PEDOT电聚合的电位较正,在氧化单体沉积到Al及铝合金基底上时,基底金属会发生溶解,阻碍涂层沉积,而且基底表面致密的氧化膜也会阻碍氧化单体的沉积。Brânzoi等[7]证实,在水溶液中金属Al (除去氧化物层之后)表面电沉积聚吡咯(PPy)较为困难,多孔且不导电的Al2O3与导电的PPy涂层在电极表面同时形成,彼此相互作用,形成复合涂层材料。Cheung等[8]研究了在甲苯磺酸四乙基铵溶液中电聚合PPy,结果表明Al基底表面会立刻形成Al2O3绝缘层,阻挡电子转移,影响PPy的聚合。因此,在Al及铝合金表面电聚合时,需要通过改变电解质溶液、电化学方法和参数等手段,突破氧化膜并减缓金属溶解速率。
电解质溶液的选择和电化学参数的改变都会对PEDOT的电化学行为和表面形貌产生重要影响,进而导致不同的缓蚀性能。Zhu等[9]在不锈钢基底上通过循环伏安法电沉积PEDOT涂层,揭示PEDOT涂层保护基底免于局部腐蚀的原因是PEDOT/金属界面因催化作用形成了致密氧化物层。Kumar等[10]研究证实了致密PEDOT涂层能够增强TiNbZr合金基底的耐腐蚀性能。Lazzaroni等[11]和Gustafsson等[12]发现在金属Al上沉积PEDOT涂层会生成共价Al—C键,改变了聚合链几何形状并减少π电子共轭。在Al及铝合金上沉积PEDOT涂层,其电子特性取决于掺杂阴离子的尺寸[13,14],当掺杂大阴离子(如聚苯乙烯磺酸盐(PSS))时,易形成Al2O3、PSS和导电率较低的聚合物层[15,16];而掺杂小阴离子(如高氯酸盐)时,导电率相对较好[17,18]。
本工作使用不同电解质溶液,分别采用循环伏安法和恒电流法在2024铝合金上电聚合PEDOT涂层,利用各种分析技术研究PEDOT/2024铝合金在稀哈里森(DHS)溶液中的缓蚀作用。
1 实验方法
1.1 仪器与试剂
采用Stemi 508体视显微镜观察PEDOT涂层宏观形貌。采用S-4800场发射扫描电子显微镜(FESEM)观察PEDOT涂层的微观表面形貌。使用Model 200扫描振动电极(SVET)研究涂层破损后的腐蚀过程,控制软件为ASET 2.0,扫描振动探针为镀铂的Pt/Ir合金丝,尖端为镀铂合金球(直径20 μm)。循环伏安法和恒电流法制备PEDOT涂层以及电偶腐蚀、电化学阻抗谱(EIS)等腐蚀测试在Gamry Reference 600+电化学工作站上完成。
实验中使用的3,4-乙烯二氧噻吩(EDOT),十二烷基硫酸钠(SDS),邻苯二甲酸氢钠(C8H5NaO4)和六氟磷酸四丁胺(TBAPF6),乙醇(C2H6O),丙酮(C3H6O),乙腈(C2H3N),硫酸铵((NH4)2SO2),氯化钠(NaCl)和高氯酸锂(LiClO4)均为分析级。
1.2 PEDOT涂层制备
将2024铝合金片密封在环氧树脂中,暴露出1 cm×1 cm基底。电极表面用400~2000号砂纸逐级打磨,然后用丙酮脱脂,乙醇冲洗干净后,保存在干燥皿中。采用三电极体系沉积PEDOT涂层,2024铝合金片为工作电极、Pt片(2.5 cm×2.5 cm)为对电极、饱和甘汞电极(SCE)为参比电极。沉积前,电解质溶液需用N2 (纯度99.99%)排气30 min。电极需用2000号的砂纸再次打磨并用乙醇冲洗吹干后立即使用。电沉积前的表面处理是为了去除氧化物层并改变表面粗糙度和润湿性,有效增加与基底表面的结合强度[10]。
分别采用循环伏安法和恒电流法在2024铝合金电极表面电沉积PEDOT涂层。选用3种电解质溶液:(1) 30×10-3 mol/L SDS和0.1 mol/L LiClO4的水溶液,加入EDOT单体量为30×10-3 mol/L;(2) 0.1 mol/L C8H5NaO4和0.14 mol/L SDS的水溶液中,加入EDOT单体量为0.1 mol/L;(3) 26×10-3 mol/L TBAPF6的乙腈中,加入EDOT单体量为0.1 mol/L。3种电解质溶液成分和相应的EDOT加入量如表1所示。沉积的PEDOT涂层用去离子水冲洗表面,静置自然干燥。
表1 3种电解质溶液成分和3,4-乙烯二氧噻吩(EDOT)单体加入量
Table 1
| Solution | Composition | EDOT addition mol·L-1 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 30×10-3 mol·L-1 sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)+0.1 mol·L-1 LiClO4 | 30×10-3 |
| 2 | 0.1 mol·L-1 sodium hydrogen phthalate (C8H5NaO4)+0.14 mol·L-1 SDS | 0.1 |
| 3 | 26×10-3 mol·L-1 tetrabutylammonium hexafluorophosphate (TBAPF6) acetonitrile | 0.1 |
1.3 电化学性能测试
将1 cm×1 cm的PEDOT/2024铝合金电极与2024铝合金电极偶接,浸入DHS溶液(3.5 g/L (NH4)2SO2+0.5 g/L NaCl)中,考察它们的电偶腐蚀情况。采用PEDOT/2024铝合金电极为工作电极、Pt片(2.5 cm×2.5 cm)为对电极、SCE为参比电极,测试电极不同浸泡时间的EIS,使用ZimpXin软件进行EIS数据分析。
使用美工刀在PEDOT涂层表面划出长约1 mm的划痕,试样周边用石蜡封好,露出基体金属将其浸泡在DHS溶液中,在划痕处进行SVET 测试。振动微电极可检测由阴、阳离子流动而造成的电位梯度变化。探针尖端距离表面100 μm处开始扫描,垂直于电极表面进行振动,频率为330 Hz,扫描区域为2 mm×2 mm,让表面划痕处于扫描区域的中心。
2 实验结果与讨论
2.1 铝合金表面PEDOT涂层的制备
2.1.1 循环伏安法制备PEDOT涂层
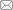
图1
图1
在不同电解质溶液中电聚合EDOT制备聚3,4-乙烯二氧噻吩(PEDOT)涂层的循环伏安曲线及涂层宏观形貌
Fig.1
Cyclic voltammetry curves (a1~a3) and macrostructures (b1~b3) of poly 3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene (PEDOT) coating prepared by electropolymerization of EDOT in solution 1+EDOT (a1, b1), solution 2+EDOT (a2, b2) and solution 3+EDOT (a3, b3) (E-galvanic potential, i-galvanic current density)
在3种电解质溶液中,EDOT的氧化峰位分别为1.1、0.5和0.1 V,说明溶液3中的TBAPF6能够明显降低EDOT的氧化电位。在溶液3中反向扫描的电流密度也明显降低,表明TBAPF6对电极的钝化程度较高,产生钝化的原因可归结为TBAPF6相对易吸附在铝合金表面形成非常薄的钝化层。上述结果说明TBAPF6不仅对基底具有钝化和缓蚀作用,而且能够显著降低EDOT的氧化电位,因此在溶液3中制备的PEDOT涂层效果最佳。但循环伏安法所制备的PEDOT涂层并不完整,明显存在空隙。
2.1.2 恒电流法制备PEDOT涂层
图2
图2
在不同电解质溶液中电聚合EDOT制备PEDOT涂层的恒电位曲线及涂层宏观形貌
Fig.2
Potentiostatic curves (a1~a3) and macrostructures (b1~b3) of PEDOT coating prepared by electropolymerization of EDOT in solution 1+EDOT (a1, b1), solution 2+EDOT (a2, b2) and solution 3+EDOT (a3, b3)
图2a2为在溶液2中,采用4 mA/cm2恒电流密度电聚合EDOT制备PEDOT的恒电流曲线。电位在100 s后上升至4 V,是由于基底表面PEDOT生长所引起。逐渐生成的PEDOT填补了氧化膜击穿处。基底表面涂层生成过程是聚合物PEDOT与铝合金阳极腐蚀之间相互竞争的过程[20],若铝合金的腐蚀速率大于PEDOT的生成速率,则PEDOT无法及时填补新生成的腐蚀坑,使其无法在基底上稳定生长。然而,较正的电位会导致大量氧化物产生,从而阻止形成连续的聚合物PEDOT涂层。宏观照片(图2b2)显示,在该电解质溶液中制备的PEDOT涂层较为完整,基本覆盖基底表面。SEM像(图3a和b)显示,虽然涂层表面大部分被覆盖,但还存在空缺部位。PEDOT涂层表面形貌呈花椰菜状,少量呈花瓣状形貌。涂层微观结构存在大量由基底腐蚀所引起的孔隙[21]。
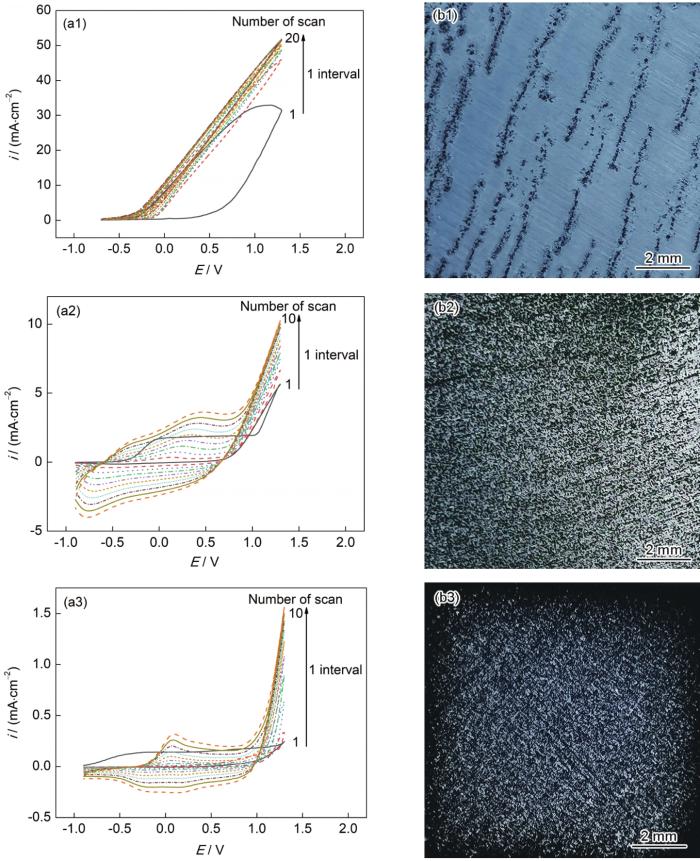
图3
图3
在不同电解质溶液中恒电流电聚合EDOT制备PEDOT涂层的SEM像
Fig.3
Low (a, c) and high (b, d) magnified SEM images of PEDOT coatings deposited by constant current density in solution 2+EDOT (a, b) and solution 3+EDOT (c, d)
比较3种电解质溶液中电聚合EDOT制备PEDOT涂层的宏观照片可以看出,溶液3中制备的涂层最为完整致密,且在较大电流密度下具有较低电位。PEDOT成球状团聚在基底表面,形成紧密的分子聚集体,这会降低涂层内部孔隙率,提高阻隔性,防止O2和H2O进入涂层传输,使涂层抗腐蚀能力显著提高。在溶液2中虽然也能制备出较为完整的PEDOT涂层,但由于金属氧化作用,涂层微观形貌显示内部仍然存在较多孔隙。EDOT进行聚合反应的同时,还伴随着金属氧化和钝化过程,它们与PEDOT涂层的生成形成竞争。因为瞬时大电流密度能击破氧化膜,强电流有利于EDOT单体的氧化和聚合,并改善具有双分子性质的自由基阳离子间的偶联反应[23,24],所以采用恒电流法制备PEDOT涂层,能够减少基底溶解,避免由循环伏安还原过程所引起的PEDOT数量减少和阳离子插入。因此,PEDOT涂层的最佳制备条件为采用恒电流法,在TBAPF6乙腈溶液中,以20 mA/cm2电流密度聚合EDOT 100 s。
2.2 铝合金表面PEDOT涂层的耐腐蚀性能
2.2.1 PEDOT涂层与铝合金的腐蚀倾向性
当PEDOT/2024铝合金电极与2024铝合金电极偶接时,在DHS溶液中的电偶电位和电偶电流密度如图4所示。可以看出,耦合电压立刻增加,在50 min时达到最大值-461 mV,之后保持平稳。PEDOT涂层的电位相对于2024铝合金为正,电位的提高也会使腐蚀速率降低。PEDOT涂层提供了较大的耦合电流密度,耦合电流密度随着时间延长迅速减小,在2.5 h后减小到-8 μA/cm2,之后基本保持不变。电流密度负值说明PEDOT/2024铝合金电极为阴极,2024铝合金电极为阳极,PEDOT涂层对基底起到了保护作用。
图4
图4
在DHS溶液(3.5 g/L (NH4)2SO2+0.5 g/L NaCl)中PEDOT/2024铝合金电极与2024铝合金电极偶接时的电位(E)和电流密度(i)
Fig.4
Galvanic potential and galvanic current density of the PEDOT/2024 aluminium electrode connected to the 2024 aluminium electrode in DHS solution (3.5 g/L (NH4)2SO2+0.5 g/L NaCl)
2.2.2 PEDOT涂层的耐蚀性
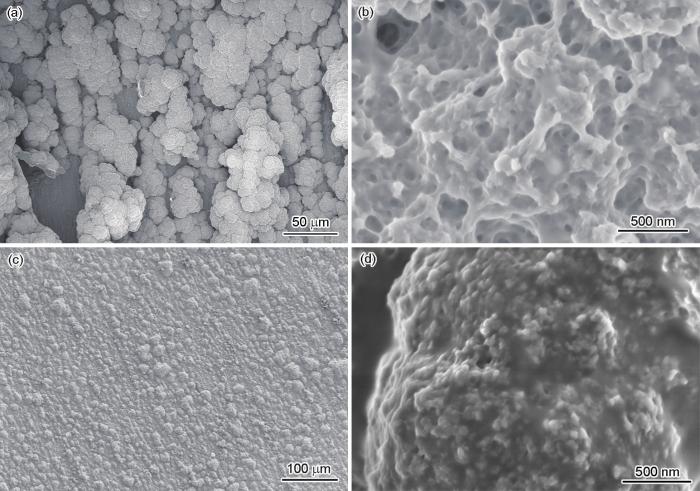
图5是在DHS溶液中2024铝合金电极和PEDOT/2024铝合金电极的EIS。从图5a可以看出,2024铝合金电极Nyquist图中的半圆直径随时间延长而增大,这是由于2024铝合金电极表面产生腐蚀,形成了Al2O3阻挡层。随着腐蚀产物的增加,绝缘层电阻逐渐增大,因此半圆直径变大。然而,当浸泡第8 d时,由于腐蚀产物扩散到溶液中,阻挡层电阻随着Al2O3的减少而下降。2024铝合金电极相角-频率图(图5c)中存在2个容抗弧。中低频区容抗弧由电极表面腐蚀产生,而高频区容抗弧归属于原始界面的双电层现象。中低频容抗弧随着浸泡时间延长而上升,极化电阻随浸泡时间延长而增大,表明电极表面腐蚀产物的积累,即Al2O3阻挡层厚度的增加,但并未对腐蚀产生阻碍。Bode图(图5b)中中低频区曲线基本重合,高频区曲线保持水平且随时间延长缓慢上升,说明基底持续腐蚀。
图5
图5
在DHS溶液中2024铝合金电极和PEDOT/2024铝合金电极的EIS
Fig.5
Nyquist plots (a, d), Bode plots (b, e) and phase angle plots (c, f) of 2024 aluminium electrodes (a~c) and PEDOT/2024 aluminium electrodes (d~f) in DHS solution (ZIm-imaginary part of impedance, ZRe-real part of impedance, |Z|-impedance modulus)
PEDOT/2024铝合金电极的Nyquist图(图5d)由一个高频区容抗弧和一条倾斜角大于π/4的斜线组成。在浸泡初期,高频区容抗弧与半圆更加接近,表明弥散效应小,PEDOT涂层表面平整。随着浸泡时间的延长,容抗弧的半圆越来越不完整,并且其圆心位于第四象限内,说明弥散效应严重,PEDOT涂层表面已不平整。PEDOT/2024铝合金电极相角-频率图(图5f)显示在浸泡初期时,相角-频率关系为一条斜线,相角在中频区起伏不大,表面PEDOT涂层可以当作一个阻值大、电容小的绝缘层。随着浸泡时间的延长,相角在第3 d达到最大,曲线向低频区方向移动,说明此时已在基底表面形成钝化层,导致其电阻增大,电容减小。由于PEDOT是一种电活性涂层,氧化后具有较高的正氧化还原电位,可以起到催化活性金属表面形成钝化层的作用。PEDOT/2024铝合金电极的低频区阻抗模|Z| (0.01 Hz)和容抗弧都在浸泡第3 d时达到最大,表明PEDOT涂层在前3 d的浸泡过程中对基底产生了保护作用。浸泡3 d之后,容抗弧开始下降,Bode图(图5e)中高频区曲线重合在一起,相角-频率图中相位角迅速向高频区移动后又缓慢移向低频区,曲线也在明显下降后又缓慢上升,说明电解液的渗透引起了少量腐蚀氧化物的产生。由于涂层中掺杂的阴离子会对腐蚀性阴离子(如Cl-和SO
图6
图6
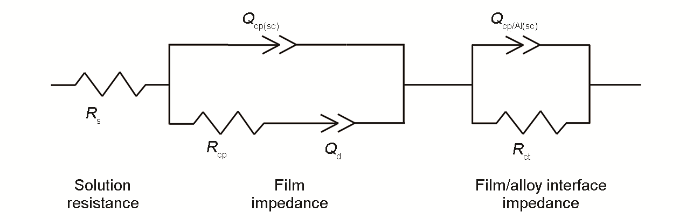
浸泡电极的等效电路图
Fig.6
Equivalent circuit of immersed electrodes (Rs—electrolyte resistance, Qcp(sc)—coating capacitance, Rcp—coating resistance, Qd—diffusion capacitance, Qcp/Al(sc)—interface capacitance of coating and substrate, Rct—charge transfer resistance)
2.2.3 PEDOT涂层腐蚀行为检测
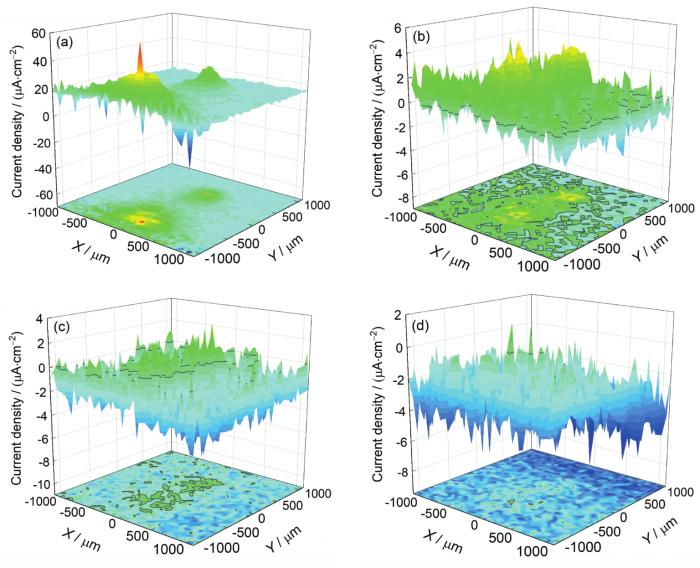
采用SVET方法研究涂层破损后的腐蚀过程。将表面有划痕的PEDOT/2024铝合金电极浸入DHS溶液中,不同浸泡时间的SVET电流密度分布如图7所示。每个图像的中间区域为涂层破损区,四周为涂层区。初始涂层区平均电流密度为15 μA/cm2。浸泡1 h后,涂层区电流密度整体下降,保持在1 μA/cm2左右。浸泡3 h后,涂层区电流密度下降到-1 μA/cm2。浸泡12 h后涂层区电流密度下降到-3 μA/cm2。破损区的初始电流密度最大为60 μA/cm2。浸泡12 h后,破损区电流密度下降到最小为-6 μA/cm2。随着浸泡时间的延长,涂层区和破损区的电流密度同时下降,说明涂层与基底间的钝化膜随着时间延长在不断增加。破损区的阳极电流密度数值和范围明显减小,可能与腐蚀产物的产生和涂层表面的电荷离域有关[26]。腐蚀过程通常需要产生电荷集中,形成局部阳极或阴极区域,产生腐蚀并损坏涂层[27]。由于PEDOT的电导率相对较高,能够促进表面电荷的离域,将静态电位稳定在无源范围内(即在金属-钝化层-电解质界面处产生的开路电位)[28,29],从而有效防止局部阳极或阴极区域的形成,稳定且均匀地抑制表面电化学腐蚀[30]。在浸泡12 h后,破损区变为阴极电流,表明PEDOT涂层在破损区产生了电化学保护效应,这与Yan等[31]研究铝合金表面聚吡咯的耐腐蚀性能结果一致。涂层区的小面积氧化电流密度集中可能是由基底铝合金中Mg的富集所引起。
图7
图7
PEDOT/2024铝合金电极划痕处在DHS溶液中浸泡不同时间的扫描振动电极(SVET)电流密度分布图
Fig.7
Scanning vibrating electrode technique (SVET) current density distribution diagrams on scratched PEDOT/2024 aluminium alloy electrode in DHS solution at 0 h (a), 1 h (b), 3 h (c) and 12 h (d)
Color online
3 结论
以26×10-3 mol/L TBAPF6和0.1 mol/L EDOT的乙腈溶液为电解质,采用恒电流法在2024铝合金基底上制备所得PEDOT涂层完整且致密。涂层表面形貌呈团聚球状颗粒。介质TBAPF6不仅能够钝化2024铝合金基底,减缓溶解,而且还能显著降低EDOT的氧化电位。相比于循环伏安法,恒电流法因无还原过程,可有效减少基底溶解并增加涂层沉积速率。由于表面PEDOT涂层阻隔了腐蚀介质并使基底钝化,PEDOT/2024铝合金电极阻抗模和容抗弧在DHS溶液中浸泡3 d后达到最大。SVET结果表明,涂层破损区电流密度从60 μA/cm2降低到-6 μA/cm2,说明PEDOT涂层能够促进表面电荷离域,有效避免电荷集中并产生电化学保护。因此,PEDOT涂层对2024铝合金基底可以起到良好的防腐蚀作用。
参考文献
Generation of hydrogen by aluminium oxidation in aquaeous solutions at low temperatures
[J].
Atomistic origin of the complex morphological evolution of aluminum nanoparticles during oxidation: A chain-like oxide nucleation and growth mechanism
[J].
Pt-PEDOT/rGO nanocomposites: One-pot preparation and superior electrochemical sensing performance for caffeic acid in tea
[J].
Electrochemical determination of paracetamol based on Au@graphene core-shell nanoparticles doped conducting polymer PEDOT nanocomposite
[J].
Study of poly(3,4-ethylendioxythiphene) as a coating for mitigation of biocorrosion of AISI 304 stainless steel in natural seawater
[J].
Anticorrosion performance of epoxy coatings containing small amount of inherently conducting PEDOT/PSS on hull steel in seawater
[J].
Electrochemical activity and corrosion protection properties of doped polypyrrole electrodeposited at pure aluminium electrode
[J].
Characterization of polypyrrole electropolymerized on different electrodes
[J].
Electrochemical synthesis of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) on stainless steel and its corrosion inhibition performance
[J].
Influence of surface treatment on PEDOT coatings: Surface and electrochemical corrosion aspects of newly developed Ti alloy
[J].
The chemical and electronic structure of the interface between aluminum and conjugated polymers
[J].
Comparative study of n-doping and p-doping of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) electrosynthesised on aluminium
[J].
Electronic properties of junctions between aluminum and doped poly (3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)
[J].
Effect of side chain length on the charge transport, morphology, and photovoltaic performance of conjugated polymers in bulk heterojunction solar cells
[J].
Spectroscopic study on sputtered PEDOT·PSS: Role of surface PSS layer
[J].
Boosting performance of non-fullerene organic solar cells by 2D g-C3N4 doped PEDOT:PSS
[J].
Study on the ClO4 doped PEDOT-PEG in organic solvent using a hole injection layer for PLEDs
[J].
Electrochemical deposition of poly[ethylene-dioxythiophene] (PEDOT) films on ITO electrodes for organic photovoltaic cells: Control of morphology, thickness, and electronic properties
[J].
Fabrication of composite coatings of 4-(pyrrole-1-yl) benzoate-modified poly-3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene with phosphomolybdate and their application in corrosion protection
[J].
Electrodeposition of polypyrrole layers on aluminium from aqueous electrolytes
[J].
Scanning electron microscopy studies of PEDOT prepared by various electrochemical routes
[J].
Conditions to prepare PPy/Al2O3/Al used as a solid-state capacitor from aqueous malic solutions
[J].
Usefulness of aqueous anionic micellar media for electrodeposition of poly-(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) films on iron, mild steel and aluminium
[J].
Characterisation of the aluminium-electropolymerised poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) system
[J].
An electrochemical impedance spectroscopy study of reactions at the metal/coating interface
[J].
Novel scalable synthesis of highly conducting and robust PEDOT paper for a high performance flexible solid supercapacitor
[J].
Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) and its derivatives: Past, present, and future
[J].
Protective properties of hexacyanoferrate containing polypyrrole films on stainless steel
[J].
Tuning the degree of oxidation and electron delocalization of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene):Poly(styrenesulfonate) with solid-electrolyte
[J].
Corrosion protection of aluminum in LiPF6 by poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) nanosphere-coated multiwalled carbon nanotube
[J].
Corrosion control coatings for aluminum alloys based on neutral and n-doped conjugated polymers
[J]. J