高温合金中的微量元素对合金的液/固相线温度、凝固温度区间、枝晶搭接点温度等凝固特征温度和热物性参数具有重要影响[5~7],进而对合金的凝固过程、凝固组织和力学性能产生重要影响[5~15]。研究[7]表明,在高温合金中同时添加B和Zr元素时,合金的液相线温度(TL)和凝固温度区间均降低。B和Zr作为表面活性元素还可以降低合金的表面张力。由于B和Zr在高温合金中的固溶度较低,在凝固过程中很难进入γ基体的八面体位置,B和Zr原子在液相中的偏聚会阻碍枝晶生长,进而影响合金流动性[8,9]。大量研究[11~15]表明,适量的B和Zr可改善合金中碳化物和拓扑密排(TCP)相的尺寸和分布、提高晶界结合力以及抑制裂纹扩展,对高温合金的强度和蠕变性能有着积极作用。因此,在确保乃至提高合金力学性能的前提下,调整合金中微量元素的含量以改善其流动性,成为综合调控高温合金铸造性能和力学性能的有效手段。
本工作考察了B和Zr元素对IN718合金的凝固特征温度、TDCP和枝晶生长速率的影响,探讨了B和Zr复合添加对合金流动性的作用机理。测试了不同B和Zr含量IN718合金在650℃、620 MPa时的持久性能,以期获得兼具良好流动性和高温持久性能的B、Zr复合改性IN718合金。
1 实验方法
本实验以IN718合金为原始合金(Alloy 1),其化学成分(质量分数,%)为:C 0.056,Ni 52.54,Cr 19.15,Mo 3.11,Al 0.61,Ti 0.94,Nb 5.03,B 0.0026,Zr 0.028,Co 0.01,Fe余量。在重熔过程中分别加入不同含量的B和Zr,对应合金(Alloy 2、Alloy 3和Alloy 4)及成分如表1所示。
表1 不同B和Zr含量的IN718合金的化学成分 (mass fraction / %)
Table 1
| Alloy designation | B | Zr |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.0026 | 0.028 |
| 2 | 0.0059 | 0.028 |
| 3 | 0.0026 | 0.042 |
| 4 | 0.0059 | 0.042 |
采用ZGJL0.01-50/4-B型真空感应熔炼炉研究微量元素B和Zr以及浇注温度对流动性的影响。流动性测试模型是具有变截面的三级流动通道组成的螺旋型测试模型[16]。其中,第一级流动段内腔厚度为8 mm,长度为125 mm;第二级流动段内腔厚度为5 mm,长度为250 mm;第三级流动段内腔厚度为1.8 mm,长度为500 mm。流动性以合金液流动停止且充填完整螺旋试样的流动长度作为评价标准。通过将充填完整不同厚度处的流动长度折算成厚度为1.8 mm的流动长度来表征合金的流动性。合金的流动性为3次测试结果的平均值。流动性测试的工艺参数为过热温度1550℃,模壳温度900℃,浇注速率1 kg/s。
高温激光共聚焦显微镜(HTCLSM)可实时观察镍基高温合金的凝固过程和枝晶生长[17,18],对于分析流动性的影响机理有重要的作用。本实验采用VL2000DX-SVF18SP型HTCLSM分析B和Zr对IN718合金凝固过程的影响。实验试样为直径7.5 mm、高3.0 mm的圆柱体,试样上、下表面抛光并保持平行,以保证观察效果。将试样以60℃/min加热到1400℃后保温2 min以保证温度均匀,然后以100℃/min的冷却速率降温到1000℃观察合金凝固过程。采用Image Pro软件获得不同B和Zr含量下IN718高温合金凝固过程中液相体积分数随温度和时间的变化曲线,并对每个凝固阶段的特征进行比较。
图1
图1
双热电偶法测试示意图
Fig.1
Schematic of double thermocouple test method (TW—edge temperature of the crucible, TC—center temperature of the crucible)
采用SATEC M3试验机在650℃和620 MPa条件下进行持久性能测试,评估B和Zr元素对IN718高温合金持久寿命和延伸率的影响。
2 实验结果
2.1 流动性
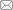
图2
图2
不同B和Zr含量的IN718合金的流动长度
Fig.2
Flow lengths of IN718 superalloy with various B and Zr contents (Lf—flow length, Tp—pouring temperature)
表2 浇铸温度为1470℃时,不同Zr和B含量IN718合金的流动长度
Table 2
| Alloy | Average length / mm | Standard deviation / % |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 275 | 7.6 |
| 2 | 416 | 8.3 |
| 3 | 421 | 9.5 |
| 4 | 523 | 9.6 |
为了评估流动性测试结果的可靠性,对3次流动长度数据进行相对标准偏差计算,结果见表2。本工作流动性测试结果的相对偏差均小于10%。考虑到影响流动性的因素极为复杂,本工作流动性测试结果的重复性较好。
2.2 凝固过程原位观察
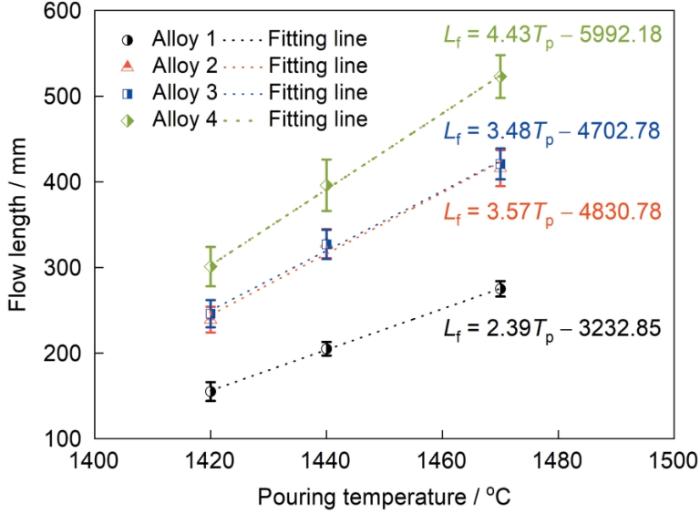
图3
图3
4种合金在冷却速率100℃/min下凝固过程的原位观察
Fig.3
In situ observations for solidification process of Alloy 1 (a1-a4), Alloy 2 (b1-b4), Alloy 3 (c1-c4), and Alloy 4 (d1-d4) at the cooling rate of 100oC/min (T—temperature)
合金凝固特征温度的变化如表3所示。随着B和Zr含量的增加,液相线温度略有降低,而固相线温度降幅较大,合金的凝固温度区间从95.3℃增大到110.2℃。
表3 高温激光共聚焦原位观察IN718合金的凝固特征温度 (oC)
Table 3
| Alloy | Liquidus temperature | Solidus temperature | Solidification temperature range |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1336.9 | 1241.6 | 95.3 |
| 2 | 1333.6 | 1232.2 | 101.4 |
| 3 | 1334.1 | 1230.7 | 103.4 |
| 4 | 1335.4 | 1225.2 | 110.2 |
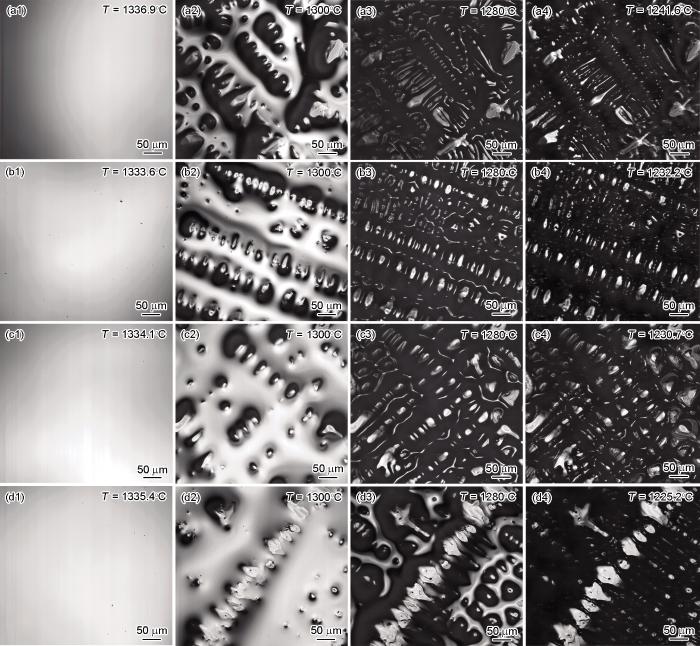
图4为原位观察获得的液相体积分数和温度的关系曲线。凝固过程中,随着B和Zr含量的增加,合金的液相分数增加,固相分数达到40%时的温度均低于原始合金。
图4
图4
不同B和Zr含量IN718合金中的液相体积分数与温度的曲线
Fig.4
Curves of liquid volume fraction with temperature for IN718 alloys with different B and Zr contents
2.3 枝晶搭接点温度
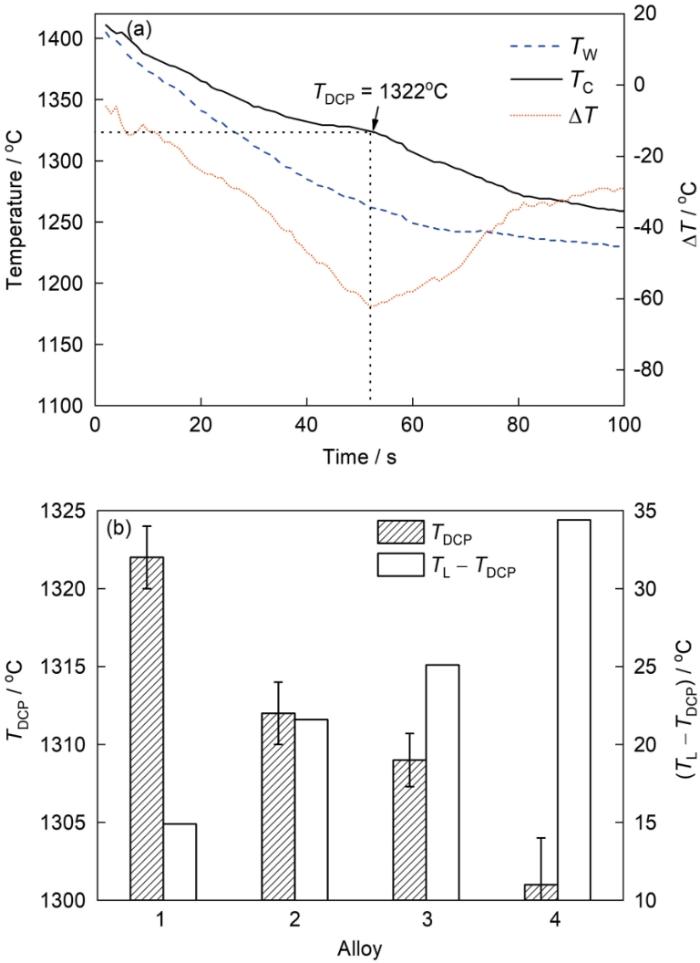
图5
图5
IN718合金冷却过程中坩埚壁和中心之间的温度差(ΔT)曲线,及B和Zr对枝晶搭接点温度(TDCP)和液相线温度(TL)与TDCP之差(TL- TDCP)的影响
Fig.5
Temperature difference curves between crucible wall and center (ΔT = TW - TC) during cooling process of IN718 alloy (a), and effect of B and Zr content on the variations of the dendrite coherency temperature (TDCP) and TL-TDCP (TL—liquidus temperature) (b)
2.4 持久性能
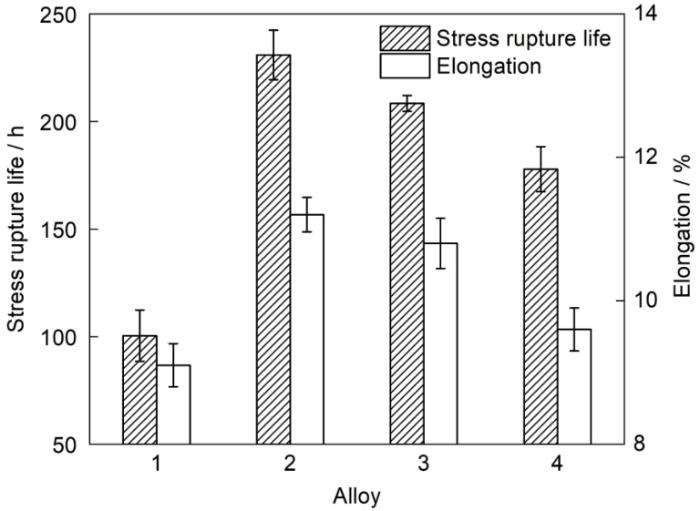
随着B和Zr含量的增加,高温合金的流动性得到改善,但其力学性能不能恶化。图6为不同B和Zr含量的IN718高温合金在650℃、620 MPa下的持久性能。Alloy 1的持久寿命为100.4 h。随着B (Alloy 2)和Zr (Alloy 3)含量的增加,合金的持久寿命分别为230.9和208.4 h,分别约为Alloy 1的2.3和2.1倍。但是,B和Zr含量均较高的Alloy 4的持久寿命为177.8 h。适量添加B和Zr可明显改善IN718合金的持久寿命和塑性。B和Zr对合金持久性能的影响主要是增加了晶界强度和改善了晶界析出相的组织特征。大量研究[12~15,23~25]表明,B和Zr与晶界、位错和空位等缺陷弹性结合能较大,易偏聚在晶界、碳化物与基体界面处,填充晶界空位,降低晶界的扩散速率,增强晶界结合力和强度,从而可有效阻碍位错和晶界运动,提高合金的力学性能。此外,B和Zr偏聚到晶界和碳化物与基体界面降低了晶界能和晶界扩散速率,阻碍δ相和碳化物形成元素在晶界处的扩散速率,进而减少δ相含量,改善碳化物尺寸与分布,从而有效减少裂纹源、阻碍位错和晶界运动[5,14,26~28]。此外,B和Zr含量增加提高了合金的流动性,减少了合金中缩松,有利于提高合金的力学性能[5]。
图6
图6
不同B和Zr含量合金在650℃、620 MPa下的持久性能
Fig.6
Stress rupture properties of four alloys with various B and Zr contents at 650oC and 620 MPa
3 分析讨论
IN718合金凝固过程的原位观察结果表明,B和Zr含量的增加,对液相线温度影响不大,但降低了固相线温度,使凝固温度区间增大,这与通常认为的凝固温度区间与流动性的关系恰好相反。实际上,对于凝固温度范围较宽的高温合金,随着凝固过程的进行和枝晶长大,合金液的黏度增加,流速减慢。当凝固过程中的固相体积分数达到20%~40%时,枝晶相互搭接成连续的网络,合金液的压力不能克服此网络的阻力,合金液停止流动[29,30]。从图3和4可以看出,固相体积分数达到40%时的温度均高于固相线温度。图3结果还表明,当合金中B和Zr含量较高时,枝晶骨架完全析出温度较低。因此,用凝固温度区间来评估流动性并不恰当。本工作认为,TDCP是影响合金流动性的关键参数。枝晶搭接是指凝固过程中枝晶相互碰撞和搭接成网状枝晶的瞬间[19~22]。在凝固过程中,当温度降低到TDCP后,熔融合金开始形成稳固的枝晶骨架,可以明显阻止流动,从而降低熔体流动性[19,21,31]。因此,TDCP越低,流动性越好。图5结果表明,随B和Zr含量的增加,TDCP降低,枝晶搭接温度范围大幅增加,从而降低了枝晶搭接速率,有利于提高合金的流动性。
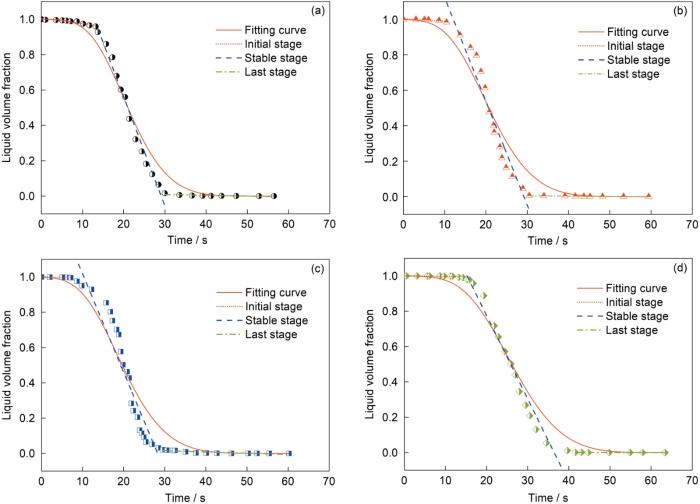
图7
图7
不同B和Zr含量合金液相体积分数和凝固时间的曲线图
Fig.7
Liquid volume fraction as a function of solidification time curves of Alloy 1 (a), Alloy 2 (b), Alloy 3 (c), and Alloy 4 (d)
表4 合金在不同凝固阶段的枝晶生长速率 (s-1)
Table 4
| Alloy | Initial stage | Stable stage | Last stage |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.96 × 10-3 | 6.12 × 10-2 | 4.34 × 10-4 |
| 2 | 1.42 × 10-3 | 5.85 × 10-2 | 2.08 × 10-4 |
| 3 | 4.71 × 10-4 | 5.57 × 10-2 | 6.99 × 10-4 |
| 4 | 4.83 × 10-4 | 4.72 × 10-2 | 3.85 × 10-5 |
由于B和Zr元素与Ni元素的电子特性和原子半径的差异,在基体中的固溶度较低,在凝固过程中很难进入γ枝晶的八面体位置[8,9,15,32]。在凝固过程中,B和Zr不断偏聚到剩余液相中,并在固/液界面前沿形成B和Zr的富集层,降低了枝晶间液体的凝固点,阻碍了其他合金元素的扩散,进而影响枝晶的生长[8,9,32,33]。此外,残余液相中B和Zr富集会降低固液表面能而增加晶界能,使凝固过程需要额外的过冷度,从而延缓凝固过程[7,32,33]。由表4可知,B和Zr含量最高的Alloy 4具有较低的枝晶生长速率,有效降低了枝晶搭接点温度,表现出极好的流动性。B和Zr元素阻碍枝晶生长的现象,有力地支持了它们降低枝晶搭接点温度的结论。综上所述,微量元素B和Zr对合金流动性的影响,是枝晶搭接点温度和液相分数共同作用的结果。其中,B和Zr延缓了糊状区的枝晶生长,使得枝晶搭接点温度降低,是流动性提高的主要原因。
4 结论
(1) 复合添加B和Zr元素在不降低合金持久性能的前提下可有效提高IN718合金的流动性。合金中B和Zr质量分数分别为0.0059%和0.042%时,流动性最好,比原始合金提高了90%以上,持久寿命提高了77%。
(2) 复合添加B和Zr元素降低了合金的枝晶搭接点温度,增加了残余液相分数及液相线温度与枝晶搭接点温度的变化范围。
(3) 复合添加B和Zr元素降低了枝晶生长速率和枝晶搭接点温度,是IN718合金流动性提高的主要原因。
参考文献
Research and development of equiaxed grain solidification and forming technology for nickel-based cast superalloys
[J].Equiaxed grain cast superalloys are widely used in aeroengine and other fields due to their low manufacturing cost and excellent mechanical properties at medium and low temperatures. Aeroengine casing is a typical complex thin-walled equiaxed superalloy castings used at medium and low temperatures. The complex thin-walled superalloy investment castings with the complex structures, the accurate size and the lightweight are the key components for advanced aeroengines. The coordinated control of the precise forming and the solidification microstructure for these castings is very difficult. Correspondingly, the requirements for materials, casting technologies, structure controls and mechanical properties in superalloy integral structure castings are becoming increasingly higher. In this paper, the development and application of polycrystalline superalloys, solidification and forming, the simulations and the new technologies are reviewed.
镍基铸造高温合金等轴晶凝固成形技术的研究和进展
[J].
Investment casting technology and development trend of superalloy ultra limit components
[J].Superalloy casting is an important hot component in major aerospace equipment. It is being developed for larger and more complex structures and thinner wall thickness than traditional superalloy casting. The requirements of its internal metallurgical quality and external dimensional accuracy are becoming increasingly stringent, gradually exceeding the manufacturing limit of traditional investment casting technology. Shrinkage porosity defect control, thin-walled complete filling, dimensional accuracy, and surface quality control have become key challenges in the manufacturing of large and complex thin-walled superalloy castings. This paper systematically summarizes the research status of the superalloy casting process design, mold shell preparation, whole process dimensional accuracy, and adjusted pressure casting technique at home and abroad. This paper also analyzes and predicts the development trend of intelligent casting based on big data.
高温合金超限构件精密铸造技术及发展趋势
[J].高温合金铸件是航空航天重大装备中不可或缺的热端部件,正向尺寸更大、结构更复杂和壁厚更薄的方向发展,对其内部冶金质量和外部尺寸精度的要求也愈加严苛,逐渐超出了传统熔模精密铸造技术的成型极限。疏松缺陷控制、薄壁完整充型、尺寸精度和表面质量控制已经成为大型复杂薄壁高温合金铸件制造的关键难题。本文系统综述了国内外高温合金铸造工艺设计、模壳制备、全流程尺寸精度和调压成型技术的研究现状,并对基于大数据的铸造智能化发展趋势进行了分析与展望。
Thermal properties of cast nickel based superalloys
[J].
Ni based superalloy: Casting technology, metallurgy, development, properties and applications
[J].
Effects of boron and zirconium additions on the fluidity, microstructure and mechanical properties of IN718C superalloy
[J].
A solidification model for prediction of castability in the precipitation-strengthened nickel-based superalloys
[J].
Effect of Zr and B on castability of Ni-based superalloy IN792
[J].
Effect of Zr on solidification segregation behavior of K417G alloy and its anomalous effect during rapid cooling process
[J].
The role of boron in modifying the solidification and microstructure of nickel-base alloy U720Li
[J].
On the segregation behavior and influences of minor alloying element Zr in nickel-based superalloys
[J].
Hot tearing in polycrystalline Ni-based IN738LC superalloy: Influence of Zr content
[J].
On the role of boron on improving ductility in a new polycrystalline superalloy
[J].
Effect of homogenization heat treatments on the cast structure and tensile properties of nickel-base superalloy ATI 718Plus in the presence of boron and zirconium additions
[J].
Effect of boron addition on the microstructure and mechanical properties of K4750 nickel-based superalloy
[J].The effect of boron addition at 0, 0.007 wt. % and 0.010 wt. % on the microstructure and mechanical properties of K4750 nickel-based superalloy was studied. The microstructure of the as-cast and heat-treated alloys was analyzed by SEM, EPMA, SIMS and TEM. Lamellar M5B3-type borides were observed in boron-containing as-cast alloys. After the full heat treatment, boron atoms released from the decomposition of M5B3 borides were segregated at grain boundaries, which inhibited the growth and agglomeration of M23C6 carbides. Therefore, the M23C6 carbides along grain boundaries were granular in boron-containing alloys, while those were continuous in boron-free alloys. The mechanical property analysis indicated that the addition of boron significantly improved the tensile ductility at room temperature and stress rupture properties at 750 ℃/430 MPa of K4750 alloy. The low tensile ductility at room temperature of 0B alloy was attributed to continuous M23C6 carbides leaded to stress concentration, which provided a favorable location for crack nucleation and propagation. The improvement of the stress rupture properties of boron-containing alloys was the result of the combination of boron segregation increased the cohesion of grain boundaries and granular M23C6 carbides suppressed the link-up and extension of micro-cracks.
Influence of grain boundary precipitation and segregation on cracking of cast and wrought superalloys containing B and Zr
[J].
A method for preparing fluidity testing mould and sample of superalloy
[P].
一种高温合金流动性测试模具及测试试样的制备方法
[P].
Dendrite growth in nickel-based superalloy with in-situ observation by high temperature confocal laser scanning microscopy and numerical simulation
[J].
Solidification process of conventional superalloy by confocal scanning laser microscope
[J].
Development and characterization of low-silicon cast aluminum alloys for thermal dissipation
[J].
Development of thermal strain in the coherent mushy zone during solidification of aluminum alloys
[J].
Effect of grain refinement on the dendrite coherency point during solidification of the A319 aluminum alloy
[J].
Determination of dendritic coherency in solidifying melts by rheological measurements
[J].
On the role of grain boundary serration in simulated weld heat-affected zone liquation of a wrought nickel-based superalloy
[J].
Grain boundary segregation in Ni-base alloys: A combined atom probe tomography and first principles study
[J].
Effect of serrated grain boundaries on the creep property of Inconel 718 superalloy
[J].
Effects of Zr addition on the microstructure and mechanical behavior of a fine-grained nickel-based superalloy at elevated temperatures
[J].
Effect of boron additions on the microstructure and transverse properties of a directionally solidified superalloy
[J].
Effect of boron and carbon on the fracture toughness of IN 718 superalloy at room temperature and 650oC
[J].
Evaluation of the effect of grain refiners on the solidification characteristics of an Sr-modified ADC12 die-casting alloy by cooling curve thermal analysis
[J].
Effect of B, Zr, and C on hot tearing of a directionally solidified nickel-based superalloy
[J].
Effect of boron content on microstructure evolution during solidification and mechanical properties of K417G alloy
[J].Boron is a key element in superalloys and many other metallic materials for strengthening the grain boundaries. However, it also has harmful effect on aggravating the solidification segregation of the alloys. Although the mechanism for the influences of B on the alloys has been studied extensively, it is still required to study in some alloys currently because the compositive effects of boron in different alloys are sometimes distinct. K417G, a cast superalloy with good comprehensive properties, has been applied in aero engines of China. In the present work, the effects of boron content on the microstructure evolution during the solidification and the mechanical properties of the as cast K417G alloy have been investigated, providing some fundamental information for the control of boron addition in the alloy. It has been found that boron aggravated the elemental segregation and promoted the eutectic (γ+γ') precipitation at the final stage of the solidification of K417G alloy. In addition, boron decreased the precipitation temperature, and hence reduced the nucleation rate of the γ matrix. When the boron content was below 0.036%, the grain size was increased with the increment of B content, which is caused by the decreased nucleation of the γ phase. When the B addition was increased up to 0.060%, the grain was refined at some local places, because the growth of the dendrites was inhibited and the γ phase could nucleate at the inner part of the subcooled liquids. The mechanical properties of K417G alloy were significantly influenced by the precipitation of the boride at the grain boundaries. The borides were precipitated as fine particles at the grain boundaries when the B addition was below 0.036%, and the tensile properties at 900 ℃ and the stress rupture properties at 900 ℃ and 315 MPa were markedly improved with the increasing B content in this addition range. When the B content was increased to 0.060%, the boride was precipitated as eutectic form in front of the eutectic (γ+γ'). The tensile and stress rupture properties were decreased due to the weak cohesion between the eutectic (γ+γ') and the eutectic form borides.
B含量对K417G合金凝固过程中组织演变和力学性能的影响
[J].研究了B含量对K417G合金凝固过程中相析出以及铸态组织和力学性能的影响。研究不仅证实了B显著促进元素偏析以及凝固后期(γ+γ')共晶析出,还发现B对K417G合金凝固早期基体γ相的析出和长大具有明显影响。B降低基体γ相的析出温度,抑制γ相的形核,并阻碍γ相生长。当B含量低于0.036%时,由于B降低γ相形核率,导致K417G合金的晶粒组织随B含量增加明显粗化。当B含量增加至0.060%时,尽管B仍然降低γ相形核率,但由于其阻碍γ相枝晶的早期生长,使熔体内部过冷度升高,局部发生晶粒细化。B对K417G合金力学性能的影响决定于硼化物的晶界析出形态,当B含量低于0.036%时,硼化物以颗粒状在晶界析出并对晶界产生强化作用,合金的900 ℃拉伸性能和900 ℃、315 MPa持久性能随B含量的增加而显著提高。当B含量达到0.060%时,共晶态硼化物在(γ+γ')前沿析出,导致共晶态硼化物与(γ+γ')的界面显著弱化,拉伸和持久性能显著降低。