FGH4720Li合金也称为P/M Udimet 720Li,是由GH4720Li合金(国外近似牌号为Udimet 720Li)通过粉末冶金生产工艺制备而来的,不但可以解决铸锻态GH4720Li合金在凝固过程中的偏析问题,提高合金化水平,还能够获得细晶组织,进一步改善合金的力学性能[9]。目前,关于热处理对FGH4720Li合金以及GH4720Li合金组织及性能的影响已有较多研究,Radis等[10]研究了固溶处理后冷却速率对GH4720Li合金组织的影响,Wan等[11]研究了固溶温度对GH4720Li合金组织以及室温~750 ℃拉伸性能的影响,Mao等[12]研究了冷却速率对FGH4720Li合金中γ'相尺寸及强化效果的影响。在拉伸蠕变性能方面,黄子琳等[13]分析了GH4720Li合金中晶粒组织与γ'相对高温拉伸性能的协同作用机制,Yuan等[14]研究了在725 ℃、630 MPa蠕变实验前后GH4720Li合金显微组织的变化,Terzi等[15]研究了粗晶状态FGH4720Li合金在不同温度及应力下的蠕变行为。在热变形方面,Zhao等[16]研究了碳化物对均匀态GH4720Li合金热变形和动态再结晶行为的影响,Wang等[17]通过等温压缩实验研究了GH4720Li合金在不同温度和不同应变速率下的热变形行为。在疲劳性能方面,Pang和Reed[18]研究了在650 ℃下GH4720Li合金中微观组织对疲劳裂纹萌生和短裂纹扩展的影响,Tucker等[19]研究了在650和725 ℃下FGH4720Li合金的疲劳裂纹扩展路径及机理。但对于FGH4720Li合金在温度和应力叠加下持久状态的组织和力学性能演变的研究仍鲜有报道。
本工作将标准热处理态的FGH4720Li合金在500 MPa、600和650 ℃进行长达2000 h的持久实验,通过观察不同持久实验条件下γ'相的形貌特征,分析总结γ'相形貌演变的原因及规律,建立近服役条件下合金组织演变与力学性能之间的联系,从而为该合金在实际服役过程中的性能变化提供理论和数据参考,也可为其他镍基难变形高温合金用于涡轮盘的制造提供参考。
1 实验方法
实验材料采用粉末冶金工艺生产的FGH4720Li合金(P/M Udimet 720Li),主要化学成分(质量分数,%)为:Al 2.55,Co 14.75,Cr 15.72,Mo 2.96,Ti 4.82,W 1.3,C 0.016,Ni余量。制备工艺为:Ar气雾化制粉后经热等静压、热挤压及等温锻造成型,热处理制度为:1105 ℃、4 h、油冷 + 650 ℃、24 h、空冷+ 760 ℃、16 h、空冷。
在热处理后的坯料中通过电火花切割取出标距段长度159 mm、直径13 mm的持久试样,之后分别在大气条件下选用RMT-D5型持久蠕变机进行温度为600和650 ℃,应力为500 MPa,时间为500、1000以及2000 h的持久实验;在坯料中切取直径20 mm、长120 mm的圆棒进行650 ℃,时间分别为500、1000以及2000 h的时效处理。在坯料中取出3 mm厚圆片用于热处理后的组织观察。在经650 ℃持久/时效前后的长棒中通过电火花切割取出棒状拉伸试样,选用AG-250KNIC电子万能试验机进行650 ℃下的拉伸实验,分别测试长期持久实验及时效处理后合金的拉伸性能。持久实验完成后在试样中切取3 mm厚圆片用作组织观察。
对切取的组织观察样品分别用水磨砂纸逐级打磨至2000号,每换一道砂纸均垂直于原来方向进行打磨,直至划痕都为同一方向,然后进行机械抛光成镜面,之后做侵蚀处理。电解抛光试剂为20 mL Cr2O3 + 80 mL CH3OH。电解抛光电压为10 V,时间为5 s;电解侵蚀试剂为15 g CrO3 + 10 mL H2SO4 + 150 mL H3PO4,电解侵蚀电压为5 V,时间为3 s。经过电解抛光和电解侵蚀后,使用Supra 55场发射扫描电镜(SEM)观察合金组织中各相形貌。电子背散射衍射(EBSD)试样经机械抛光后,使用20 mL H2SO4 + 80 mL CH3OH溶液进行电解抛光以去除表面的残余应力,通过EBSD系统获取合金晶粒尺寸变化情况,步长0.3 μm,利用HKL Channel 5软件对数据进行分析。通过F200X透射电镜(TEM)观察持久实验后合金中的位错形态,TEM样品制备方法为:在持久实验后的试样上切取厚度0.3 mm的圆形薄片,用砂纸逐渐打磨到厚度50 μm,之后使用5%~10% (质量分数)高氯酸酒精溶液双喷电解。使用Image J软件统计经不同条件持久实验后合金中二次γ′相及三次γ′相的面积分数和等效尺寸,根据体视学原理,将面积分数等同于γ'相的体积分数,每个条件下选取3张以上SEM像进行统计分析。
2 实验结果
2.1 合金初始组织
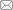
图1
图1
热处理后FGH4720Li合金微观组织的SEM像
Fig.1
SEM images showing the distribution character-istics of different γ' phases in heat treated FGH4720Li powder metallurgy (P/M) superalloy
(a) primary γ' phase
(b) secondary γ' phase
(c) tertiary γ' phase
根据Radis等[10]的研究可知,FGH4720Li合金中形成这3种尺寸不同的γ'相与Al、Ti等γ'相形成元素的不均匀分布有关,这2种元素在过固溶处理后的冷却过程中大量富集在晶界处,因此大尺寸的一次γ'相会优先在晶界上析出,进而使得晶界附近的Al、Ti元素含量较低,相对而言,在远离晶界的晶粒中心位置Al、Ti元素含量较高。随着温度继续下降,晶粒心部Al、Ti元素含量达到过饱和,析出尺寸较大的二次γ'相。随着冷却的进行,晶粒边缘的Al、Ti元素达到γ'相的析出水平,但含量相对心部较少,因此析出尺寸较小的二次γ'相[21]。最后,虽然二次γ'相的析出已使基体中Al、Ti含量大幅降低,但是残余的Al、Ti元素成分依然达到过饱和,在二次γ'相之间和晶界上析出尺寸更小的三次γ'相[22]。
2.2 持久实验过程中的组织演变规律
2.2.1 持久实验过程中一次γ'相及晶粒演变
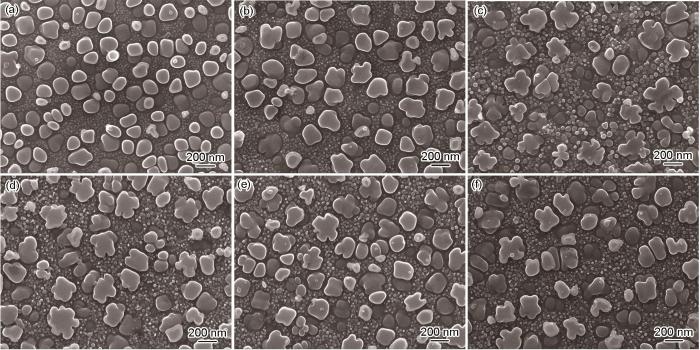
图2
图2
FGH4720Li合金经不同条件持久实验后的EBSD像
Fig.2
EBSD images of FGH4720Li P/M superalloy with inverse pole figure color after stress rupture at 600 oC (a-c) and 650 oC (d-f) for 500 h (a, d), 1000 h (b, e), and 2000 h (c, f)
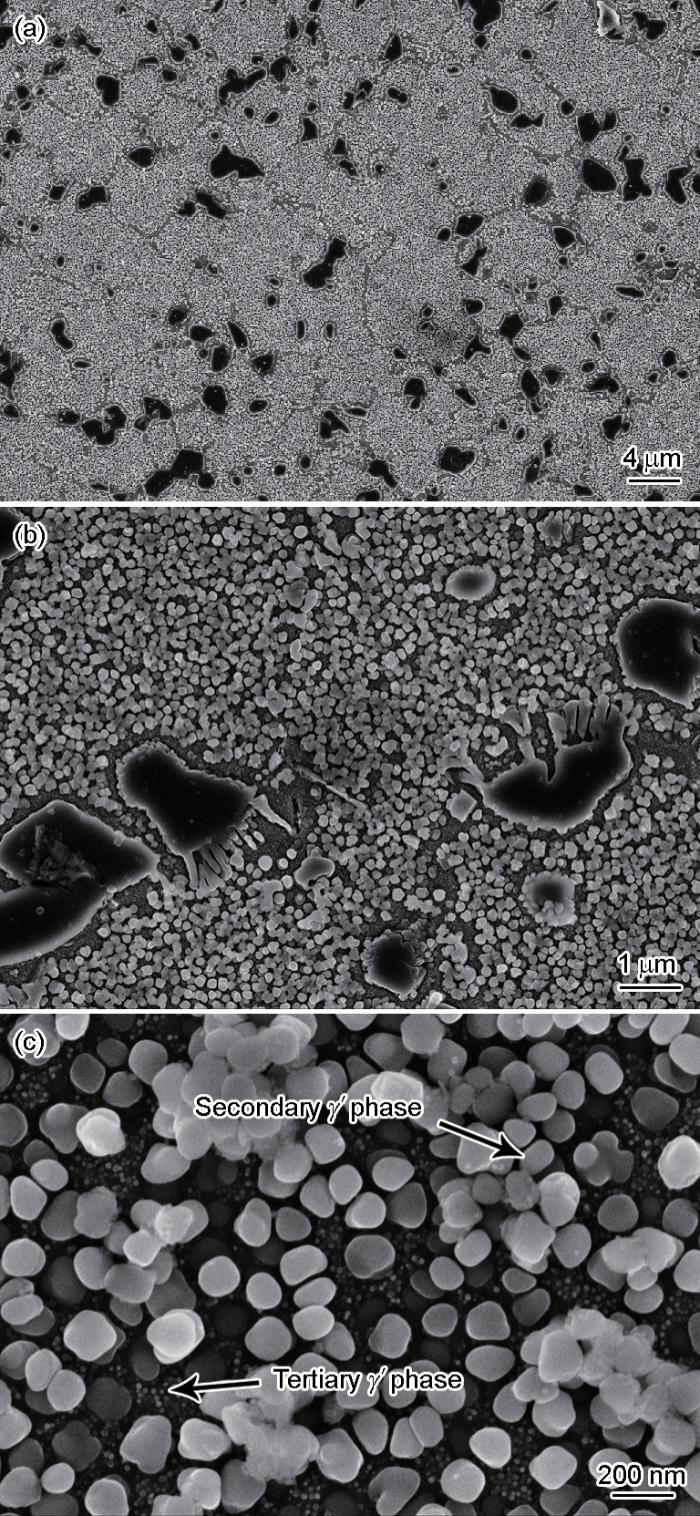
图3
图3
不同条件持久实验后FGH4720Li合金的晶粒尺寸演变
Fig.3
Evolutions of grain size in FGH4720Li P/M superalloy after stress rupture under different conditions
2.2.2 持久实验过程中二次/三次γ'相的演变规律
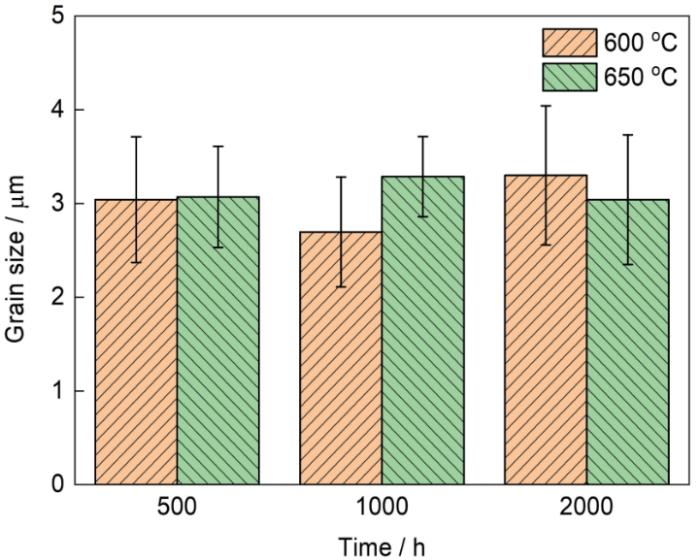
图4
图4
FGH4720Li合金经不同条件持久实验后二次γ'相的SEM像及粒径分布
Fig.4
SEM images and particle size distributions (insets) of secondary γ' phase in FGH4720Li P/M superalloy after stress rupture at 600 oC (a-c) and 650 oC (d-f) for 500 h (a, d), 1000 h (b, e), and 2000 h (c, f)
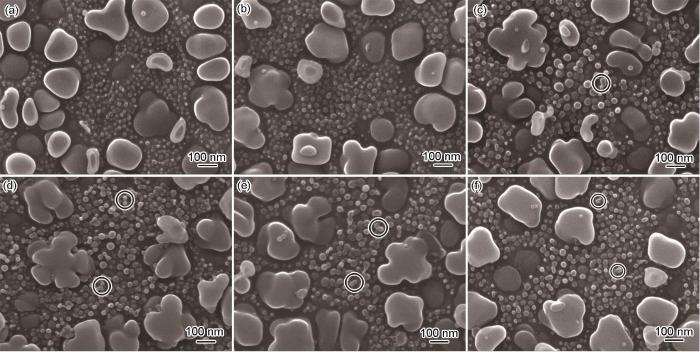
由更高放大倍数的图5可以看出,在500 MPa下,600 ℃持久时间为500 h时,二次γ'相尺寸长大程度较小,仍然保持椭球状形貌(图5a);随着持久时间延长至1000 h时,二次γ'相尺寸进一步增大,数量逐渐减少,有部分形状为椭球状的二次γ'相发展出花瓣状形貌(图5b)。持久时间延长到2000 h时,花瓣状形貌的二次γ'相数量变多,尺寸进一步增大(图5c)。在650 ℃下,持久时间为500 h时就已经有许多二次γ'相生长成为花瓣状(图5d),相比于600 ℃、500 h时的花瓣状形貌特征明显增强;持久时间延长到1000 h时二次γ'相进一步长大,花瓣状的二次γ'相向带圆角的立方状发展(图5e);持久时间延长到2000 h时,大部分二次γ'相发展成为带圆角的立方状(图5f)。这种现象出现的主要原因是Al、Ti等二次γ'相形成元素在二次γ'相不同位置扩散聚集的倾向不同所导致的。当合金中γ基体拥有足够的过饱和度时,二次γ'相凸界面的元素扩散驱动力要比凹界面的扩散驱动力大[23],使得具有凸界面的位置越发向外发展,直至长成花瓣状形貌。而随着持久时间的延长,γ基体中溶质原子的过饱和度降低,之前凸起部分的溶质原子含量较高,凸起部分的溶质元素向凹陷部分扩散,使得花瓣状的二次γ'相生长成为具有圆角的立方体的形貌。
图5
图5
FGH4720Li合金经不同条件持久实验后二次γ'相的高倍SEM像
Fig.5
High magnified SEM images of secondary γ' phase in FGH4720Li P/M superalloy after stress rupture at 600 oC (a-c) and 650 oC (d-f) for 500 h (a, d), 1000 h (b, e), and 2000 h (c, f)
图6为FGH4720Li合金在500 MPa下600和650 ℃持久500、1000和2000 h后三次γ'相的SEM像。可见,在600 ℃持久条件下三次γ'相的尺寸明显增大,在650 ℃持久条件下三次γ'相尺寸变化趋势较小,但其数量相比于600 ℃持久相同时间的数量明显减少。另外可观察到部分呈葫芦状的三次γ'相(图6c~f中圆圈所示),表明在持久实验过程中出现了大尺寸三次γ'相吸收小尺寸三次γ'相的聚合粗化现象,由于并未发现明显的二次γ'相吸收三次γ'相的现象,且已有研究[24,25]证明了三次γ'相在高温时效及持久过程中存在一定程度的溶解,所以三次γ'相的聚合粗化及在基体中溶解是其数量减少的主要原因。刘超等[21]研究表明,FGH4720Li合金在600 ℃时效至3000 h时三次γ'相仍未发生明显变化;而在650 ℃持久3000 h后,三次γ'相出现了明显的长大,进一步说明持久实验中施加的应力促进了溶质原子的扩散,增加了γ'相长大粗化的速率。
图6
图6
FGH4720Li合金经不同条件持久实验后三次γ'相形貌的SEM像
Fig.6
SEM images of tertiary γ' phase in FGH4720Li P/M superalloy after stress rupture at 600 oC (a-c) and 650 oC (d-f) for 500 h (a, d), 1000 h (b, e), and 2000 h (c, f) (Circles in Figs.6c-f show the gourd shaped tertiary γ' phases)
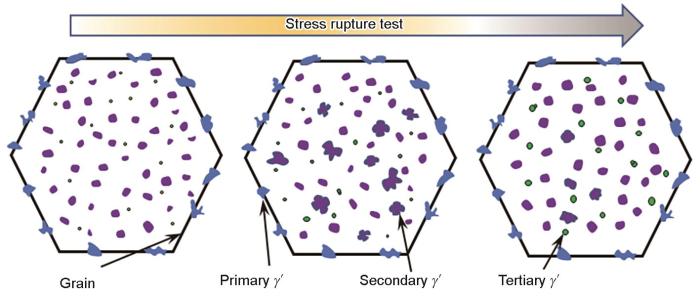
图7为FGH4720Li合金持久实验过程中γ'相的演变示意图。在整个持久实验过程中,随着持久时间的延长,在晶界上存在的一次γ'相的形貌和尺寸并未发生明显的变化,尺寸稳定在3 μm左右。随着持久实验时间延长,二次γ'相的形貌先由椭球形演变为花瓣状,在之后的持久实验过程中,Al、Ti等γ'相形成元素的过饱和度降低,其形貌又逐渐向带圆角的立方状发展,此时基体中仍然存在花瓣状的二次γ'相,主要是由于在持久实验过程中存在一定数量的小尺寸三次γ'相的溶解,维持了基体中部分区域溶质元素的过饱和度导致的。此外,在持久实验过程中,三次γ'相还会以葫芦状聚合生长的方式粗化,以及较小尺寸三次γ'相溶解而较大尺寸三次γ'相长大的方式而粗化。
图7
图7
持久实验过程中FGH4720Li合金晶粒及γ'相形貌演变示意图
Fig.7
Schematic showing the evolution of grain size and γ' phase morphology characteristics in FGH4720Li P/M superalloy during stress rupture
2.2.3 持久实验过程中的位错形态
为了探究持久实验过程中γ'相的演化是否会对合金变形机制产生影响,通过TEM观察FGH4720Li合金在600和650 ℃下持久实验2000 h后的位错形态,结果如图8所示。可见,2种条件下均可以观察到由先导位错(leading dislocation)及尾随位错(trailing dislocation)组成的位错对,在切应力作用下,位错成对切割γ'相粒子,其中尾随位错在同一平面内滑动以去除由先导位错引入γ'相中的反向畴界(APB)。根据Raynor和Silcock[26]的研究,位错对剪切主要分为弱对耦合及强对耦合2种形式,主要的区别在于驱动位错剪切γ'相粒子的弯曲位错的长度,该长度由在γ'相中切割的位错的角度控制。根据TEM像中先导位错的角度及位错对之间的间距(均小于二次γ'相的平均尺寸),可以判断FGH4720Li合金在持久实验过程中主要发生的是强对耦合的位错对切割。
图8
图8
FGH4720Li合金经不同条件持久实验后位错形态的TEM明场像
Fig.8
Bright-field TEM images of FGH4720Li P/M superalloy after stress rupture at 600 oC (a) and 650 oC (b) for 2000 h (ESF—extended stacking fault)
此外,可以在图8a中观察到数量不多的贯穿γ基体及γ'相粒子的连续层错(extended stacking fault,ESF),其形成的主要原因是:由于FGH4720Li合金的基体通道较窄,在持久实验的变形过程中,一些已经完全穿透γ'相粒子的a / 3<121>不全位错并未在γ/γ'界面与a / 6<211>不全位错重新结合,而是迅速移动到基体通道中,再次切割基体通道前端的γ'相粒子[27,28]。值得注意的是,本工作并未观察到明显的位错发生Orowan绕过机制所产生的位错环。这与Goodfellow[29]和Kozar等[30]的结果一致,即在具有高γ'相体积分数的沉淀强化高温合金中很少观察到Orowan绕过机制产生的位错环。研究[31]表明,在具有高体积分数γ'相的镍基高温合金中,即使γ'相粒子的尺寸超过200 nm,位错剪切机制仍然没有被Orowan绕过机制取代,这是因为与不相干和不可变形粒子相比,二次γ'相与基体之间的低晶格失配度及其显著的塑性变形能力导致Orowan绕过机制的临界分切应力(CRSS)高于沉淀剪切引起的CRSS。此外,环绕在γ'相周围的位错(图8b)可能只会在位错切过γ'相粒子前暂时弯曲和堆积,在γ'相粒子周围轻微弯曲的位错有助于降低切过γ'相粒子所需的CRSS[29],一旦施加的应力足够大,这些位错可能会被迫剪切γ'相粒子。
3 持久实验后的拉伸性能
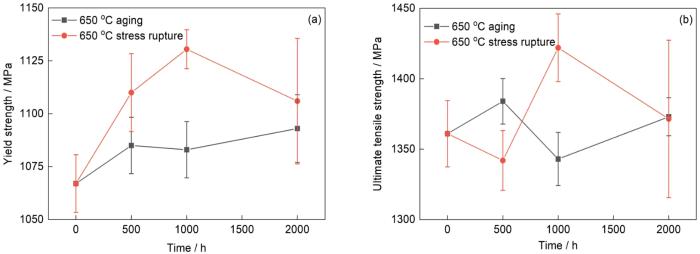
图9
图9
FGH4720Li合金经650 ℃时效和持久实验不同时间后的拉伸性能
Fig.9
Tensile properties of FGH4720Li P/M superalloy at 650 oC after aging and stress rupture at different time
(a) yield strength (b) ultimate tensile strength
表1 FGH4720Li合金持久实验过程中二次γ'相和三次γ'相的平均体积分数及尺寸
Table 1
| Experimental condition | fs % | rs nm | ft % | rt nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 650 oC, 500 h | 33.2 | 104.9 | 3.12 | 12.4 |
| 650 oC, 1000 h | 34.3 | 108.0 | 2.83 | 12.6 |
| 650 oC, 2000 h | 35.9 | 114.9 | 2.27 | 12.9 |
高温合金中屈服强度(σY)可看作是以下4种强化机制的共同贡献[37]:(Ⅰ) 位错切过机制的贡献(σP);(Ⅱ) 固溶强化机制的贡献(σSS );(Ⅲ) 晶界强化机制的贡献(σD);(Ⅳ) 位错绕过机制的贡献(σOro):
σP可以由下式计算[38]:
式中,Nsec和Nter分别为二次γ'相和三次γ'相的数量密度;M为Taylor因子;τp,sec和τp,ter分别是位错切割尺寸为r的二次γ'相粒子和三次γ'相粒子所需要的剪切应力,为计算出其数值,分别根据位错对中先导位错和尾随位错的受力状态可以得到[38]:
式中,τP为适用于所有粒径γ'相的临界分切应力,l1为在γ'相中切割的前导位错的长度,Λ1和Λ2分别为前导位错和尾随位错切入沉淀粒子的距离,FPair为每单位长度位错对之间的作用力。联立
σD可以由Hall-Petch关系得到[42]:σD =
σOro计算公式为σOro = MτOro,τOro为所需要的剪切应力:σOro =
图10
图10
理论计算的FGH4720Li合金经650 ℃不同时间持久实验后的屈服强度与实验值的对比
Fig.10
Comparisons of theoretical calculated and experimental yield strengths of FGH4720Li P/M superalloy after stress rupture at 650 oC for different time
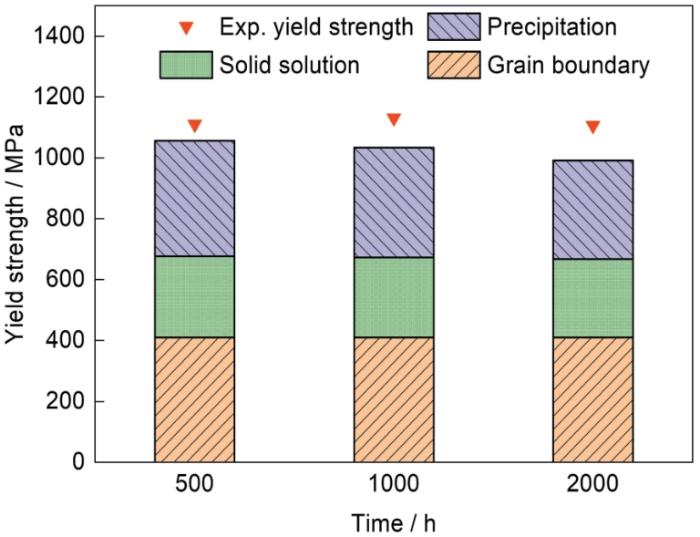
由计算结果可见,预测屈服强度与实验值较为相符,误差均在实验平均值3%内。误差出现的可能原因是:在650 ℃持久实验过程中二次γ'相形貌发生了较为明显的改变,而理论计算所得的等效尺寸可能会对呈球形以外的不同形貌估计不够准确。研究[30,38,42]指出,三次γ'相是沉淀强化高温合金的主要沉淀强化来源,本工作中合金屈服强度变化的主要原因也是三次γ'相的体积分数以及平均尺寸的变化。合金在经650 ℃持久实验不同时间后较未经持久实验合金的屈服强度升高且最终维持在1120 MPa左右,这是由于经持久实验后三次γ'相的平均尺寸明显增加,相比于其初始尺寸,更接近在拉伸实验温度下的弱对耦合与强对耦合发生转变的γ'相粒子尺寸,所以屈服强度会出现一定程度的增加,并且维持在较高水平。在650 ℃下经过1000 h的持久实验后,合金中部分二次γ'相形貌由花瓣状转变为带圆角的立方状,这种演变使其分布变得更为均匀。在此阶段,三次γ'相的体积分数呈降低趋势,但其数量未明显减少,且平均尺寸明显增加,其平均粒子间距并未发生明显变化[45],所以整体上γ'相粒子阻碍位错运动的能力略有提升,屈服强度仍然出现了一定程度的增加。在650 ℃持久2000 h后,作为合金中最重要的强化源的三次γ'相的体积分数进一步减少,粒子间距明显增加,导致屈服强度明显下降。经650 ℃不同时间持久实验后,合金的屈服强度均高于时效相同时间的合金的屈服强度,其主要原因是:在650 ℃时效过程中,二次γ'相的尺寸和含量未出现明显变化,仍然处于形态、尺寸较为不均匀的状态[21],使得合金的二次γ'相对于位错的阻碍能力略低于相同时间持久实验的合金,从而导致时效态合金的屈服强度较低。通过上述定量分析,可以清楚地了解FGH4720Li合金在650 ℃持久实验过程中由于二次和三次γ'相体积分数及尺寸变化对于屈服强度的影响。可以推断,为了保持FGH4720Li合金优异的力学性能,控制合金中三次γ'相的尺寸细小、分布均匀且保持较高的体积分数,是较为可行的举措。
4 结论
(1) FGH4720Li合金在温度为600和650 ℃,应力为500 MPa,时间为500、1000以及2000 h的持久实验中,分布在晶界上的一次γ'相的尺寸及形貌未发生明显变化,晶粒尺寸稳定在3 μm左右,保持了良好的细晶强化作用。
(2) FGH4720Li合金在持久2000 h后出现了位错对剪切γ'相粒子以及不全位错切割γ'相粒子产生的连续层错,未观察到Orowan绕过机制所产生的位错环。
(3) FGH4720Li合金在持久实验过程中,二次γ'相形貌发生了由椭球状转变成花瓣状再转变成圆角立方状的演化,这种形貌的演变主要是由于基体中的Al、Ti等γ'相形成元素在不同过饱和度情况下于二次γ'相附近聚集所导致的。
(4) FGH4720Li合金中的三次γ'相是屈服强度的主要强化来源,650 ℃持久至2000 h时,由于三次γ'相的体积分数显著下降、尺寸明显增大,使合金的屈服强度降低。
参考文献
Effect of tension-torsion coupled loading on the mechanical properties and deformation mechanism of GH4169 superalloys
[J].GH4169 superalloys are used in gas turbine engines and power plants owing to their excellent mechanical properties and corrosion resistance at temperatures exceeding 600oC. Because of their service condition, involving high temperature and complex stress, much attention has been attracted to the effect of temperature and loading mode on the mechanical properties and deformation mechanism. The effect of the loading mode, especially the multiaxial or coupled loading, on the mechanism of plastic deformation is still an outstanding open question despite numerous investigations on the effect of temperature on mechanical properties. In this study, the effect of tension-torsion coupled loading on deformation behavior was investigated, where the microstructures and underlying mechanism were revealed using SEM, TEM, EBSD, and neutron diffraction. It is found that the mechanical properties are dependent on the tension-torsion loading. For the tension specimens, the yield and ultimate strengths increase with the pretorsion angle; for instance, at the pretorsion angle of 720°, the increase rate is approximately 150% and 13%, respectively. At the pretension strain of 20%, the yield strength and elongation increase by approximately 31% and 16%, respectively. The density of dislocations increases in those samples after tensile and torsional deformations compared to the undeformed samples. Moreover, the density of dislocations for specimens deformed under the coupled loading is lower than those deformed under axial loading, indicating the dislocation annihilation effect. The yield strength is enhanced due to the strengthening effect of the initial dislocations produced during the preloading. The ultimate strength for the torsional specimens after pretension decreases because of the dislocation annihilation effect during the subsequent coupled loading. However, for the tensile specimens after pretorsion, such dislocation annihilation effect can be counteracted to some extent by the strengthening effect of the formed gradient structure by pretorsion on mechanical strength. These findings provide some insight into the regulation of the microdeformation mechanism process of materials through designing the coupled or multiaxial loading modes and the coordinated improvement of strength and toughness based on the achievement of gradient or hierarchical microstructure.
拉伸-扭转复合加载对镍基高温合金GH4169力学性能与变形机理的影响
[J].研究镍基高温合金在近服役条件下的力学性能与内在变形机理具有重要意义,但现有研究主要集中于单轴加载下的力学行为,多轴加载相关研究报道较少。为此,本工作对比研究了单轴和复合加载下多晶镍基高温合金GH4169的力学性能变化规律及其微观变形机制差异。在25℃下对多晶镍基高温合金GH4169进行拉伸-扭转复合加载,结合SEM、TEM、EBSD和中子衍射研究了加载方式对其力学性能、微观组织以及变形机理的影响。结果表明,拉伸样品的屈服强度和极限强度均随预扭转角度增加而增大(增幅分别约为150%和13%);在20%预拉应变下,扭转样品的屈服强度和延伸率均有所增加(增幅分别约为31%和16%)。拉伸和扭转变形后样品中的位错密度明显增大;同时复合加载下位错密度相较于单轴加载略小,表明存在位错湮灭效应。预加载产生的位错强化效应提高了屈服强度,而随后复合加载下位错湮灭效应使预拉伸扭转样品的极限强度有所降低。预扭转形成梯度结构的力学强化作用一定程度上抵消了位错湮灭效应的影响。研究表明,多轴加载方式可调控材料微观结构和变形机制,进而实现材料强度和韧性的协调提升。
Impact of aging heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of a newly developed GH4096 disk superalloy
[J].
On some advanced nickel-based superalloys for disk applications
[J].
Effects of solutioning and ageing treatments on properties of Inconel-713C nickel-based superalloy under creep loading
[J].
The effect of long-term thermal exposure on the microstructure and stress rupture property of a directionally solidified Ni-based superalloy
[J].
Heat treatment of UDIMET 720Li: The effect of microstructure on properties
[J].
Tensile properties of three newly developed Ni-base powder metallurgy superalloys
[J].
Prediction of yield strength in a polycrystalline nickel base superalloy during interrupt cooling
[J].
Effect of micron-sized particles on the crack growth behavior of a Ni-based powder metallurgy superalloy
[J].
Multimodal size distributions of γ′ precipitates during continuous cooling of UDIMET 720 Li
[J].
Effect of solution treatment on microstructure and tensile properties of a U720LI Ni-based superalloy
[J].
Cooling precipitation and strengthening study in powder metallurgy superalloy U720LI
[J].
Tensile properties of Ni-based GH4720Li superalloys with different microstructures at 650 oC
[J].
GH4720Li镍基合金显微组织对650 ℃拉伸性能影响
[J].
Creep mechanisms of U720Li disc superalloy at intermediate temperature
[J].
Modelling the plastic deformation during high-temperature creep of a powder-metallurgy coarse-grained superalloy
[J].
Role of carbides on hot deformation behavior and dynamic recrystallization of hard-deformed superalloy U720Li
[J].
Hot deformation behavior and microstructure of U720Li alloy
[J].
Microstructure effects on high temperature fatigue crack initiation and short crack growth in turbine disc nickel-base superalloy Udimet 720Li
[J].
High temperature fatigue crack growth in powder processed nickel based superalloy U720Li
[J].
The feasibility and process control of uniform equiaxed grains by hot deformation in GH4720Li alloy with millimeter-level coarse grains
[J].For nickel-based GH4720Li superalloys, fine-grained structures can be obtained via hot deformation in a two-phase area. However, obvious recrystallized grains' coarsening occurs because of the lack of prime γ' pinning grain boundary when hot deformation occurs in a single-phase area. Much attention is directed to the hot deformation of GH4720Li alloys with fine grains. Moreover, several studies have reported the hot deformation behavior of coarse-grained GH4720Li alloys, with maximum grain sizes of several hundred microns. However, only a few studies report about the hot deformation of GH4720Li alloy with millimeter-level coarse grains. Coarse grains recrystallize incompletely and can reduce the hot deformation plasticity of GH4720Li alloy. Thus, to clarify the coordination feasibility between recrystallization and the hot deformation plasticity of GH4720Li alloy with millimeter-level coarse grains, the hot deformation behavior of GH4720Li alloy with millimeter-level coarse grains was investigated under different deformation parameters (deformation temperature of 1130, 1160, and 1190°C; strain rates of 0.001, 0.01, 0.1, and 1 s-1; and engineering strain of 50%) and compared with the hot deformation behavior of fine-grained GH4720Li alloy. The results show that the GH4720Li sample with millimeter-level coarse grains is more sensitive to the deformation temperature, but the fine-grained GH4720Li alloy is more sensitive to strain rate. The completely recrystallized structure of the GH4720Li sample with millimeter-level coarse grains can be obtained in the range of 1160-1190°C and 0.001-0.01 s-1. However, a meager strain rate can cause an undesirable and obvious grain growth. After comprehensively combining the recrystallization control range and the hot deformation plasticity of millimeter-level coarse-grained GH4720Li alloy, it was found that the millimeter-level coarse-grained GH4720Li alloy should be thermally deformed at a moderate deformation temperature and a reduced strain rate of 1160oC and 0.01 s-1, respectively, to obtain the uniform equiaxed grains structure without cracking, and better deformation.
GH4720Li合金毫米级粗大晶粒热变形获得均匀等轴晶粒的可行性及工艺控制
[J].
Microstructure evolution behavior of powder superalloy FGH4720Li at near service temperature
[J].GH4720Li is used for turbine disks in a large number of civil and military propulsion systems because of its excellent mechanical properties and corrosion resistance. GH4720Li turbine disk is mainly manufactured through cast and wrought conventionally, but the addition of a high mass fraction of Ti, Al, and Mo can cause severe element segregation and more difficult microstructure control, which can become more severe as the turbine disk gets larger. Owing to this difficulty, the turbine disk quality cannot be guaranteed if the GH4720Li turbine disk is still in cast and wrought form, and the manufacturing process will be more complex, resulting in increased costs. However, the powder metallurgy method can efficiently eliminate element segregation and produce a more uniform microstructure than the cast and wrought methods. GH4720Li alloys manufactured using the powder metallurgy method are called FGH4720Li alloys. As there has been limited research on FGH4720Li and no report on the microstructure evolution during long-term ageing for FGH4720Li to date, it is necessary to study the microstructure evolution behavior during long-term ageing for FGH4720Li to obtain improved microstructure stability. In this study, field emission scanning electron microscopy and extractive phase analysis were used to investigate the microstructure evolution of FGH4720Li in the temperature range of 600-730oC up to 3000 h. The results showed that primary gamma prime was the most stable; whereas, secondary and tertiary gamma prime microstructure evolutions were comparatively complex. At 600oC, there was no microstructure change. At 650oC, only the tertiary gamma prime grew, but there was no microstructure change for the other gamma primes up to 3000 h. When the ageing temperature increased to 730oC, the tertiary gamma prime grew faster before coarsening rapidly. After 200 h, the secondary gamma prime coarsened noticeably, but the big secondary gamma prime coarsened by Ostwald ripening first, absorbing a large amount of tertiary gamma prime and splitting up between 300 and 500 h, before ageing with further processing. Big secondary gamma prime mainly coarsens by amalgamation; whereas, small secondary gamma prime always coarsens by amalgamation during ageing. The divergence between these two types of secondary gamma prime is related to the distribution characteristics of the tertiary gamma prime.
粉末高温合金FGH4720Li在近服役温度下的组织演变规律
[J].
Influence of the initial cooling rate from γ′ supersolvus temperatures on microstructure and phase compositions in a nickel superalloy
[J].
Morphological instability of γ′ phase in nickel-based powder metallurgy superalloys
[J].
镍基粉末冶金高温合金中γ′相形态不稳定性研究
[J].较系统地研究了低错配度FGH98I和FGH96合金在热处理条件下γ'相的形态演化行为. 结果表明: γ'相的形态失稳形式可归纳为γ'相分裂和γ'相不稳定长出形态, γ'相分裂主要是γ/γ'相间弹性应变场的各向异性和溶质元素富集相互作用造成, 而形状不规则的不稳定长出形态主要是由于基体或晶界局部溶质原子浓度(或过饱和度)变化导致γ'相的非平衡性生长, 讨论了γ'相分裂和不稳定长出形态同时发生现象, 及不连续脱溶析出导致扇形结构的形成机理.
Microstructural evolution and stress rupture behaviour of a Ni-Based wrought superalloy during thermal exposure
[J].
Influence of tertiary gamma prime (γ′) size evolution on dwell fatigue crack growth behavior in CG RR1000
[J].
Strengthening mechanisms in γ′ precipitating alloys
[J].
The role of <112> {111} slip in the initial plastic deformation of Ni-base superalloys at room temperature
[J].
Tensile deformation behavior of a new Ni-base superalloy at room temperature
[J].
Strengthening mechanisms in polycrystalline nickel-based superalloys
[J].
Strengthening mechanisms in polycrystalline multimodal nickel-base superalloys
[J].
Precipitation hardening of superalloys by ordered γ′-particles
[J].
Microstructure and property stability of powder metallurgy nickel-based U720Li superalloy during long-term aging
[J].
Gamma prime phase evolution during long-time exposure for GH738 superalloy
[J].
GH738高温合金长期时效过程中γ′相演变规律
[J].
Influence of grain size and heat treatment on the microstructure and mechanical properties of the nickel-base superalloy U 720 LI
[J].
Strengthening mechanisms of carbon in modified nickel-based superalloy Nimonic 80A
[J].
Effect of cooling rate and resulting microstructure on tensile properties and deformation mechanisms of an advanced PM nickel-based superalloy
[J].
Factors contributing to the strength of a polycrystalline nickel-cobalt base superalloy
[J].
On the prediction of the yield stress of unimodal and multimodal γ′ nickel-base superalloys
[J].
On the critical resolved shear stress of solid solutions containing coherent precipitates
[J].
Yield strength prediction in Ni-base alloy 718Plus based on thermo-kinetic precipitation simulation
[J].
Physics and phenomenology of strain hardening: The FCC case
[J].
Tailoring of nanoscale γ′ precipitates and unveiling their strengthening mechanisms in multimodal nickel-based superalloy GH4720Li
[J].
A statistical theory of solid solution hardening
[J].
Multi-component solid solution hardening: part 2 Agreement with experimental results
[J].
Some new aspects concerning particle hardening mechanisms in γ′ precipitating nickel-base alloys—II. Experiments
[J].