射电镜观察证实,不全位错滑动激活锯齿形CTBs退孪生。另有研究表明,fcc结构Ni-Fe合金[25]和Ni-Cr-Mo合金[26]经剧烈变形后,大量位错在CTBs附近塞积,形成应力集中,破坏CTBs的共格特征。
1 实验方法
实验所用原料为C-5钢管,其化学成分(质量分数,%)为:Ni 24.79,Cr 22.20,Mo 0.09,Mn 0.38,W 3.40,Si 0.20,Cu 3.00,Co 1.56,Nb 0.46,C 0.07,N 0.21,P 0.019,S 0.001,Fe余量。原料经过1250℃保温30 min后水淬。
沿钢管轴向切割制备直径为12 mm圆柱形试样,经线切割获得两端螺纹夹持疲劳样品,工作段标距18 mm、直径6 mm,对工作段表面进行打磨和抛光处理。在EHF-EM200k1-070-0A电液伺服疲劳试验机上进行低周疲劳实验,采用轴向对称应变控制方式,加载波形为三角波,总应变幅(εt)为0.3%~0.7%,测试温度为700℃,恒定应变速率为3 × 10-3 s-1。
固溶态C-5钢经过研磨、机械抛光后用溶液(5 g FeCl3 + 50 mL HCl + 100 mL H2O)腐蚀,借助AxioVert.A1光学显微镜(OM)进行金相组织观察。通过Talos F200X透射电镜(TEM)及其自带的能谱(EDS)仪研究试样的微观组织及成分,试样制备方法为:利用线切割从固溶态C-5钢块上切取0.3 mm的薄片,经机械磨光厚度至40 μm,再截取直径3 mm圆片经离子减薄制备样品。利用Sigma 500扫描电子显微镜(SEM)及附件电子背散射衍射(EBSD)探头研究TBs分布情况。样品制备方法为:机械抛光+电解抛光,电解抛光选用体积比为15%CH₃COOH + 85%CH₃OH的溶液,电解温度、电压和持续时间分别为0℃、20 V和30 s;EBSD测试操作电压为20 kV,扫描步长5 μm,通过HKL-Channel 5软件对EBSD数据进行分析处理。
在离C-5钢疲劳试样断裂面约1 mm处横向截取样品,利用SEM、EBSD和TEM进行组织形貌分析。SEM样品的制备方法与上述OM样品相同,在Nova Nano SEM 430场发射SEM上观察微观组织。EBSD和TEM样品制备及测试方法同上,不同之处是EBSD扫描步长为0.2 μm。
2 实验结果
2.1 不同应变幅下退孪生
图1
图1
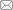
经1250℃保温30 min水淬后C-5钢的OM像、TEM像、SAED花样及EDS结果
Fig.1
OM (a) and TEM (b) images of C-5 steel after water quenching at 1250oC for 30 min, SAED pattern of the twin in Fig.1b (c), and EDS analysis of Z phase marked by a box in Fig.1b (d) (TBs─twin boundaries, CTBs─coherent TBs, ITBs─incoherent TBs)
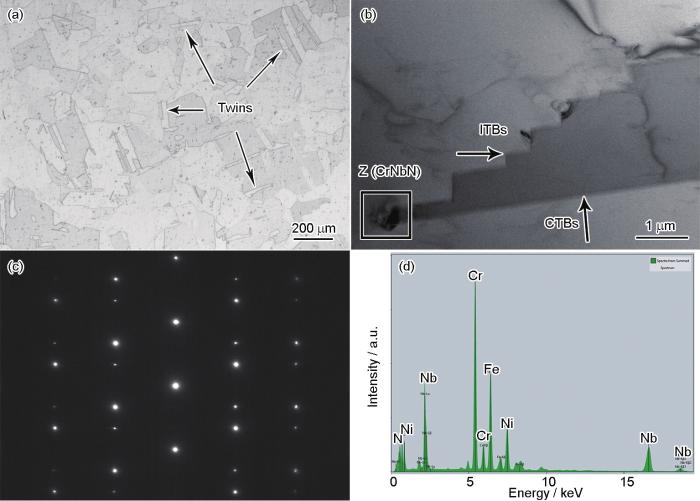
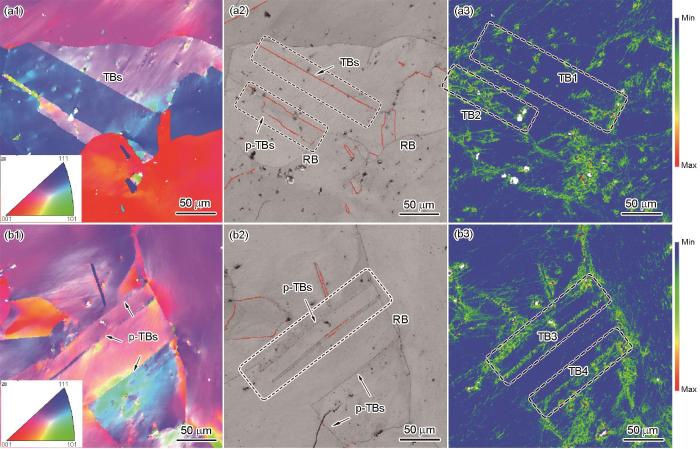
图2是固溶态及在700℃疲劳加载下C-5钢组织的EBSD分析。由图可见,固溶态试样中存在大量孪晶,分别如图2a1中条状组织和图2a2中红线所示,这表明经过固溶处理后试样中形成了大量ΣCSL晶界,比例高达69%,且绝大部分为Σ3型TBs,与图1结果一致。经过700℃和εt = 0.3%~0.7%低周疲劳加载后,试样中的条带组织显著减少,即大量TBs退孪生(图2b1~d1)。研究[20,28]表明,几何必须位错(geometrically necessary dislocation,GND)密度与局部取向差(又称KAM)成正比。由图2a3可见,C-5钢经固溶处理后GND密度很低。与固溶态组织相比,在低εt (0.3%)下,试样中的TBs比例显著下降(图2b2),在KAM图中可见局部绿色区域(图2b3),表明GND密度增加。在εt = 0.5%条件下,TBs比例下降(图2c2),KAM图中有较多绿色区域(图2c3),表明GND密度进一步增加。当εt = 0.7%时,TBs比例进一步下降(图2d2),而在KAM图中出现大面积绿色,局部有红色区域(图2d3),表明在高εt下,GND密度显著增加。
图2
图2
固溶态C-5钢及其在700℃低周疲劳下组织的EBSD分析
Fig.2
Inverse pole figures (IPFs) (a1-d1), band contrast (BC) maps (Red lines show the TBs) (a2-d2), and kernel average misorientation (KAM) maps (a3-d3) of the solution-treated (ST) C-5 steel (a1-a3) and under low-cycle fatigue (LCF) loading at 700oC with total strain amplitude εt = 0.3% (b1-b3), 0.5% (c1-c3), and 0.7% (d1-d3)
图3
图3
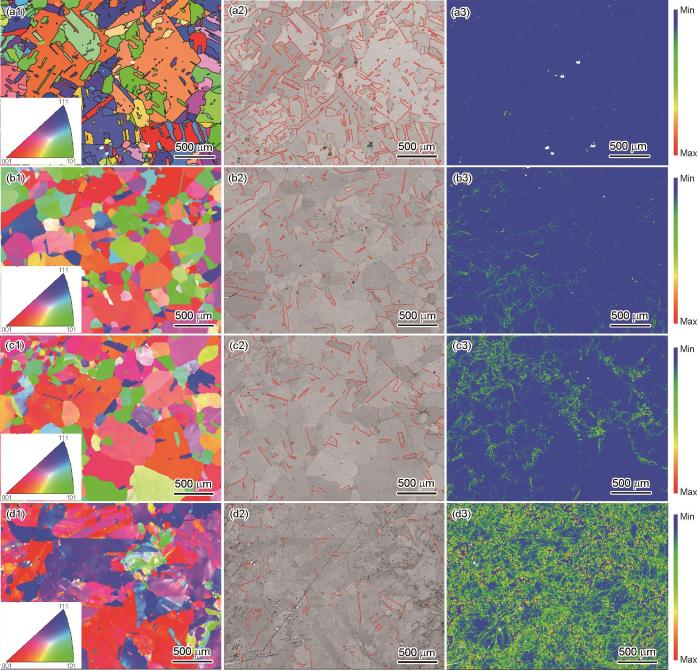
在700℃低周疲劳下C-5钢中TBs比例随总应变幅(εt)的变化
Fig.3
Variation of the length fraction of TBs with εt in C-5 steel under LCF loading at 700oC
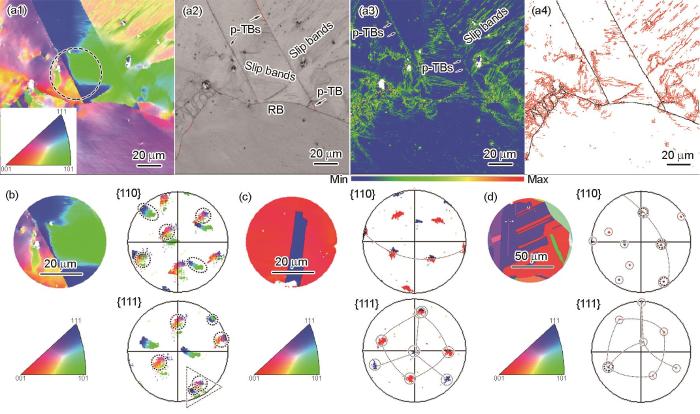
对700℃高温疲劳加载后残留TBs进一步研究,εt = 0.3%及0.7%下残留TBs的EBSD分析如图4所示。由图4a1和b1可见,在εt = 0.3%下,TBs较为清晰,而在εt = 0.7%下,TBs变得模糊。在图4a2中左上虚线框内一段TBs较好保留了孪晶取向,而左下虚框内部分TBs共格关系已消失,即孪晶碎片化。图4b2显示几处初始TBs几乎全部转为普通晶界,仅保留极少量孪晶碎片。由TBs转化而来的普通晶界,仍然保留平直界面的特点。本工作将碎片化的TBs称为赝孪晶界(pseudo-TBs,p-TBs),以示与TBs和随机晶界(RB)的区别。在图4a3和b3中,可以看出虚框内标记为TB1的孪晶界上GND密度与基体相当,而标记为TB2~TB4及RB上的GND密度较高,这表明部分p-TBs处塑性变形局域化较为严重。究其原因,可能与p-TBs附近析出相有关。
图4
图4
C-5钢在700℃低周疲劳下TBs碎片化的EBSD分析
Fig.4
IPFs (a1, b1), BC maps (Red lines show the TBs) (a2, b2), and KAM maps (a3, b3) of TBs fragmentation in the C-5 steel under LCF loading at 700oC with εt = 0.3% (a1-a3) and 0.7% (b1-b3) (RB─random boundary, p-TBs─pseudo-TBs)
2.2 位错-孪晶界交互作用
图5a为εt = 0.7%下C-5钢疲劳试样的EBSD分析。由图5a1和a2可知,经过疲劳加载后,原TBs保持平行线轮廓,但图5a2左侧TBs完全失去共格关系,转变为普通晶界,而右侧TBs碎片化,转变为p-TBs。通过图5a1~a4对比分析发现,在TBs附近有平行的滑移带与其交互作用。滑移带是变形局域化区域,在对应的KAM图区域表现为绿色平行线(图5a3),表明滑移线处位错密度很高,同时,在图5a4中对应区域有大量红线所示的小角晶界(LAGB,定义为晶界角度≤ 15°)。当滑移带遇到TBs时,将产生强烈的碰撞作用,导致TBs两侧晶粒取向发生变化,在IPF图中表现为孪晶区域颜色差异化(图5a1),对取向关系的转变进行了极图研究,如图5b所示。为了对比,图5c和d还列出了εt = 0.7%疲劳试样中残留TBs和固溶态C-5钢中TBs的极图。由图5d可见,固溶态C-5钢中TBs的{110}和{111}极图中投影近似为点(图中圆圈示出),这是由于C-5钢经高温固溶处理,试样中位错密度极低(见图1b),TBs两侧晶粒近似为理想晶体。由于Σ3-TBs的对称性,TB两侧晶粒的{110}极图中各有3个极点重合,{111}极图中各有1个极点重合(图中虚线连接)。而在高温循环载荷下,位错滑移与位错繁殖导致试样中位错密度显著增加,晶格畸变严重,在极图上呈现为极点发散。当位错-TBs交互作用较弱时,极图上极点分散性较小(图5c),晶界仍然保持Σ3共格关系。随着位错-TBs交互作用增强,极点分散性增大,转变为不规则的面(图5b),此时孪晶取向关系解离,TBs转变为p-TBs或普通晶界。
图5
图5
700℃低周疲劳下C-5钢和固溶态组织中TBs的EBSD及极图分析
Fig. 5
IPF (a1), BC map (Red lines show the TBs) (a2), KAM map (a3), and the contour lines of low angle grain boundary (LAGB, red lines) and high angle grain boundary (HAGB, black lines) (a4) of the C-5 steel under LCF loading at 700oC with εt = 0.7%, enlarged IPF and pole figures (PFs) of p-TBs in the selection area in Fig.5a1 (b), IPF and PFs of Σ3-type TBs with εt = 0.7% (c) and in ST C-5 steel (d)
图6为C-5钢在700℃疲劳载荷下的位错结构。在εt = 0.3%下,塑性变形以平面滑移为主,试样中位错密度较低(图6a和b),与图2b3中KAM图的结果相一致。在图6a中观察到TBs上有位错缠结;在图6b中可见位错滑移至TBs处塞积,晶界阻碍位错运动。在εt = 0.7%下,试样中位错密度显著增加,在图6c左侧有多条近似平行的位错滑移带,位错-TBs发生强烈的交互作用。结合图5中EBSD分析结果可知,位错滑移带对TBs产生强烈的周期性碰撞,导致TBs两侧晶粒取向关系发生变化,原孪晶取向关系逐步消失。随着εt的增加,试样中位错密度随之增加,有更多的位错滑移带形成,与TBs交互作用的频率和强度逐步增加。最终导致大部分TBs退孪生,如图2d2所示。
图6
图6
C-5钢在700℃低周疲劳下位错与TBs交互作用的TEM像
Fig.6
TEM images of interaction between dislocation and TBs under LCF loading at 700oC with εt = 0.3% (a, b) and 0.7% (c)
2.3 孪晶界处相析出
图7
图7
C-5钢在700℃、εt = 0.5%下TBs处析出相的SEM像
Fig.7
SEM images of the precipitates at TBs in C-5 steel with εt = 0.5% at 700oC
(a) precipitates along the CTBs (b) precipitates along the ITBs
图8
图8
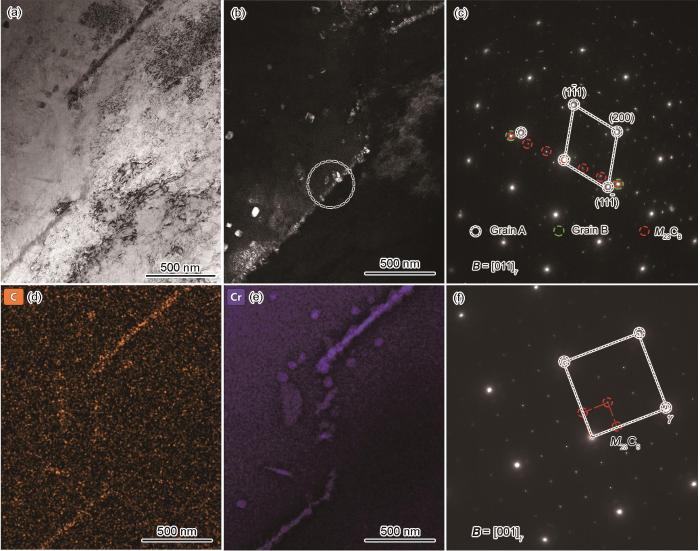
C-5钢在700℃和εt = 0.5%下TBs上析出相的TEM像、SAED花样和EDS面扫描图
Fig.8
TEM images, SAED patterns, and EDS maps of the precipitates at TBs with εt = 0.5% at 700oC
(a) bright field TEM image
(b) dark field TEM image (c, f) SAED patterns of the precipitates in the circular area in Fig.8b (d, e) EDS element maps of C and Cr, respectively
常用晶格失配(δ)表征共格/半共格界面第二相的形核阻力,M23C6/γ相界的δ表达式为[33]:
式中,
本工作发现,在高温疲劳下部分CTBs上有M23C6相析出,可能与高温疲劳下强烈热-力耦合作用有关。一方面,C-5钢及Sanicro25钢在700℃拉伸和应变疲劳下会出现动态应变时效现象[19,37],溶质原子如Cr和C更容易通过林位错通道快速扩散[27,38]。另一方面,由于位错在CTBs附近塞积致使晶界处晶格畸变加大,CTBs由低能态向高能态转变,诱发溶质原子向CTBs附近偏聚。上述2个因素耦合促使合金原子Cr和C等在部分CTBs上偏聚,最终形成M23C6相。709不锈钢在蠕变-疲劳下也观察到CTBs和ITBs上有M23C6形成的现象[13]。有研究[10]表明,高氮奥氏体不锈钢在高温退火下CTBs和ITBs上形成了纳米级M23C6相,这与试样退火前冷轧处理有关。
2.4 退孪生机制
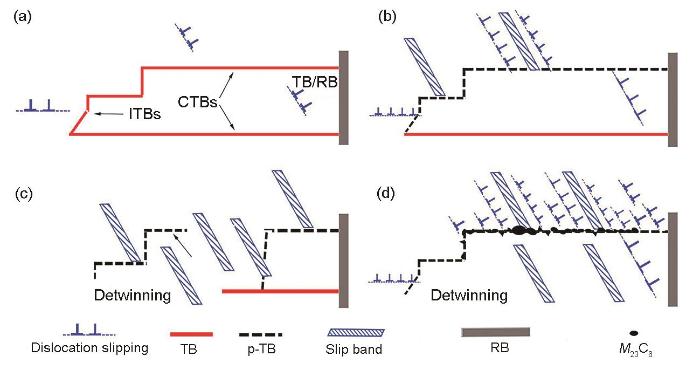
综上所述,在700℃低周疲劳下C-5钢中退孪生的微观机制如图9所示。首先,在疲劳载荷下位错开动和增殖,当位错滑移到部分TBs (主要是CTBs)时,位错-TBs发生交互作用;在循环载荷初期,由于试样中位错密度较低,位错-TBs作用不会改变孪晶取向关系(图9a)。随着循环周次的增加,位错增殖加速诱发试样中形成了较多位错滑移带并碰撞TBs,由于位错滑移带具有高剪切应力,位错-TBs作用导致部分晶界的共格关系消失,TBs随即转化为p-TBs,即出现了TBs碎片化现象(图9b)。随着循环周次进一步增加,更多的滑移带碰撞p-TBs和TBs,导致原始TBs湮灭(图9c)。由于高温疲劳加载下热-力耦合作用,位错-TBs反应诱导M23C6相析出,析出相强化位错-TBs交互作用,加速退孪生过程(图9d)。
图9
图9
C-5钢在700℃低周疲劳下的退孪生机制示意图
Fig.9
Schematics of detwinning in C-5 steel under LCF at 700oC
(a) dislocations slip to TBs under fatigue loading
(b) dislocation increases to form slip bands that impact TBs, resulting in TBs fragmentation
(c) annihilation of partial TBs
(d) precipitation at TBs accelerates detwinning
2.5 残留TBs与疲劳裂纹扩展
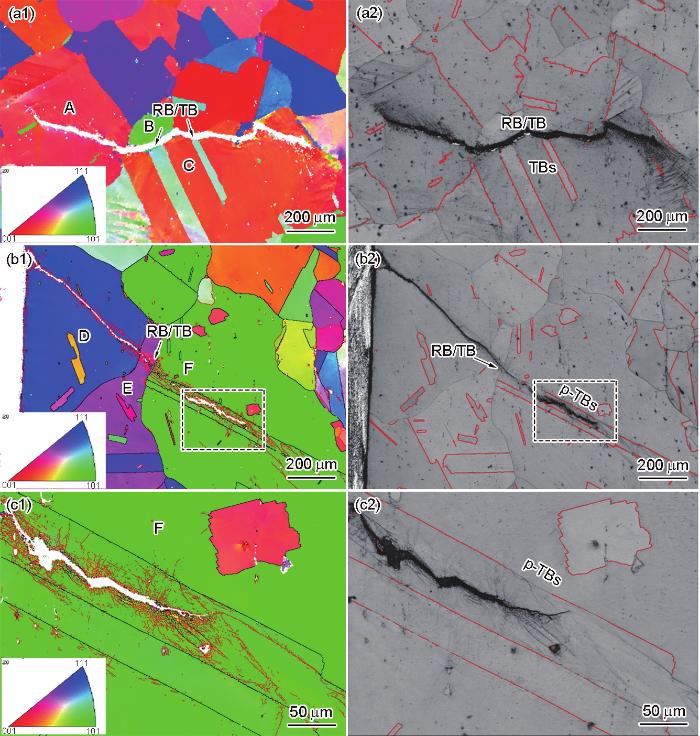
由图2可发现,C-HRA-5耐热钢即使在700℃高εt下,仍然有一些残留TBs和p-TBs。超(超)临界过热器TP347HFG钢管在工况(570℃、24 MPa)下服役7.5 × 104 h后,也保留部分孪晶特征晶界[40]。这些残留的TBs或p-TBs必将对材料的性能产生重要的影响。本工作通过EBSD技术进一步研究残留TBs和p-TBs对疲劳性能的影响。图10为700℃下εt = 0.3%和0.7%试样中疲劳裂纹的EBSD分析。由图可见,疲劳裂纹最先在晶粒A内扩展,然后进入晶粒A、B和C三角晶界处并沿晶粒B/C晶界扩展,再途径TBs与RB晶界的交汇处(标记为RB/TB),此处TBs碎片化程度较低;最后,裂纹穿越2处RB/TB后又转入晶粒C内部,呈现穿晶扩展(图10a1和a2)。在图10b1和b2中裂纹先穿晶通过晶粒D和E,再由RB/TB晶界进入晶粒F中孪晶内部,此处TBs明显碎片化;裂纹在孪晶内部扩展时未与p-TBs交汇,p-TBs也未开裂(图10c1和c2)。综上可知,疲劳试样中未观察到疲劳裂纹沿着p-TBs和残留TBs扩展,以及这2类晶界开裂的现象。这表明p-TBs和残留TBs具有较高的强度,抗裂性高于RB。在S31025[13]、AISI 304[14]和316L[15]奥氏体不锈钢中,Σ3型CTBs也具有延缓疲劳裂纹扩展的特点。
图10
图10
C-5钢中疲劳裂纹与残留TBs的EBSD分析
Fig.10
IPF (a1-c1) and BC (Red lines show the TBs) (a2-c2) maps of the C-5 steel under LCF loading at 700oC with εt = 0.3% (a1, a2) and 0.7% (b1, b2), and enlarged images of the square area in Figs.10b1 and b2 (c1, c2)
3 结论
(1) C-HRA-5奥氏体耐热钢在700℃低周疲劳下,出现了显著的退孪生现象,且退孪生程度随着总应变幅的增加而增加,TBs比例由69%减少到3.9%。退孪生现象表现为几种形式:TBs碎片化,TBs转化为普通晶界,以及TBs湮灭。
(2)退孪生机制主要与位错-TBs交互作用和TBs析出相关。在循环载荷下,塑性变形以平面滑移的方式运动,形成了大量位错滑移带结构。这些位错结构与TBs交互作用导致TBs滑动和迁移,引起TBs取向关系解离、TBs碎片化直至完全退孪生。高温疲劳下,热-力耦合作用诱导Cr和C等原子向部分TBs附近偏聚,析出了M23C6相,相析出增强了位错-TBs相互作用,从而加速退孪生。
(3)与C-HRA-5钢中随机晶界相比,残留TBs和p-TBs仍然具有较高的强度,具有阻碍疲劳裂纹的萌生与扩展的作用。
参考文献
Systematical innovation of heat resistant materials used for 630-700oC advanced ultra-supercritical (A-USC) fossil fired boilers
[J].
630~700℃超超临界燃煤电站耐热管及其制造技术进展
[J].迄今,600 ℃超超临界是世界最先进商用燃煤电站技术。630~700 ℃超超临界燃煤电站研发将奠定我国火电技术的国际领先地位,对实现国家节能减排目标具有重要战略意义。耐热材料是制约火电机组蒸汽温度进一步提升的技术瓶颈,本文简述了国内外630~700 ℃超超临界电站耐热材料研制现状,指出了我国急需研发的关键耐热材料。阐述了作者团队在多年实践中总结的电站耐热材料“全流程选择性冶金过程设计和选择性强韧化设计”观点,重点介绍了在该设计观点指导下,我国成功研发了用于630~650 ℃的马氏体耐热钢G115<sup>?</sup>,用于650~700 ℃的固溶强化型镍基耐热合金C-HRA-2<sup>?</sup>、C-HRA-3<sup>?</sup>,以及用于700~750 ℃的析出强化型镍基耐热合金C-HRA-1<sup>?</sup>,系统构建了我国630~700 ℃超超临界燃煤锅炉耐热材料体系,并已成功制造了上述新型耐热材料锅炉管。
Development of model heat resisting seamless tube C-HRA-5 for ultra-supercritical power plant boiler
[J].
超超临界锅炉用新型耐热无缝管C-HRA-5的开发
[J].
Research progress of austenitic heat resistant steel Sanicro 25 used in ultra supercritical unit
[J].
超超临界机组用Sanicro 25耐热钢研究进展
[J].
The precipitation control of grain boundary M23C6 phases and the ductility improvement in aged 22Cr-25Ni-WCuNbN austenitic stainless steel by Co addition
[J].
Effect of grain boundary network on the intergranular stress corrosion cracking of 304 stainless steel
[J].
晶界网络特征对304不锈钢晶间应力腐蚀开裂的影响
[J].
TEM investigation of M23C6 carbide precipitation behaviour on varying grain boundary misorientations in 304 stainless steels
[J].
Application of grain boundary engineering to improve intergranular corrosion resistance in a Fe-Cr-Mn-Mo-N high-nitrogen and nickel-free austenitic stainless steel
[J].
Grain boundary engineering of AL6XN super-austenitic stainless steel: distinctive effects of planar-slip dislocations and deformation twins
[J].
Improving the intergranular corrosion resistance of the weld heat-affected zone by grain boundary engineering in 304 austenitic stainless steel
[J].
晶界工程对于改善304奥氏体不锈钢焊接热影响区耐晶间腐蚀性能的影响
[J].
Effects of twins and precipitates at twin boundaries on Hall-Petch relation in high nitrogen stainless steel
[J].
Formation of annealing twins in f.c.c. crystals
[J].
Tensile and fatigue properties and deformation mechanisms of twinning-induced plasticity steels
[J].
孪生诱发塑性钢拉伸与疲劳性能及变形机制
[J].随着汽车工业的高速发展,以开发先进高强钢为重点的车辆轻量化设计已经成为各大汽车厂商的发展共识。本文基于国内外孪生诱发塑性(TWIP)钢强韧性和抗疲劳设计的成果以及本课题组多年来在该领域的研究工作,系统地总结了TWIP钢的研究现状及最新进展,探讨了影响TWIP钢拉伸性能与变形机制的影响因素,包括合金成分、组织状态、应变速率等。重点介绍TWIP钢的高、低周疲劳性能和微观损伤行为,并提出一种客观评价和预测低周疲劳寿命的方法。从TWIP钢的服役环境和实际应用角度出发,试图为新一代高性能TWIP钢的开发提供新的思路和实验证据。
Performance of Alloy 709 under creep-fatigue at various dwell times
[J].
Correlation of the M23C6 precipitation morphology with grain boundary characteristics in austenitic stainless steel
[J].
Surface cracking on Σ3, Σ9 CSL and random grain boundaries in helium implanted 316L austenitic stainless steel
[J].
A possibility to synchronously improve the high-temperature strength and ductility in face-centered cubic metals through grain boundary engineering
[J].
Influence of annealing time on Σ3 boundary and Σ9 boundary evolutions in hastelloy C-276 Alloy
[J].
Chromium concentration near grain boundaries with various characters in Inconel alloy 600
[J].
Inconel 600合金中不同类型晶界处铬的浓度
[J].应用TEM、EDS和EBSD等技术研究了Inconel 600合金在715℃时效过程中不同类型晶界处碳化物的结构、形貌和晶界附近Cr浓度的分布。结果表明,不同类型晶界处碳化物的结构和形貌有较大的不同:在Σ3<sub>c</sub>晶界析出的碳化物很少,在Σ3<sub>i</sub>晶界析出不规则形状的M<sub>23</sub>C<sub>6</sub>碳化物,在Σ9晶界析出较大的M<sub>23</sub>C<sub>6</sub>碳化物颗粒,在Σ27晶界随机析出粗大的M<sub>7</sub>C<sub>3</sub>碳化物颗粒。富Cr碳化物在晶界的析出使晶界附近贫铬,在相同的时效条件下晶界的Σ值越高其附近贫铬越严重。随着时效时间的延长各晶界附近贫铬区的宽度不同程度地增大,时效15 h贫铬区的深度最大,时效50 h后深度不同程度地减小。
Microstructure mechanism, cyclic deformation behavior of an Fe-Ni-Cr alloy considering non-masing behavior
[J].
EBSD based studies on various modes of cyclic deformation at 923 K in a type 316LN stainless steel
[J].
Twin boundary: Stronger or weaker interface to resist fatigue cracking?
[J].
Detwinning mechanisms for growth twins in face-centered cubic metals
[J].
Detwinning behavior induced by local shear strain in nanotwinned Cu
[J].
纳米孪晶Cu中局部剪切应变诱导的退孪生行为
[J].对择优取向纳米孪晶结构Cu样品进行室温轧制变形. 微观结构研究发现, 当变形压下量为15%时, 样品中出现了与轧制方向呈30o~45°方向(最大剪切应力方向)分布的退孪生带. 退孪生带中孪晶片层明显粗化, 孪晶界上出现大量Shockley位错. 塑性变形过程中较小应变时, 纳米孪晶Cu中局部退孪生机制是协调局部剪切应变的主要机制.
Migration kinetics of twinning disconnections in nanotwinned Cu: An in situ HRTEM deformation study
[J].
Effect of severe plastic deformation on the structure and mechanical properties of bulk nanocrystalline metals
[J].
剧烈塑性变形对块体纳米金属材料结构和力学性能的影响
[J].
Portevin-Le Chatelier effect, twinning-detwinning and disordering in an aged Ni-Cr-Mo alloy during large plastic deformation
[J].
Planar dislocation structure during creep-fatigue interactions of TP347H heat-resistant austenitic steel at 600oC
[J].
Microstructure control to improve creep strength of alumina-forming austenitic heat-resistant steel by pre-strain
[J].
Microstructure and dislocation arrangements in Sanicro 25 steel fatigued at ambient and elevated temperatures
[J].
Effect of high-temperature ageing on microstructure and creep properties of S31042 heat-resistant steel
[J].
高温时效处理对S31042耐热钢组织和蠕变性能的影响
[J].以S31042奥氏体耐热钢为研究对象,采用短时高温时效处理后在700℃下对其进行长期蠕变性能测试。通过OM、SEM和TEM等手段表征了S31042钢蠕变过程析出相的类型和演化规律,并利用蠕变实验分析了高温时效处理对S31042钢高温性能的影响。结果表明,经1050℃时效10 h处理后,S31042钢组织中析出大量尺寸在100 nm左右的Z相,降低了固溶态S31042钢中合金元素Cr和Nb的过饱和度,减小了M<sub>23</sub>C<sub>6</sub>相的形核驱动力,将蠕变过程晶界上析出M<sub>23</sub>C<sub>6</sub>相的形态由连续的链状调控为断续的短棒状。短棒状M<sub>23</sub>C<sub>6</sub>相的形成能够在不影响材料塑性的前提下,增大晶界滑动的阻力,改善材料的持久塑性。
Precipitates and precipitation strengthening of sanicro 25 welded joint base metal crept at 973 K
[J].
Relationship between the evolution of phase parameters of grain boundary M23C6 and embrittlement of HR3C super-heater tubes in service
[J].
HR3C钢运行过热器管的脆化与晶界M23C6相参量演化的关系
[J].
Microstructure evolution in HR3C austenitic steel during long-term creep at 650oC
[J].
Study on diversified carbide precipitation in high-strength low-alloy steel during tempering
[J].
Formation of M23C6-type precipitates and chromium-depleted zones in austenite stainless steel
[J].
How big is the difference between precipitation at twin boundary and normal grain boundary in an alumina-forming austenitic steel during creep at 700oC?
[J].
Characterization of austenitic stainless steels deformed at elevated temperature
[J].
Mechanism of dynamic strain aging in a niobium-stabilized austenitic stainless steel
[J].
Dependence of dynamic strain ageing on strain amplitudes during the low-cycle fatigue of TP347H austenitic stainless steel at 550oC
[J].