现代工程结构件中大量使用异种材料的连接件,这样不仅有利于发挥材料各自性能优势,同时还可以降低成本。当前,Cu和不锈钢的连接在许多领域得到广泛应用[1,2]。由于Cu具有良好的热传导及加工性能,常用于制作各种管路组件,但Cu的强度相对较低;不锈钢以其高强度和优异的抗氧化和耐腐蚀性能可以很好地弥补Cu在性能上的不足[3]。然而钢和Cu在物理性能、冶金特性及化学相容性上存在较大差异,导致2者在焊接过程中存在诸多问题:如通过熔焊和钎焊等方法实现钢和Cu的焊接,易产生热裂纹和渗透裂纹,降低接头力学性能,另外液相反应还会在接头处产生金属间化合物[4,5]。扩散焊连接可以避免熔焊和钎焊的缺陷,并通常采取加入扩散阻挡层(如金属Ni等)的方式以改善焊接性能[6,7]。
近些年,扩散连接技术已成为异种材料最有效的连接手段之一,而实现有效扩散连接的关键是减少界面处脆性化合物的形成。研究能够与有色金属材料有效连接的新型合金是未来解决异种材料连接的最可能的突破方向[8,9]。高熵合金是一种新型的金属材料,含有5种或5种以上主要元素(原子分数在5%~35%之间)[10,11]。由于其元素的多样性,体系混乱度远超传统合金,因此高熵合金具有优于传统合金的性能,如高强度、高硬度、优异的耐磨性和耐腐蚀性等[12,13,14,15]。研究[16,17,18]表明,高熵合金具有以下4大效应:热力学上的高熵效应、结构上的晶格畸变效应、动力学上的迟滞扩散效应和性能上的“鸡尾酒效应”。其中高熵效应使其倾向于形成固溶体相,迟滞扩散效应使高熵合金中原子的扩散比较缓慢。因此,以高熵合金作为扩散中间层将大大降低扩散界面产生金属间化合物的几率,得到性能良好的接头[19,20,21,22]。陈凯等[23]采用Ti10Fe10Cr5Ni35Cu40高熵合金中间层扩散连接Ti和钢,实现了塑性结合,焊缝组织细小均匀,未出现金属间化合物。Tsai等[24]用高熵合金薄膜作为Cu和Si的扩散阻挡层,发现在700 ℃高温下可阻挡Cu-Si扩散长达30 min。
单相fcc结构CoCrFeMnNi高熵合金具有良好的加工性能、优异的综合力学性能以及扩散系数小等特点[20]。目前,关于异种材料扩散焊的研究多局限于焊接方法和工艺,而对其扩散机理的研究尚待深入。高熵合金的迟滞扩散效应,使其成为一种潜在的中间层过渡材料,为解决异种金属连接中存在的接头处易产生金属间化合物相的问题提供可能的解决途径。因此,本工作采用真空扩散焊技术,以CoCrFeMnNi高熵合金为中间层实现Cu/304不锈钢扩散连接,分析扩散界面的原子扩散行为、微观组织以及接头力学性能等,进而探讨CoCrFeMnNi高熵合金作为扩散中间层的可行性。
1 实验方法
实验用材料为等摩尔比CoCrFeMnNi高熵合金(HEA)、纯Cu (纯度大于99.95%,质量分数)和304不锈钢(304SS),实验所用材料的化学成分如表1所示。HEA采用WK-II型非自耗真空电弧炉熔炼,冷却方式为铜模水冷,试样重约50 g。熔炼时先将熔炼炉的炉腔抽真空至5×10-3 Pa,再向炉体中填充99.99% (质量分数)的高纯Ar气至正常压力。熔炼试样时,先将坩埚中的纯Ti熔化,目的是利用Ti在熔化过程中容易和O2反应,生成氧化物,从而进一步降低炉体内O的含量,保证熔炼的合金不会被氧化。为了确保合金熔化均匀,每个合金反复熔炼4次。采用VTHK-350 高真空退火炉对铸态HEA进行均质化处理,为保证良好的热处理效果,设置2个保温平台:第一阶段升温到500 ℃,用时25 min,保温30 min;第二阶段升温到1000 ℃,用时25 min,并在1000 ℃真空下保温10 h,随炉冷却。将均质化处理后的HEA切割成薄片(厚度2~3 mm)并用不同型号的砂纸打磨至表面平整,然后进行抛光处理。焊前对Cu、304SS以及HEA进行超声波清洗并去除表面氧化膜,之后迅速将其放入WZK-3型真空扩散焊炉中进行装配。扩散温度的选取原则一般为(0.6~0.8)Tm (Tm为材料熔点),以3种材料中熔点较低者为准,根据表2[25],选定扩散焊接温度分别为800、850和900 ℃,扩散反应时间为90 min。利用JSM-6510LA型场发射扫描电子显微镜(SEM)及能谱分析仪(EDS)对接头试样进行显微形貌观察以及区域成分分析。用XRD-6000型X射线衍射仪(XRD)分析接头横截面附近物相组成。采用HXS-1000TAC型半自动硬度计测量扩散层及合金硬度。为了更加准确地分析接头处硬度分布规律,在扩散界面附近选取450 μm×400 μm的区域,平均划分为50 μm×50 μm的小格,每个小格中打点取硬度,代表这个小格所在区域的硬度,最终得到硬度分布图。
表1 焊接材料的化学成分 (mass fraction / %)
Table 1
| Material | Mn | Cr | Co | Ni | C | Si | P | S | Mo | Cu | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304SS | 1.93 | 18.98 | - | 9.33 | 0.11 | 0.65 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.32 | 0.17 | Bal. |
| Electrolytic Cu | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 99.95 | - | |
| HEA | 19.23 | 19.07 | 20.50 | 21.88 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 19.32 |
| Element | VEC | Atomic radius / nm | Melting point / ℃ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Co | 9 | 0.125 | 1495 |
| Cr | 6 | 0.128 | 1857 |
| Fe | 8 | 0.126 | 1538 |
| Mn | 7 | 0.135 | 1244 |
| Ni | 10 | 0.124 | 1453 |
| Cu | 11 | 0.128 | 1085 |
| HEA | - | - | 1290~1340 |
2 实验结果
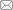
图1为不同连接温度时Cu/HEA/304SS扩散界面微观形貌及元素分布图。经800 ℃保温后扩散界面结合良好,无裂纹出现,但在靠近Cu/HEA侧界面处,存在少量形状不规则的孔洞。当扩散温度升高至850 ℃时,扩散界面结合良好,孔洞基本消失,Cu/HEA/304SS扩散偶实现了稳固连接。此外,在800~900 ℃温度范围内,扩散层厚度随温度的升高而逐渐增加,Cu/HEA侧扩散层厚度从3.2 μm增加到8.5 μm,HEA/304SS侧扩散层厚度从3.6 μm增加到8.9 μm,相比较而言,HEA/304SS侧扩散层的厚度略大于Cu/HEA侧扩散层的厚度。对扩散界面附近进行线扫描分析可见,Cu/HEA扩散界面处Cu、Co、Cr、Fe、Mn和Ni元素均发生了明显的互扩散;HEA/304SS界面处,由于Cr元素在扩散界面两侧的含量接近,故并未显示出明显的差异,而其它元素均发生了明显的互扩散。而且,扩散层中各元素均呈连续变化趋势。
图1
图1
不同连接温度时Cu/HEA/304SS扩散界面微观形貌及元素分布
Fig.1
SEM images and elemental composition distributions of Cu/HEA/304SS diffusion samples produced at 800 ℃ (a), 850 ℃ (b) and 900 ℃ (c)
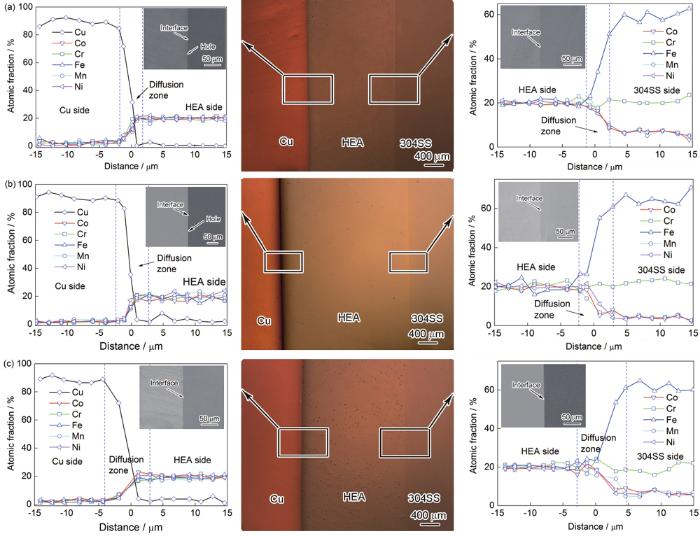
图2
图2
850 ℃时Cu/HEA/304SS扩散偶的XRD谱
Fig.2
XRD spectra of the Cu/HEA/304SS diffusion couple after annealing at 850 ℃ (Interface—interface of Cu/HEA/304SS diffusion couple. Inset shows the enlarged detail of the diffraction peaks near 44°)
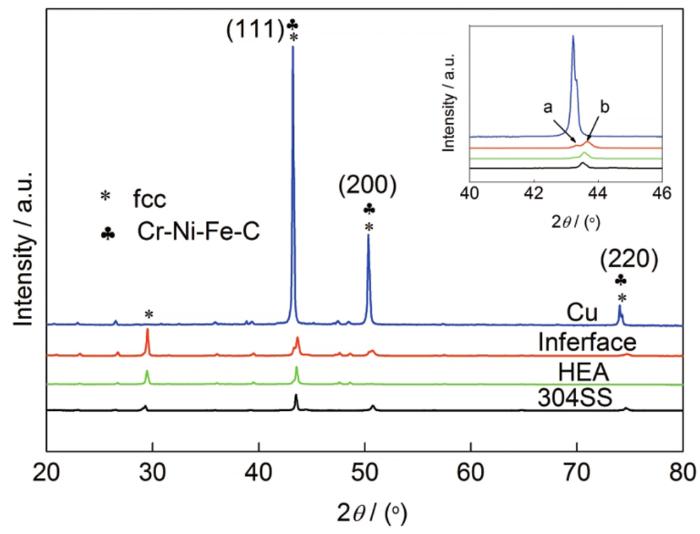
图3
图3
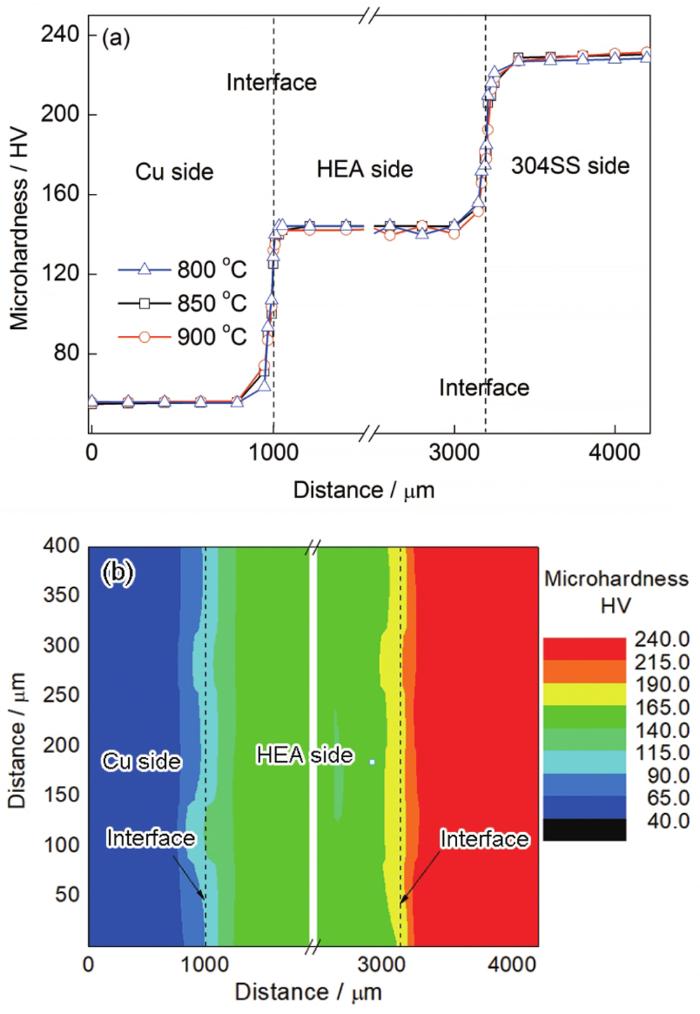
不同温度下界面附近显微硬度和850 ℃扩散偶的硬度分布图
Fig.3
The microhardness near the interface at different temperatures (a) and the distribution of the hardness of the diffusion couple interface at 850 ℃ (b)
Color online
3 分析讨论
将Cu原子和Fe原子向高熵合金一侧的扩散视为在无限长物体中的扩散,借助Fick第二定律可求出Cu原子和Fe原子在高熵合金中的扩散系数。取界面位置为原点(x=0),C0为Cu或304SS基体中Cu或Fe原子的摩尔浓度。假设在整个扩散过程中Cu或304SS基体侧界面处Cu或Fe原子的浓度始终保持不变,为C0。由
方程的初始条件(t=0时)为:
边界条件(t≥0时)为:
式中,D为Cu或Fe原子的扩散系数;C为x处Cu或Fe原子的摩尔浓度;t为扩散时间,取5400 s。
令误差函数
由
式中,n为扩散偶界面元素的数量;
| Atom | Cr | Fe | Mn | Ni | Cu |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co | -4 | -1 | -5 | 0 | 6 |
| Cr | - | -1 | 2 | -7 | 12 |
| Fe | - | - | 0 | -2 | 13 |
| Mn | - | - | - | -8 | 4 |
| Ni | - | - | - | - | 4 |
表4 扩散偶不同区域的元素含量
Table 4
Temperature ℃ | Diffusion couple | Element composition (atomic fraction / %) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co | Cr | Fe | Mn | Ni | Cu | ||
| 800 | Cu/HEA side | 16.0 | 16.7 | 16.1 | 15.7 | 16.5 | 19.0 |
| HEA/304SS side | 17.2 | 16.0 | 32.3 | 16.7 | 17.8 | - | |
| 850 | Cu/HEA side | 17.5 | 17.9 | 15.8 | 14.7 | 20.1 | 14.0 |
| HEA/304SS side | 16.3 | 18.2 | 30.2 | 16.4 | 18.9 | - | |
| 900 | Cu/HEA side | 19.0 | 19.0 | 17.6 | 11.0 | 18.4 | 15.0 |
| HEA/304SS side | 17.7 | 16.6 | 31.3 | 17.4 | 17.0 | - | |
表5 扩散偶参数计算结果
Table 5
Temperature ℃ | Diffusion couple | ΔHmix (kJ·mol-1) | δ % | VEC | ΔSmix (J·K-1·mol-1) | Phase |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 800 | Cu/HEA side | 2.08 | 2.7 | 8.57 | 12.26 | fcc |
| HEA/304SS side | -3.44 | 2.9 | 8.04 | 13.03 | fcc | |
| 850 | Cu/HEA side | 0.48 | 2.7 | 8.49 | 12.54 | fcc |
| HEA/304SS side | -3.60 | 2.8 | 8.01 | 13.13 | fcc | |
| 900 | Cu/HEA side | 1.15 | 2.5 | 8.52 | 12.40 | fcc |
| HEA/304SS side | -3.45 | 2.9 | 8.01 | 13.08 | fcc |
4 结论
(1) CoCrFeMnNi高熵合金与Cu和304SS实现了稳固连接,界面处各元素均发生了互扩散。理论计算表明,800、850和900 ℃下Cu原子在CoCrFeMnNi高熵合金中的平均扩散系数分别为1.19×10-16、2.84×10-16和5.36×10-16 m2/s,Fe原子在CoCrFeMnNi高熵合金中的平均扩散系数分别为4.56×10-16、7.26×10-16和2.29×10-15 m2/s。随着温度的升高,Cu/Fe在CoCrFeMnNi高熵合金中的平均扩散系数增加。
(2) Cu和304SS与CoCrFeMnNi高熵合金连接均形成fcc型固溶体反应层,扩散界面处并无金属间化合物产生。参数计算结果显示,扩散偶界面的混合熵、混合焓、原子半径差和价电子浓度均符合经典的固溶体相形成判据,且与实验结果一致。
(3) 扩散界面处硬度呈连续变化趋势,基体与反应层之间的硬度差别不大。说明CoCrFeMnNi高熵合金具有良好的扩散阻挡作用,能够实现Cu和304SS异种材料的有效连接。
参考文献
Investigation of micro-crack occurrence conditions in diffusion bonded Cu-304 stainless steel couple
[J].
Electrical and thermal properties of the interface at diffusion-bonded and soldered 304 stainless steel and copper bimetal
[J].
Research status and development of copper-steel welding
[J].
铜-钢异种金属焊接的研究现状和进展
[J].综述了国内外铜-钢异种金属焊接的可行性、焊接方法及焊接接头组织性能方面的研究现状.分析了铜-钢焊接过程中存在的热裂纹和铜渗透裂纹等问题.介绍了多种实现铜-钢焊接的方法及每种方法的特点和应用范围.冷金属过渡焊接是一种比较新的焊接方法,具有广阔的应用前景.对铜-钢焊接接头结合机理方面的研究多集中于对青铜和钢焊接后的接头组织,对于紫铜与钢的焊接还需进一步探讨.
Interface characteristics and performance of magnetic pulse welded copper-steel tubes
[J].
Laser butt welding for copper-steel joint
[J].
铜钢激光对接焊研究
[J].
Diffusion bonding of 410 stainless steel to copper using a nickel interlayer
[J].
Microstructure and mechanical property of two-step vacuum diffusion welded joint of ZK60/5083 using zinc as interlayer
[J].
Zn作中间层的ZK60/5083二次真空扩散焊接头显微组织与力学性能
[J].
Microstructure and property of diffusion welded titanium alloy/stainless steel joint with Nb and Cu as composite interlayer
[J].
以铌+铜为复合中间层扩散焊接钛合金/不锈钢接头的组织与性能
[J].
The study of diffusion welding of high entropy alloy with aluminum, copper and stainless steel
[D].
高熵合金与铝、铜及不锈钢异种材料扩散焊研究
[D].
Formation of simple crystal structures in Cu-Co-Ni-Cr-Al-Fe-Ti-V alloys with multiprincipal metallic elements
[J].
Mechanical performance of the AlxCoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloy system with multi principal elements
[J].
Phases, microstructures and properties of multi-component FeCoNi-based alloys
[J].
Microstructure and electrochemical properties of high entropy alloys—A comparison with type-304 stainless steel
[J].
Adhesive wear behavior of AlXCoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloys as a function of aluminum content
[J].
Microstructure stability and oxidation behaviour of (FeCoNiMo)90(Al/Cr)10 high-entropy alloys
[J].
The effect of Mn content on the microstructure and properties of CoCrCu0.1Fe0.15Mo1.5MnxNi near equiatomic alloys
[J].
Microstructure and solidification behavior of multi-component CoCrCux FeMoNi high-entropy alloys
[J].
Microstructure evolution of CoCr-FeMnNi high-entropy alloy during quasi-static tensile
[J].
准静态拉伸过程中CoCrFeMnNi高熵合金显微组织的演变
[J].
Sluggish diffusion in Co-Cr-Fe-Mn-Ni high-entropy alloys
[J].
Orientation dependence of twinning in single crystalline CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy
[J].
The phase stability of equiatomic CoCr-FeMnNi high-entropy alloy: Comparison between experiment and calculation results
[J].
Resistance welding of TA2 and Q235 base on high entropy interlayer alloys
[J].
基于高熵合金中间层的TA2与Q235电阻焊研究
[J].
Diffusion barrier properties of AlMoNbSiTaTiVZr high-entropy alloy layer between copper and silicon
[J].
Classification of bulk metallic glasses by atomic size difference, heat of mixing and period of constituent elements and its application to characterization of the main alloying element
[J].
CoCrCuFeMnNi high-entropy alloy coating prepared by plasma cladding on Q235 steel
[J].
Q235钢等离子熔覆 CoCrCuFeMnNi高熵合金涂层
[J].在Q235钢基体上采用等离子弧熔覆法制备了CoCrCuFeMnNi高熵合金涂层。采用SEM、EDS、XRD等研究了涂层的组织,利用显微硬度计测试了涂层的显微硬度分布。结果表明:采用等离子熔覆等摩尔Co、Cr、Cu、Fe、Mn、Ni单质金属混合粉,形成了无裂纹、无孔等与基体冶金结合的高熵合金涂层。涂层厚度约为1mm,主要由FCC1固溶体枝晶和少量枝晶间组织组成,枝晶间为BCC、FCC2相。涂层的显微硬度大约为260~390 HV0.2,明显高于基体的硬度150~180 HV0.2。
Diffusion bonding of SSNC 304L/Cu
[J].
表面自纳米化304L不锈钢/T2铜扩散连接
[J].