随着发动机和发电厂锅炉管材的发展,镍基高温合金的抗高温蠕变性能成为评价、设计高温合金力学性能的重要指标之一[14~17]。Song等[18]研究了单一γ'相强化型Haynes 282合金在700和750 ℃下的蠕变行为,发现高温变形会使合金的显微组织发生明显变化,并表征了位错与γ'相之间的变形机制。Chen等[19]研究了Allvac 718Plus合金在650~750 ℃之间的蠕变行为,发现位错与γ'相的交互作用随着蠕变温度和施加应力的变化而改变。Caliari等[20]研究了单一γ''相强化型Inconel 718合金短期蠕变行为,发现热处理析出的γ''强化相可以提高合金的抗蠕变性能以及显微硬度。Wang等[21]研究了单一γ''相强化型Inconel 718合金在不同温度和应力下的蠕变行为,发现在蠕变过程中γ''相会粗化转变为δ相,位错在δ相附近聚集促进孔洞形核,降低了合金的蠕变性能。
有关单一γ'或γ''相强化型镍基高温合金的蠕变行为和机制已进行了相关研究[22,23],但针对γ'和γ''相复合析出强化镍基高温合金蠕变行为和变形机制的研究还较少。通过合金成分设计,可制备获得γ'和γ''相复合析出的镍基高温合金。本课题组前期对γ'和γ''相复合析出镍基高温合金在室温下的拉伸力学性能和变形机制研究[24]发现,合金的拉伸强度随着γ'/γ''相的粗化逐渐降低。合金的变形机制也随着γ'/γ''相的变化而改变,由位错对剪切转变为Orowan绕过,最终变为单根位错剪切。拉伸实验用于表征合金的瞬时力学性能,试样承受持续增加的载荷[25,26]。蠕变是一种与时间相关的变形行为,蠕变特性反映合金在长期静态载荷下抵抗塑性变形的能力[27,28]。本工作系统研究了不同形貌特征的γ'和γ''相复合析出强化镍基高温合金在750 ℃下的蠕变行为、组织演变和变形机制,以期为后续γ'/γ''相复合强化型镍基高温合金的组织设计和调控提供数据参考。
1 实验方法
铸态镍基高温合金采用真空感应熔炼结合电渣重熔技术,合金的化学成分为64Ni-18Cr-10Fe-5Nb-1.5Ti-1.5Al (质量分数,%)。利用电火花切割机将试样从合金铸锭中切出,随后将试样置于电阻炉中加热进行热处理。首先将试样在1150 ℃保温1.5 h后取出并空冷至室温,以消除铸锭中因偏析造成的有害沉淀物。随后将试样进行直接双时效处理:加热至720 ℃,等温8 h;随后以50 ℃/h的冷速炉冷至620 ℃,在620 ℃等温8 h;空冷至室温,最后将试样分别在700、800和900 ℃下时效100 h,空冷至室温。为指代方便,下文中将通过3种不同热处理条件所得到的试样根据时效温度的不同分别称之为HDA-7、HDA-8和HDA-9。对蠕变试样进行机械加工,使其成型方向与加载轴平行。将3种试样在RDL50高温蠕变试验机上进行单轴拉应力控制下的高温蠕变实验,测试温度750 ℃,测试应力120 MPa,测试介质为空气,选取蠕变断裂后的最后应变点为试样的最终蠕变应变率。
采用JSM-7800F场发射扫描电子显微镜(SEM)观察试样表面的微观形貌,加速电压15 kV。采用JSM-7800F上配备的电子背散射衍射(EBSD)系统获得局部取向差(KAM)图,分析晶粒内部及晶界的局部变形程度。将热处理后的试样用砂纸逐级研磨至7000号,在20 V电压下将磨好的试样置于10%HClO4 + 90%CH3CH2OH (体积分数)溶液中电解抛光10 s用于EBSD分析。在试样上截取0.3 mm厚的薄片,然后机械磨至厚度50~70 μm,用5%HClO4 + 95%CH3CH2OH (体积分数)溶液进行双喷减薄,操作电压和温度分别为40 V和-20 ℃。采用Tecnai G20型透射电镜(TEM)观察试样微观组织形貌。采用Image Pro Plus软件对γ'和γ''相粒径尺寸进行统计分析。
2 实验结果
2.1 热处理后的组织
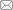
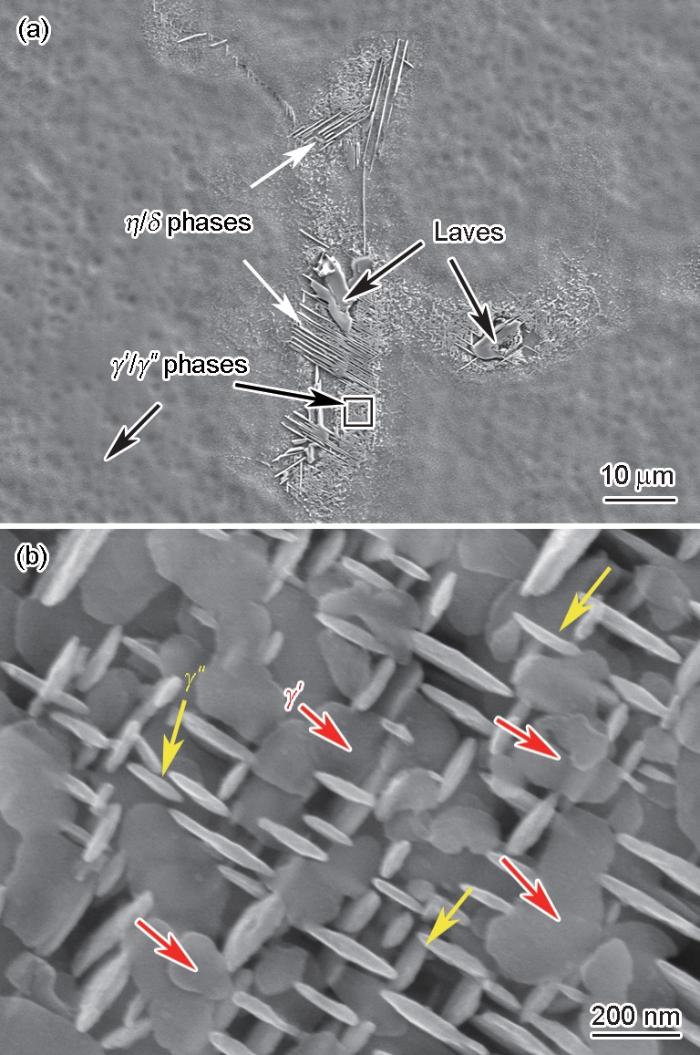
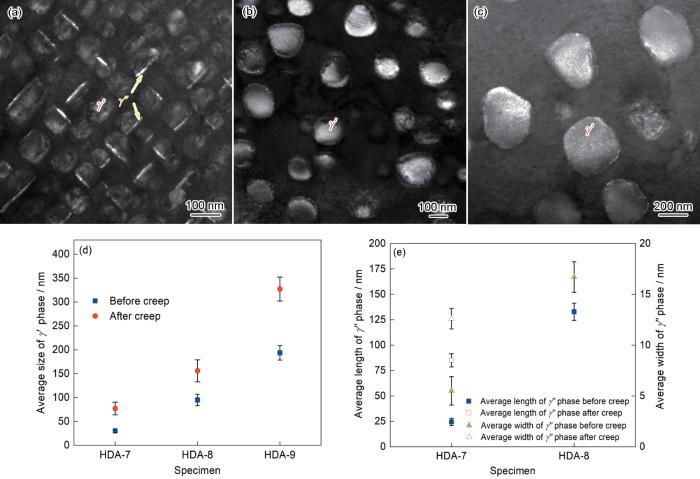
图1为镍基高温合金的原始铸态组织SEM像,由枝晶干γ相基体和枝晶间组织构成。枝晶间区域存在大尺寸的岛状Laves相和长针状δ/η相[24] (图1a),图1b为图1a中黑色方框区域放大图,可清晰观察到球形γ′相和盘状γ″相呈复合结构析出。热处理能够溶解Laves相并可调控γ'/γ''相和η/δ相的析出[29,30]。图2为不同热处理试样的SEM和TEM像。由图2a~c可见,热处理后,在HDA-7试样中,晶界(GBs)处析出少量不连续的短棒状η/δ相,致密的球形γ'相和盘状γ''相分布在晶粒内部。在HDA-8试样中,晶界处析出许多较大尺寸的针状η/δ相(图2d),γ通道显著宽化,粗化的盘状γ''相与γ'相继续保持复合结构(图2e和f)。随着时效温度升高到900 ℃ (图2g~i),HDA-9试样中γ''相全部消失,只有粗化明显的γ'相存在于基体中,η/δ相急剧生长并向晶内延伸。
图1
图1
铸态镍基高温合金微观组织的SEM像
Fig.1
SEM images of as-cast Ni-based superalloy
(a) interdendritic region
(b) γ′/γ″ phases
图2
图2
不同热处理试样的SEM和TEM像
Fig.2
SEM images (a, d, g) and TEM images with different magnifications (b, c, e, f, h, i) of Ni-based superalloy after heat treatment (GB—grain boundary)
(a-c) HDA-7 (d-f) HDA-8 (g-i) HDA-9
2.2 蠕变性能
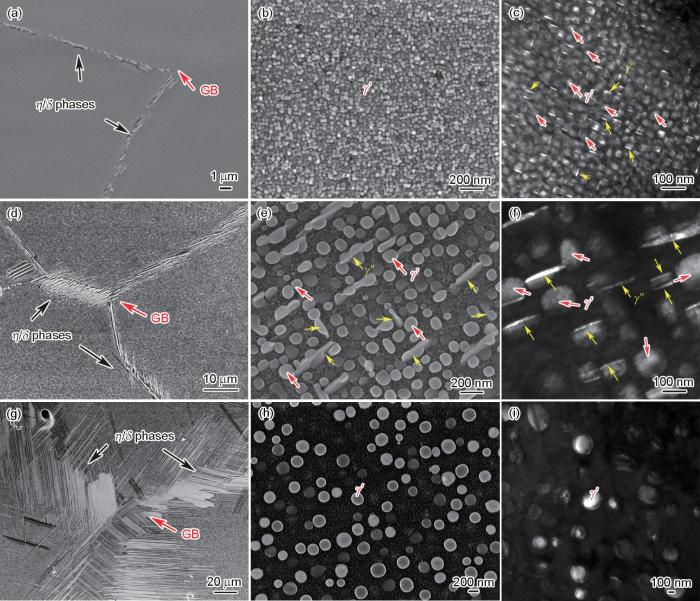
图3为3种测试样品的蠕变曲线。表1给出了3种试样的蠕变性能(蠕变寿命、蠕变应变和稳态蠕变速率)。从图3a可以看出,HDA-8试样的蠕变寿命最长(1898.6 h),HDA-9试样的蠕变寿命(1793.5 h)略低于HDA-8试样,而HDA-7试样的蠕变寿命最短(257.6 h)。HDA-8试样和HDA-9试样的蠕变曲线具有减速蠕变阶段、稳态蠕变阶段和加速蠕变阶段。而HDA-7试样则在蠕变过程中迅速失效。从表1中可以看出,HDA-8和HDA-9试样的蠕变应变相差1倍以上。此外,从图3b可以看出HDA-7、HDA-8和HDA-9试样的稳态蠕变速率分别为1.1 × 10-5、4.9 × 10-7和2.2 × 10-6 h-1。
图3
图3
不同热处理态镍基高温合金试样的高温蠕变曲线
Fig.3
High-temperature creep curves (750 oC, 120 MPa) of Ni-based superalloy specimens after different heat treatments
(a) creep time-strain curves (b) creep time-strain rate curves
表1 不同热处理试样的高温蠕变性能
Table 1
| Specimen | Creep life / h | Creep strain / % | Steady creep rate / h-1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| HDA-7 | 257.6 | 0.2 | 1.1 × 10-5 |
| HDA-8 | 1898.6 | 0.7 | 4.9 × 10-7 |
| HDA-9 | 1793.5 | 1.5 | 2.2 × 10-6 |
2.3 蠕变后的组织
图4a~c为蠕变后γ'/γ''相的SEM像。与蠕变前组织相比,试样蠕变断裂后微观组织形貌发生明显变化。HDA-7样品在蠕变后γ'和γ''相发生明显粗化,γ'/γ''相仍旧保持复合结构(图2c和4a)。HDA-8样品蠕变后只剩下粗化的γ'相存在于基体中,蠕变前组织中存在的亚稳γ''相在长时间蠕变过程中全部消失(图2f和4b)。此外,由图4c可以看出,HDA-9样品蠕变后组织中γ'相与蠕变前组织中γ'相(图2i)相比,尺寸显著增大,形貌发生失稳。对蠕变前后3种试样的γ'/γ''相平均粒径尺寸进行统计,结果如图4d和e所示。γ''相为亚稳相,高温下无法稳定存在。在750 ℃经历1898.6 h的蠕变变形后,HDA-8样品蠕变前组织中存在的粗化γ''相全部消失,因此只对HDA-7样品蠕变后的γ''相做粒径统计。HDA-7样品γ'相的平均尺寸由蠕变前的30.3 nm变为77.2 nm,γ''相的平均长度和宽度分别由蠕变前的24.5和5.5 nm变为85.1和12.6 nm。HDA-8样品γ'相的平均尺寸由蠕变前的95.0 nm变为156.0 nm,γ''相蠕变前的平均长度和宽度分别为132.9和16.7 nm。HDA-9样品γ'相的平均尺寸由蠕变前的193.7 nm变为327.3 nm。以上结果表明,高温蠕变使得γ'/γ''相发生不同程度的粗化。
图4
图4
蠕变后γ'/γ''相的TEM像及γ'/γ''相平均粒径尺寸统计
Fig.4
TEM images of γ'/γ'' phases of HDA-7 (a), HDA-8 (b), and HDA-9 (c) specimens after crept, and the average sizes of γ' (d) and γ'' (e) phases
图5
图5
3种热处理试样蠕变后微观结构的TEM像
Fig.5
TEM images of microstructures of HDA-7 (a-c), HDA-8 (d, e), and HDA-9 (f, g) specimens after creep (SFs—stacking faults)
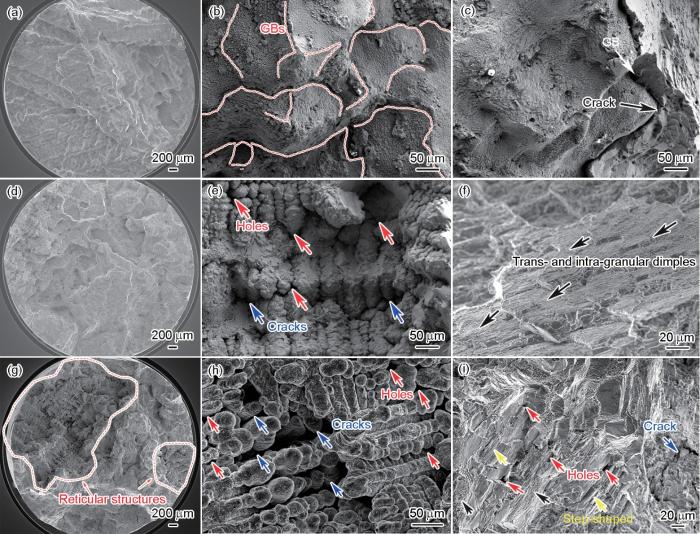
图6为样品蠕变断裂后断口形貌的SEM像。在HDA-7试样中,整个断口表面平坦呈放射状(图6a),晶界处的裂纹清晰可见,随着蠕变进行,裂纹沿晶界继续扩展发生沿晶脆性断裂(图6b和c)。从图6d~f可以看出,HDA-8样品的断口表面存在凸起和孔洞,晶内和晶间区域发现由塑性条纹扩展形成的细小交叉的网格状亚结构。晶内细小塑性条纹的形成表明了其更低的晶内应变扩展速率,与其更低的稳态蠕变速率相对应[32]。如图6g红色箭头所标记,HDA-9试样的断口表面存在明显的网状结构,网状结构周围有大量的微孔和裂纹,同时台阶状断口附近孔洞的出现表明微孔随着η/δ相向晶内的延伸不断萌生(图6h),微孔和裂纹的扩展与萌生一定程度上降低了合金的蠕变寿命。
图6
图6
HDA-7、HDA-8和HDA-9蠕变试样断口表面形貌的SEM像
Fig.6
SEM images of creep fracture surfaces of HDA-7 (a-c), HDA-8 (d-f), and HDA-9 (g-i) specimens with different magnifications
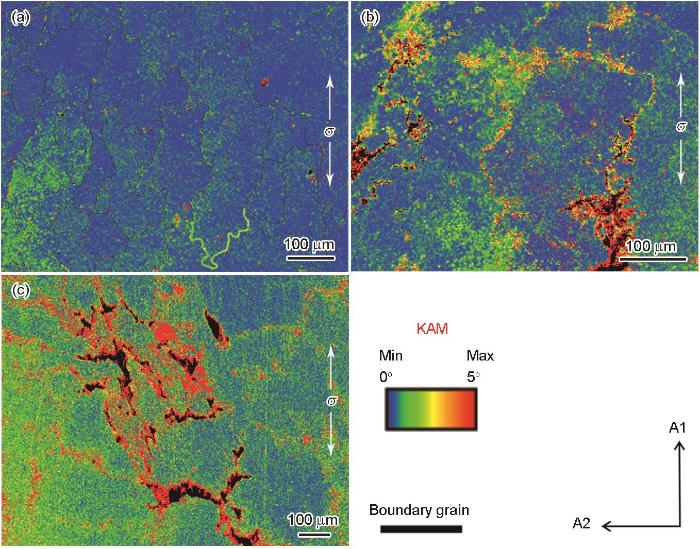
由3个试样的EBSD-KAM图观察其应变分布,分析样品的蠕变变形行为,结果如图7所示。图中蓝色、绿色和红色区域分别代表低、中、高3种应变水平。在HDA-7蠕变样品中(图7a),应变水平分布均匀。由于晶界η/δ相的数量较少,承担的载荷有限,晶界处未观察到明显的应力集中,这也说明晶界处强度有限[33]。从图7b和c可以看出,HDA-8和HDA-9试样的晶界具有更高的应变水平,表明HDA-8和HDA-9试样的晶界承受了更多的载荷。在HDA-9蠕变样品中,晶界和晶粒内均存在高应变水平区域。裂纹在晶界和大晶粒中清晰可见,且裂纹附近的应力集中最为明显。HDA-9试样晶粒内高应变水平的出现,表明在蠕变过程中超大尺寸的η/δ相积累了大量应变,裂纹沿着η/δ相萌生并不断向晶内扩展。
图7
图7
蠕变试样的电子背散射衍射-局部取向差(EBSD-KAM)图
Fig.7
EBSD-KAM maps of HDA-7 (a), HDA-8 (b), and HDA-9 (c) specimens (KAM—kernel average misorientation, σ—creep stress)
图8
图8
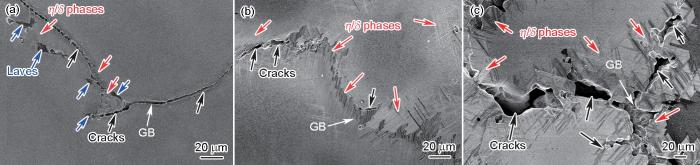
蠕变试样断口附近的轴向变形组织的SEM像
Fig.8
SEM images of longitudinal sections near the fractures of HDA-7 (a), HDA-8 (b), and HDA-9 (c)
3 分析讨论
图9为蠕变过程中组织演变、裂纹扩展、变形机制的示意图。HDA-7试样在蠕变过程中Laves相重新析出,微孔在Laves相附近产生(图8a和9d)。结合图5c、6c和8a可知,晶界处位错堆积促进裂纹的形核,η/δ相由于析出数量较少而对晶界的强化作用有限,使裂纹在晶界迅速扩展最终连接到一起,形成沿晶断裂,加速合金失效。由于γ'/γ''相尺寸较小,导致位错可动性显著降低,仅少量位错切入γ'/γ''相中(图5a和9d)。大量细小γ'/γ''相分布在基体中使得基体通道变窄,从而促进连续层错的形成(图5b和9d)[31]。大尺寸连续层错的形成会阻碍其他位错的运动,使得位错在局部塞积引起应变局域化[34]。如图5c和9d所示,大量位错在晶界附近堆积从而促进裂纹的萌生,导致合金过早断裂[17]。
图9
图9
蠕变过程中组织演变、裂纹扩展、变形机制的示意图
Fig.9
Schematics of microstructure evolution, crack propagation, and deformation mechanism before (a-c) and after (d-f) creep
(a, d) HDA-7 (b, e) HDA-8 (c, f) HDA-9
HDA-8样品中,排列紧密的针状η/δ相在蠕变过程中能够起到钉扎晶界的作用,抑制沿晶裂纹的产生,提高晶界强度(图8b和9e)[35~37]。位错剪切γ'相的应力随γ'相粗化而减小[38],因此位错容易切入γ'相。且部分位错在γ'相中分解形成层错,在晶内析出的少部分η/δ相附近也发现位错堆积(图8d)。HDA-9样品中粗大的η/δ相会在蠕变过程中继续粗化,晶界处的裂纹迅速扩展,同时裂纹随着η/δ相向晶内的延伸不断向晶内扩展,加速试样的断裂从而降低蠕变寿命(图8c和9f)。宽的γ通道使得位错绕过γ′相所需的阻力降低,位错切入γ′相的阻力变大,因此位错倾向于在γ/γ′界面堆积(图5g和9f),呈环状包裹γ′相[17]。
4 结论
(1) 在750 ℃、120 MPa条件下,具有不同形貌特征的镍基高温合金蠕变寿命存在显著差异。HDA-7 (700 ℃时效)样品中析出小尺寸γ'/γ''相,晶界处仅析出少量不连续的短棒状η/δ相,蠕变寿命仅为257.6 h。HDA-8 (800 ℃时效)样品中γ'/γ''相尺寸增大,晶界处析出排列紧密的针状η/δ相,合金蠕变寿命显著提升(1898.6 h)。HDA-9 (900 ℃时效)样品中γ'相数量减少,晶内析出高密度、大尺寸长针状η/δ相,合金蠕变寿命降低(1793.5 h)。
(2) 蠕变行为随合金组织的变化而发生改变。在HDA-7样品细小γ'/γ''相中,大尺寸的层错贯穿基体和γ'/γ''相;较低数量的η/δ相对晶界强化作用有限,合金蠕变性能较差。γ'/γ''相尺寸增大(HDA-8样品),位错剪切γ'相所需应力减小,位错易切入γ'相,并分解形成层错;析出的连续规则针状η/δ相有效钉扎晶界,发挥晶界强化的作用,显著提高了合金蠕变抗力。HDA-9样品中粗化的γ'相在蠕变过程中进一步长大,宽γ通道使得位错绕过γ′相所需阻力降低,位错在γ/γ'界面堆积呈环状包裹γ'相;晶内析出的粗大η/δ相促进微孔形核,加速合金失效。
参考文献
Effect of Ta on the microstructure and creep properties of a hot-corrosion resistant Ni-based single-crystal superalloy after long-term exposure
[J].Innovative, massive gas turbines have emerged as critical equipment for achieving the goals of energy conservation and the development of new clean energy sources. As the inlet temperature of industrial gas turbines continues to rise, the high-temperature capabilities of hot corrosion-resistant single-crystal turbine blades should be enhanced. This work investigates the effects of Ta on the microstructural stability and creep properties of hot corrosion-resistant Ni-based single-crystal superalloys with varying Ta contents (2Ta, 5Ta, and 8Ta) during long-term thermal exposure at 900oC. The findings revealed that after various thermal exposure times, the addition of Ta had no observable influence on the size of γ' precipitates, but it considerably increased the cubic degree of γ' precipitates and continuously decreased the number of tertiary γ' precipitates in γ matrix. With the increase of Ta content from 2% to 5%, the volume fraction of γ' precipitates of 5Ta alloy is higher than that of 2Ta alloy except that which is close to each other when thermal exposure at 4000 h. In addition, the volume fraction of γ' precipitates increased was higher than that of 2Ta and 5Ta alloys, as the Ta content increased from 5% to 8% after various thermal exposure times. The creep lives of the three alloys at 900oC and 275 MPa exhibited different trends as thermal exposure time increased; there was no obvious fluctuation in the 2Ta alloy after thermal exposure from 0 to 4000 h, but it significantly decreased after thermal exposure at 8000 h; the creep lives of the 5Ta and 8Ta alloys increased initially and then decreased, and the peak creep lives were 500 and 2000 h, respectively. With the addition of Ta, the steady-state creep rate continuously decreased, the creep life significantly increased, and the peak creep life shifted backward. Simultaneously, the degree and structural integrity of the rafted γ' precipitates after creep rupture increased steadily. Hence, the improvement of the creep life of the alloys was attributed to a combination of factors, such as the increase in the volume fraction of the γ' precipitates in the initial state of the creep, the increase in rafted structural integrity, and thickness of the rafted γ' precipitates during the creep process.
Ta对一种抗热腐蚀镍基单晶高温合金长时热暴露组织和蠕变性能的影响
[J].
Deformation behaviour of an advanced nickel-based superalloy studied by neutron diffraction and electron microscopy
[J].
Effect of Cr/Mo/W on the thermal stability of γ/γ′ coherent microstructure in Ni-based superalloys
[J].
Cr/Mo/W元素对镍基高温合金γ/γ′共格组织热稳定性的影响
[J].近年来,随着航空航天发动机的持续发展,对其关键热端部件的承温能力要求越来越高,而高温合金共格组织热稳定性是影响其力学性能的关键因素,本工作在团簇成分式[Al-Ni<sub>12</sub>](Al<sub>1</sub>(Ti, Nb, Ta)<sub>0.5</sub>(Cr, Mo, W)<sub>1.5</sub>)基础上,保持其他元素含量不变,改变Cr、Mo、W的含量设计了系列镍基高温合金(含Cr<sub>1.0</sub>Mo<sub>0.5</sub>的S1-CM、Cr<sub>1.0</sub>W<sub>0.5</sub>的S2-CW和含Cr<sub>0.7</sub>Mo<sub>0.4</sub>W<sub>0.4</sub>的S3-CMW),研究Cr、Mo、W含量变化对合金γ /γ′共格组织热稳定性的影响。采用非自耗真空电弧炉制备合金铸锭,并对其在1300℃固溶15 h后在900℃下进行长期时效处理,并对时效态样品进行微观组织表征和力学性能测试。结果表明,这3个合金的微观组织均表现为高体积分数(f > 70%)的γ′粒子均匀地分布在fcc-γ基体中。其中,S1-CM和S2-CW合金在900℃、50 h时效后γ′粒子形貌均呈椭球形,而S3-CMW合金则表现为方形,这是由于后者具有更负的γ /γ′点阵错配度(后者δ = -0.47%,前者δ = -0.25%~-0.33%)。500 h长期时效后,各合金中的γ′粒子形貌没有发生变化,且都具有较慢的粗化速率(K = 10~18 nm<sup>3</sup>/s);尤其S3-CMW合金表现出最高的γ /γ′共格组织稳定性(γ′粒子的粗化速率K = 10.02 nm<sup>3</sup>/s),且晶界处的第二相粒子析出明显低于其他合金。系列合金的硬度基本不随时效时间发生变化,也进一步表明了共格组织的稳定性;其中S3-CMW合金的显微硬度为397~418 HV,时效200 h后的室温压缩屈服强度为818 MPa。
Effect of Ta content on high temperature creep deformation behaviors and properties of PM nickel base superalloys
[J].The nickel base powder superalloy prepared by modern powder metallurgy (PM) technology is selected because it has the characteristics of compatibility with strength and damage tolerance. Moreover, it is the preferred material for the fabrication of a new generation of aero-engine turbine disks. In this study, experimental techniques, such as FESEM and TEM, are used to systematically evaluate the creep properties of powder metallurgy nickel base superalloys with different Ta contents under the conditions of 750°C and 600 MPa. Additionally, the characteristics of microstructure and defosrmation behavior during creep and the effect of stacking fault energy of the alloy on creep property are also investigated. The results show that with increase in Ta content, the energy associated with alloy stacking fault decreases, demonstrating a nonlinear relationship. The deformation behavior and dislocation configuration changes in each creep deformation stage are closely related to the stacking fault energy. The stacking fault energy of alloys with low Ta content is relatively high, the matrix dislocation a/2<110> is prevented at the γ/γ' interface, and the dislocation is not easy to decompose. Furthermore, it can directly enter the γ' phase to form antiphase boundary or to bypass the γ' phase through the Orowan ring bow bending mode. If the alloy contains a moderate amount of Ta, the stacking fault energy of the alloy is reduced, promoting the decomposition of matrix dislocations at the γ/γ' interface. This results in a/6<112> Shockley incomplete dislocations and starts to shear the γ' phase, forming superlattice stacking faults (superlattice intrinsic stacking faults (SISFs) or superlattice extrinsic stacking faults (SESFs)) and extended stacking faults (ESFs), which are then transformed into deformation twins. Therefore, presenting the co-strengthening effect of stacking faults and deformation twins, which improves the creep property. The stacking fault energy of alloys with high Ta content is very low, which is favorable to the simultaneous formation of wide-sized ESFs on different {111} slip planes. The occurrence of inter-crossing stacking faults inhibits the formation of deformation twins and accelerates the development of creep deformation cracks. These experimental results demonstrate that the addition of an appropriate amount of Ta to the alloy can effectively reduce the stacking fault energy, improve the ability to form both partial dislocation shear γ' phase and micro-twins, increase creep resistance, and effectively improve the alloy creep property.
Ta含量对镍基粉末高温合金高温蠕变变形行为和性能的影响
[J].采用FESEM、TEM等实验技术,系统研究了750℃、600 MPa条件下,不同Ta含量的镍基粉末高温合金的蠕变性能和蠕变过程中显微组织和变形行为特征以及合金层错能对蠕变行为的影响。结果表明,随着Ta含量的增加,合金层错能呈非线性关系降低。蠕变变形各阶段的变形行为和位错组态的变化与层错能密切相关。低Ta含量合金层错能相对较高,基体位错a/2<110>滑移被阻止在γ/γ'内界面处,不易发生位错分解,可直接进入γ'相中形成反相畴界(APB)或通过Orowan环弓弯模式绕过γ'相;当合金中Ta含量中等时,合金层错能降低,促进在γ/γ'内界面处基体位错发生分解,产生a/6<112> Shockley不全位错开始剪切γ'相,形成超点阵层错(超点阵内禀层错(SISF)或超点阵外禀层错(SESF))和扩展层错(ESF)进而转化形成形变孪晶,呈现层错和形变孪晶共同强化效应,提高蠕变性能;而高Ta含量合金层错能很低,有利于位错在不同{111}滑移面上同时形成尺寸较宽的扩展层错,并出现相互交结的交叉层错抑制形变孪晶的形成,加快蠕变形变裂纹发展。因此,合金中加入适量Ta能有效降低层错能,提高形成不全位错剪切γ'相能力和形成显微孪晶能力,增加蠕变抗力,有效改善合金蠕变性能。
Enhancing tensile properties of wrought Ni-based superalloy ATI 718Plus at elevated temperature via morphology control of η phase
[J].
Effect of tension-torsion coupled loading on the mechanical properties and deformation mechanism of GH4169 superalloys
[J].GH4169 superalloys are used in gas turbine engines and power plants owing to their excellent mechanical properties and corrosion resistance at temperatures exceeding 600oC. Because of their service condition, involving high temperature and complex stress, much attention has been attracted to the effect of temperature and loading mode on the mechanical properties and deformation mechanism. The effect of the loading mode, especially the multiaxial or coupled loading, on the mechanism of plastic deformation is still an outstanding open question despite numerous investigations on the effect of temperature on mechanical properties. In this study, the effect of tension-torsion coupled loading on deformation behavior was investigated, where the microstructures and underlying mechanism were revealed using SEM, TEM, EBSD, and neutron diffraction. It is found that the mechanical properties are dependent on the tension-torsion loading. For the tension specimens, the yield and ultimate strengths increase with the pretorsion angle; for instance, at the pretorsion angle of 720°, the increase rate is approximately 150% and 13%, respectively. At the pretension strain of 20%, the yield strength and elongation increase by approximately 31% and 16%, respectively. The density of dislocations increases in those samples after tensile and torsional deformations compared to the undeformed samples. Moreover, the density of dislocations for specimens deformed under the coupled loading is lower than those deformed under axial loading, indicating the dislocation annihilation effect. The yield strength is enhanced due to the strengthening effect of the initial dislocations produced during the preloading. The ultimate strength for the torsional specimens after pretension decreases because of the dislocation annihilation effect during the subsequent coupled loading. However, for the tensile specimens after pretorsion, such dislocation annihilation effect can be counteracted to some extent by the strengthening effect of the formed gradient structure by pretorsion on mechanical strength. These findings provide some insight into the regulation of the microdeformation mechanism process of materials through designing the coupled or multiaxial loading modes and the coordinated improvement of strength and toughness based on the achievement of gradient or hierarchical microstructure.
拉伸-扭转复合加载对镍基高温合金GH4169力学性能与变形机理的影响
[J].研究镍基高温合金在近服役条件下的力学性能与内在变形机理具有重要意义,但现有研究主要集中于单轴加载下的力学行为,多轴加载相关研究报道较少。为此,本工作对比研究了单轴和复合加载下多晶镍基高温合金GH4169的力学性能变化规律及其微观变形机制差异。在25℃下对多晶镍基高温合金GH4169进行拉伸-扭转复合加载,结合SEM、TEM、EBSD和中子衍射研究了加载方式对其力学性能、微观组织以及变形机理的影响。结果表明,拉伸样品的屈服强度和极限强度均随预扭转角度增加而增大(增幅分别约为150%和13%);在20%预拉应变下,扭转样品的屈服强度和延伸率均有所增加(增幅分别约为31%和16%)。拉伸和扭转变形后样品中的位错密度明显增大;同时复合加载下位错密度相较于单轴加载略小,表明存在位错湮灭效应。预加载产生的位错强化效应提高了屈服强度,而随后复合加载下位错湮灭效应使预拉伸扭转样品的极限强度有所降低。预扭转形成梯度结构的力学强化作用一定程度上抵消了位错湮灭效应的影响。研究表明,多轴加载方式可调控材料微观结构和变形机制,进而实现材料强度和韧性的协调提升。
Effect of heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of nickel-based powder metallurgy superalloy processed by selective laser melting
[J].Nickel-based powder metallurgy superalloys have the characteristics of uniform structure, fine grains and no macrosegregation. Due to their excellent mechanical properties, such as excellent fatigue resistance, creep resistance, excellent high-temperature strength and crack propagation resistance, they have become the preferred materials for critical hot-end components such as aero engine turbine disks. Selective laser melting (SLM) has a high ability to form complex shape of parts, reducing post-machining procedures and completing efficient productions with low component volumes, so it has become a new technical route for the preparation of superalloys. In this work, the FGH4096M alloy was prepared by SLM technique with pre-powders prepared by vacuum induction argon atomization method. The microstructure and mechanical properties of the as build and heat-treated (HTed) alloys were investigated by OM, SEM, EBSD and so on. The as build alloy with a small number of γ' and carbide, mainly composed of austenite matrix γ phase, has the highest elongation. After heat treatment, a large amount of γ' phase precipitated in the alloy, which is one of the main factors affecting the mechanical properties of the alloy. The uniform and dense distribution of γ' precipitates in the alloy can significantly improve the strength. A higher lattice distortion between the γ' phase with cubic or petaloid shape and matrix can increase the strength of the alloy to some extent. Fine dendritic and equiaxed structures in SLM FGH4096M can improve the property of the alloy as fine grain strengthening. The higher solution temperature promotes the recovery and recrystallization of the SLM alloy, and eliminates the intra-crystal dendritics and equiaxed structures. The average elongation of the as build alloy is 24.97%. The yield strength and ultimate strength of the SLM FGH4096M alloy after direct ageing treatment are the highest, and the average values are 1459.46 and 1595.56 MPa, respectively.
热处理对选区激光熔化镍基粉末高温合金组织与力学性能的影响
[J].以Ar气雾化法制备镍基高温合金粉末,利用选区激光熔化(SLM)技术制备了FGH4096M合金。运用OM、SEM、EBSD等手段研究了SLM沉积态和热处理态合金的组织和性能。结果表明,沉积态合金以奥氏体γ相基体为主,具有最高的延伸率。热处理后合金内析出大量的γ'相,γ'相均匀致密分布于合金内,能够明显提高合金强度。立方状或花瓣状γ'相与基体存在较高的晶格畸变,也能增加合金强度。精细的树枝结构和等轴结构对合金起到细晶强化作用。较高的固溶温度会促进SLM合金内回复和再结晶的发生,同时消除晶内树枝结构和等轴结构。沉积态合金平均延伸率为24.97%。经直接时效处理后的合金屈服强度和极限强度最高,其平均值分别为1459.46和1595.56 MPa。
Effects of microstructure evolution on the deformation mechanisms and tensile properties of a new Ni-base superalloy during aging at 800 oC
[J].
Microstructural stability and tensile properties of a new γ′-hardened Ni-Fe-base superalloy
[J].
Microstructure evolution of Inconel 718 superalloy during hot working and its recent development tendency
[J].Here some critical issues existed during forging process of Inconel 718 disks involving recrystallization mechanisms, grain growth, δ-phase morphology control and residual stress are explained. Based on the potential application prospect of selective laser melting in additive manufacture of aerocraft engine components, the specialized anisotropic microstructure and mechanical performance resulted from the rapid solidification process in selective laser melting are analyzed. Furthermore, the importance and difficulty of heat treatment in eliminating Laves-phase as well as tailoring substructure and related mechanical behavior are also discussed. The deformation mechanisms of Inconel 718 alloy at high temperature are illustrated in detail, comprising of dislocation planar slip, twinning and dislocation-shearing γ″ precipitates in complex modes. At last, a newly developed wrought nickel superalloy (Allvac 718Plus, with a increase in service temperature of 55 ℃ as compared to that of Inconel 718) is introduced, and some recent progresses aimed at modifying chemical compositions and phase compositions to improve service temperature on the basis of Inconel 718 alloy are also reviewed. The results indicate that the more stable γ″-γ' composite structure is important for the further design of next-generation wrought nickel superalloys.
Inconel 718变形高温合金热加工组织演变与发展趋势
[J].本文首先针对Inconel 718合金的锻造工艺过程,较为系统地阐述了合金高温变形时的再结晶机制、晶粒长大、δ相形态控制以及存在的残余应力问题。基于选区激光熔化技术在航空发动机材料增材制造领域的潜在优势和应用前景,分析了选区激光熔化技术制造Inconel 718合金凝固组织和性能的各向异性,探讨了热处理工艺在消除有害相、改变组织结构及力学行为等方面的重要作用和局限性。结合高温服役过程的组织演变,分析了Inconel 718合金变形时涉及位错滑移、孪生、γ″相剪切方式的变形机制。最后,介绍了通过调整Inconel 718合金成分来改变强化相结构,从而进一步提高变形高温合金服役温度的有效尝试(如Allvac 718Plus合金的服役温度提高了55 ℃),指出了通过成分调整来获得热稳定性优异的γ″-γ'复合析出结构是新型变形镍基高温合金的重要发展方向。
Microsegregation behavior of Inconel 718 superalloy prepared by electron beam smelting layered solidification technology
[J].
Growth behavior of γ'/γ'' coprecipitates in Ni-base superalloys
[J].
Recent progress on evolution of precipitates in Inconel 718 superalloy
[J].
Inconel 718高温合金中析出相演变研究进展
[J].Inconel 718高温合金广泛应用于航空、航天、电力和国防等领域中复杂金属结构构件的制造, 其高温抗疲劳性能和蠕变持久强度与成形加工过程中微观组织的演变密切相关. 以往的研究侧重于镍基合金热加工(如定向凝固、热处理、锻造和焊接等)工艺参数的优化, 较少从析出相控制的角度来阐明冷轧、热变形、焊接等工艺与高温服役性能之间的内在联系. 本文介绍了该合金中不同类型的析出相, 包括: 主要强化相(γ'' 相)、辅助强化相(γ' 相)、γ'' 相的平衡相(δ相), 以及MX型碳氮化物和Laves相; 论述了镍基合金制备过程中不同类型析出相的析出机制及其对合金高温性能的影响; 指出了镍基合金高能电子束焊接过程中, 焊接热影响区微裂纹形成的影响因素.
Unidirectional columnar microstructure and its effect on the enhanced creep resistance of selective electron beam melted Inconel 718
[J].
Study on the microstructure and creep behavior of Inconel 718 superalloy fabricated by selective laser melting
[J].
High temperature creep behavior of cast Ni base superalloy K44
[J].

High temperature tensile creep behaviors of cast nickel—based superalloy K44 in the temperature range of 850---900℃ and under the applied stress range of 225---380 MPa have been studied. The results indicate that all of the creep curves of test alloys have similar shape: a short primary creep and a dominant accelerated creep stage, and the long accelerated stage is due to the interaction between rafting r’ particles and dislocations. As the creep strain is a softening stage, the accelerated creep can be approximately described by expression. The creep fracture data follow the Monkman--Grant relationship. Cracks originate from the cavities at grain boundary or interdendritic.
铸造镍基合金K44的高温蠕变行为
[J].

研究了铸造镍基高温合金K44在850---900℃, 225---380 MPa的高温拉伸蠕变行为.结果表明, 实验合金蠕变曲线具有较短的初始阶段和较长的加速阶段, 加速阶段较长是由于筏形化的r’粒子和位错相互作用促成的. 加速蠕变为应变软化阶段时, 可以由关系式来描述. 蠕变断裂数据遵守Monkman--Grant规律, 裂纹起源于晶界或枝晶界的空洞.
Creep behaviors and role of dislocation network in a powder metallurgy Ni-based superalloy during medium-temperature
[J].
Micro-mechanism during long-term creep of a precipitation-strengthened Ni-based superalloy
[J].
Creep performance and damage mechanism for Allvac 718Plus superalloy
[J].
Effect of double aging heat treatment on the short-term creep behavior of the Inconel 718
[J].
Evolution of microstructural characteristics during creep behavior of Inconel 718 alloy
[J].
Influences of composition and grain size on creep-rupture behavior of Inconel® alloy 740
[J].
Effect of heterogeneous microstructure on the tensile and creep performances of cast Haynes 282 alloy
[J].
Microstructure-performance relationships in Ni-based superalloy with coprecipitation of γ' and γ'' phases
[J].
Effects of heat treatment process on the microstructure and properties of a new cast nickel-based superalloy
[J].
热处理工艺对一种新型铸造镍基高温合金的组织和性能影响
[J].通过改变固溶热处理温度、保温时间和固溶后冷却方式, 研究了不同固溶热处理工艺对一种新型铸造高温合金组织和性能的影响. 结果表明, 将合金在不同温度固溶处理2 h后空冷, 合金在760 ℃, 660 MPa和 980 ℃, 180 MPa条件下的持久寿命随热处理温度的升高先升高而后降低; 固溶处理温度为 1220 ℃时, 760 ℃, 660 MPa条件下的持久寿命达到最高; 固溶处理温度为1180 ℃时, 980 ℃, 180 MPa条件下的持久寿命最高; 当热处理温度从1120 ℃升高到1220 ℃时, 拉伸强度随温度升高而增加, 继续升温到1240 ℃, 拉伸强度下降. 当固溶热处理温度为1120℃, 处理时间在2---8 h范围内变化时, 合金在760 ℃, 660 MPa条件下的持久寿命随时间延长而降低, 而在980 ℃, 180 MPa条件下的持久寿命随处理时间延长而升高; 当热处理时间为2和4 h时, 拉伸强度较高; 延长到6和8 h时, 拉伸强度下降. 当冷却方式不同时, 合金持久性能也发生变化. γ'相和γ/γ'共晶组织在尺寸、形态、分布和数量上的变化是导致合金力学性能变化的关键因素.
Effects of heat treatment on the microstructure evolution and the high-temperature tensile properties of Haynes 282 superalloy
[J].
High-temperature tensile and creep behaviour of Inconel 625 superalloy sheet and its associated deformation-failure micromechanisms
[J].
Recent progress in research and development of nickel-based single crystal superalloys
[J].
镍基单晶高温合金的研发进展
[J].
Influence of post-heat-treatment on the microstructure and fracture toughness properties of Inconel 718 fabricated with laser directed energy deposition additive manufacturing
[J].
Early evolution of δ phase and coarse γ″ phase in Inconel 718 alloy with high temperature ageing
[J].
The creep deformation mechanisms of a newly designed nickel-base superalloy
[J].
Improving creep resistance of nickel-based superalloy Inconel 718 by tailoring gamma double prime variants
[J].
Heat treatment of Inconel 718 produced by selective laser melting: Microstructure and mechanical properties
[J].
Tensile property and deformation behavior of a directionally solidified Ni-base superalloy
[J].
Investigations of γ′, γ″ and δ precipitates in heat-treated Inconel 718 alloy fabricated by selective laser melting
[J].
Precipitation of η phase and its effects on stress rupture properties of K4750 alloy
[J].
The microstructure of heat-treated nickel-based superalloy 718Plus
[J].
Microstructural evolution and its influence on the impact toughness of GH984G alloy during long-term thermal exposure
[J].The microstructure evolution and its effect on the impact toughness of a new Ni-Fe based alloy GH984G, used in 700 °C ultra-super critical coal-fired power plant, were investigated during thermal exposure at 650 °C-750 °C for up to 10,000 h. The results show that the impact toughness at room temperature drops rapidly at the early stage during thermal exposure at 700 °C and then has no significant change even if after exposure for 10,000 h. The significant decline of the impact toughness is attributed to the coarsening of M23C6 carbides at grain boundaries, which weakens the grain boundary strength and leads to the aging-induced grain boundary embrittlement. The M23C6 carbides have almost no change with further thermal exposure and the impact toughness also remains stable. Additionally, the impact toughness rises with the increase of thermal exposure temperature. The size of γ′ after thermal exposure at 750 °C for 10,000 h is much bigger than that at 650 °C and 700 °C for 10,000 h. Therefore, the intragranular strength decreases significantly due to the transformation of the interaction between γ′ and dislocation from strongly coupled dislocation shearing to Orowan bowing. More plastic deformation occurs within grains after thermal exposure at 750 °C for 10,000 h, which increases the impact toughness.