高性能的单晶涡轮叶片是先进航空发动机实现高推重比的最关键热端部件,单晶高温合金具有优良的高温蠕变性能、良好的组织稳定性和抗氧化能力,成为制造先进涡轮叶片的首选材料。因此,研制高性能的单晶高温合金对于提高航空发动机的性能具有至关重要的作用。
目前单晶高温合金已发展至第五代,其中第四和第五代单晶高温合金在添加6%Re (质量分数,下同)的基础上又加入了稀贵元素Ru,与含6%Re的第三代单晶高温合金相比,其承温能力的提高幅度越来越小,而成本却仍在显著增加[1~4]。与第三代单晶高温合金相比,第四代单晶高温合金在137 MPa下持久寿命为100 h,承温能力提高约20℃,但第四代单晶高温合金的母合金成本比第三代单晶高温合金约增加150万元/吨。例如法国在2000年研制出了含4%Re和4%Ru的第四代单晶高温合金MC-NG[5],但在2020年又研制了含4.9%Re的第三代单晶高温合金AGAT[6],最重要的原因就是出于成本的考虑。因此,第三代单晶高温合金因性价比突出成为最具应用前景的高性能涡轮叶片用合金材料,国内外已在第三代单晶高温合金研制方面开展了大量研究工作[7~10]。
第三代单晶高温合金的标志性特征是含有6%Re,在定向凝固过程中Re元素通常偏聚于枝晶干[11,12],由于Re是Ni基体中扩散速率最慢的元素,凝固过程中形成的偏聚难以通过热处理完全消除,如CMSX-10合金在经过多达10个固溶温度阶梯总时长达100 h的热处理后,仍然在1050℃、1000 h长期时效后开始析出拓扑密排相(TCP相),且随着时效时间延长TCP相的数量逐渐增多[13]。因此,为抑制第三代单晶高温合金析出TCP相,必须进行成分调整和工艺优化。一般说来,单晶高温合金设计面对的主要问题是提高合金的高温蠕变性能,合金的中温力学性能可以很容易地满足涡轮叶片设计的性能要求。但第三代单晶高温合金存在一个不可忽视的问题,即相对于其他代次的合金,第三代单晶高温合金的中温蠕变性能显著偏低。Diologent和Caron[14]研究表明,不含Re的第一代单晶高温合金AM1在760℃、840 MPa下的蠕变寿命为164.9 h,含5.4%Re的第三代单晶高温合金René N6在相同条件下的蠕变寿命仅为70 h。因此,中温蠕变性能成为第三代单晶高温合金安全使用的关键制约因素,即第三代单晶高温合金的研制除了要考虑单晶合金通常的高温强度、组织稳定性和抗氧化性3方面性能的平衡外,还需兼顾中、高温蠕变性能平衡的特殊问题。
本工作在初步确定的第三代单晶高温合金成分基础上,针对合金长期时效时析出少量TCP相和中温强度偏低2个问题,通过少量调整Al含量,完全抑制了TCP相的析出,再通过优化Re和Co的含量,显著提高了合金的中温蠕变性能,并通过组织观察分析了相关机理,在此基础上研制出了一种中/高温性能平衡的第三代单晶高温合金。
1 实验方法
在初步确定的第三代单晶高温合金的成分基础上,针对合金析出少量TCP相和中温性能偏低的问题,首先通过电子空位数计算和热力学计算,选定对合金组织稳定性影响最显著的元素,在此基础上少量调整该元素的含量,以达到抑制TCP相的析出但不影响合金其他性能的目的。然后按照调整后的成分采用真空感应炉熔炼母合金锭,将母合金锭在ZGD-15双区加热定向凝固炉中采用Bridgman法拉制成单晶棒,将单晶棒完全热处理后,在1100℃下分别时效至100和1000 h,金相样品采用5 g CuSO4 + 20 mL HCl + 80 mL H2O溶液腐蚀,利用S-3400N扫描电镜(SEM)观察时效后的显微组织,分析成分调整对组织稳定性的影响。在改善组织稳定性的基础上进一步优化其他元素的含量,以便提高合金的中温性能。根据同样的过程制成单晶棒后,在热处理后加工成标距段为直径5 mm、长25 mm的蠕变试样,在760℃、800 MPa下测定合金的蠕变性能,验证成分优化对合金中温性能的影响。在同样的加载条件下蠕变1 h中断实验,在试样的横截面内切取薄片,机械减薄后在10%HClO4 + 90%C2H5OH (体积分数)电解液中双喷减薄制成透射电镜(TEM)样品,电解条件为-25℃,电压为25~40 V,然后利用JEM-2100F TEM观察位错组态,分析成分优化对合金中温变形机理的影响。
2 实验结果
2.1 组织稳定性的改善
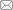
本工作第三代单晶高温合金的设计思路为:合金性能首先满足高温强度和抗氧化性能,同时兼顾组织稳定性,然后根据性能特点调整合金成分。合金化措施包括降低Cr含量以添加更多的W、Re、Ta,从而提高强化水平;提高Co含量以促进成分均匀化,抑制TCP相的析出;加入高含量的Al和低含量的Mo以增强合金的抗氧化能力。从而初步选定了合金的初始成分(质量分数)为:Co 12%,Al 6.1%,Cr + W + Mo 11%,Ta 8%,Re 5%,Hf 0.1%,Ni余量。采用金相法测定合金的初熔温度,然后根据初熔温度确定了合金的热处理工艺为:1325℃、16 h + 1335℃、16 h +空冷,1150℃、4 h +空冷,870℃、24 h +空冷。合金具有优异的高温强度,在1120℃、135 MPa的持久寿命达到100 h,但该成分合金的中温持久性能偏低,在760℃、800 MPa的持久寿命仅为40 h左右。合金在1100℃长期时效100 h后在枝晶干区域析出少量的TCP相,在时效1000 h后TCP数量有所增加,尺寸明显增大,如图1所示。
图1
图1
初始成分单晶高温合金在1100℃长期时效100和1000 h后微观组织的SEM像
Fig.1
SEM images of single crystal superalloy with original composition after 1100oC thermal exposure for 100 h (a) and 1000 h (b) (TCP—topologically close-packed)
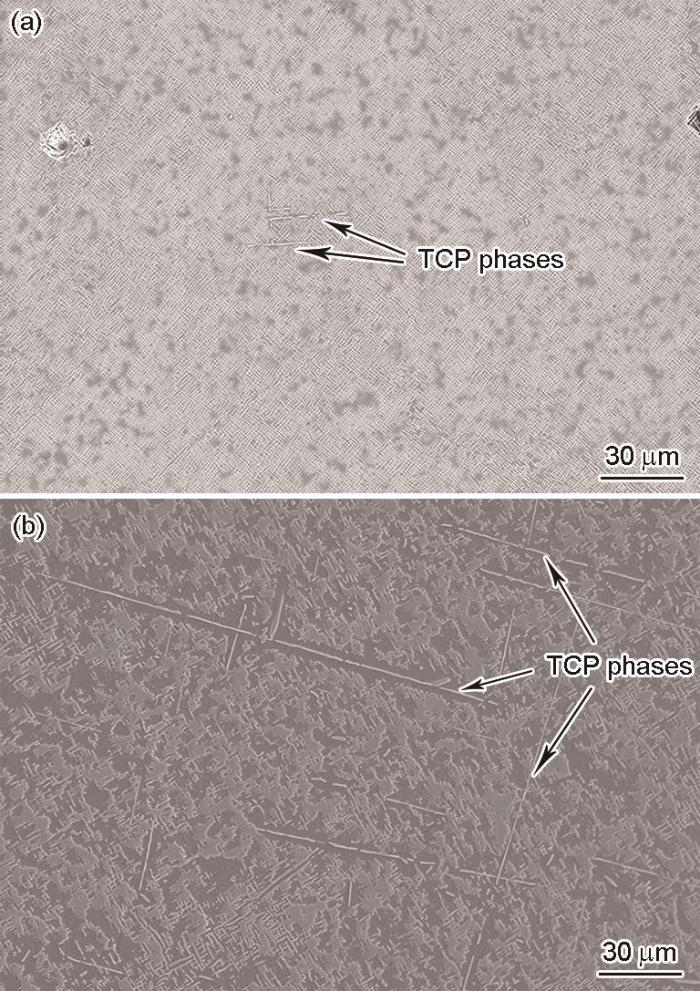
高温合金中析出TCP相的部分原因是由于残余的枝晶偏析,也有合金组织稳定性不足的内在原因[15]。为保证合金的长期安全使用,必须改善合金的组织稳定性。研究[16]认为,σ相、μ相等TCP相是由3d电子空位形成的化学键结合而成的,因而合金的电子空位数(Nv)可用于预测合金析出TCP相的倾向。为提高合金的组织稳定性,首先需要确定对合金TCP相析出倾向影响最大的元素,因此计算了在初始成分基础上将元素含量分别降低0.1% (质量分数,下同)后的Nv变化量(ΔNv),结果如图2所示。可见,Al含量降低0.1%后,Nv的降低幅度最大,即Al是改善合金组织稳定性效果最显著的元素,因此抑制TCP相最有效的成分调整方案是少量降低Al元素的含量。为了尽量减小对合金其他性能的影响,本工作采用的方案为将Al含量降低0.4%,预期可明显改善合金的组织稳定性。
图2
图2
各元素含量分别降低0.1%时电子空位数的变化量(ΔNv)
Fig.2
Variation of number of electron vacancy (ΔNv) with 0.1% reduction of each element
表1 Al和Re含量分别降低0.4%时合金中各组成相的含量与初始成分的对比 (%)
Table 1
| Alloy | γ' phase | γ phase | μ phase |
|---|---|---|---|
| Original composition | 58.28 | 35.91 | 5.80 |
| Al content reduction 0.4% | 52.25 | 42.89 | 4.86 |
| Re content reduction 0.4% | 58.25 | 36.60 | 5.15 |
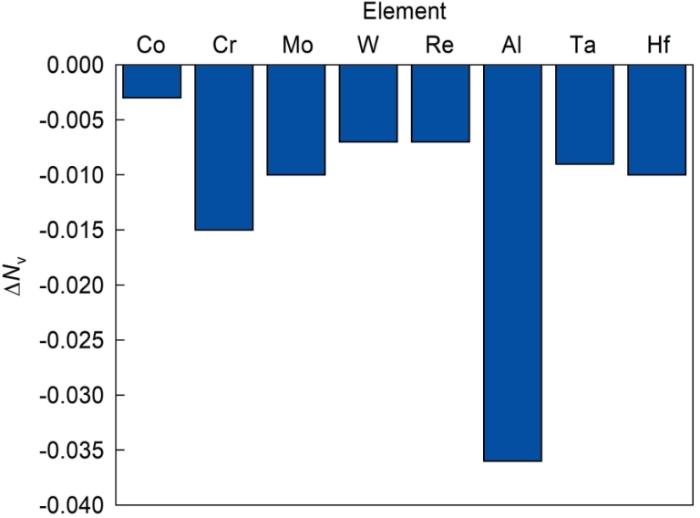
依据预测结果,按照成分调整方案,制备了Al含量降低0.4%的单晶高温合金,将合金进行完全热处理后,在1100℃长期时效至1000 h,合金中无TCP相析出,如图3所示。表明少量降低Al含量完全抑制了TCP相的析出,显著改善了合金的组织稳定性。同时合金的高温和中温性能未发生变化,即合金仍然保持优越的高温性能,但中温性能仍然偏低。
图3
图3
Al含量降低0.4%后的合金在1100℃长期时效100和1000 h后微观组织的SEM二次电子像
Fig.3
SEM-SE images of single crystal superalloy with 0.4% reduction of Al after 1100oC thermal exposure for 100 h (a) and 1000 h (b)
2.2 中温性能的提高
为了改善合金的中温性能,必须在少量降低Al含量的基础上,进一步优化合金成分,以实现合金中/高温性能平衡的目标。根据Rae等[18]的研究结果,单晶高温合金的中温变形过程与基体位错分解产生的超Shockley位错切入γ'相并形成层错有关,层错能是超Shockley位错切入γ'相的阻力,因此,要提高合金的中温持久寿命,关键在于通过调整合金的成分增大合金的层错能,从而增加中温变形阻力并延长中温持久寿命。
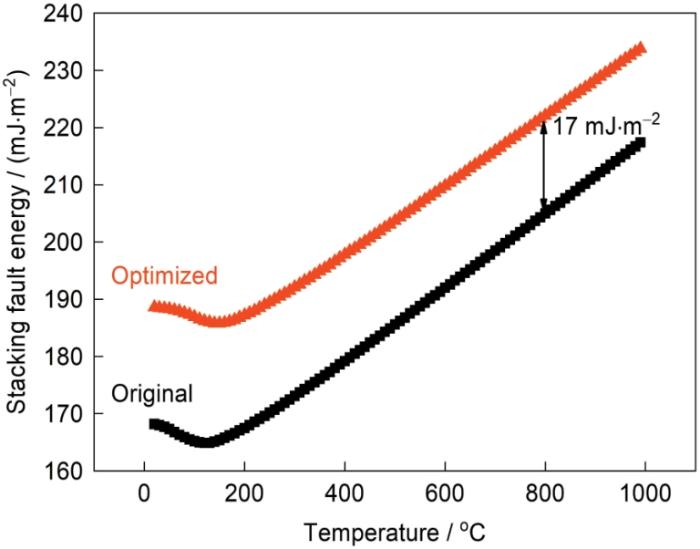
根据Ma等[19]和Kumar等[20]的研究结果,降低Co和Re含量虽然可增大γ'相的层错能,却是增大效果较弱的元素。虽然这2种元素主要分布在γ基体中,但在γ'相中也有一定分布。因此,进一步的合金成分调整方案为少量降低Co和Re的含量以增加合金的层错能,采用JMatPro热力学软件可简单计算合金的层错能,其计算依据为:认为层错是一薄层hcp相,层错能即fcc相转变为hcp相的自由能之差,根据热力学数据计算相变自由能之差即为层错能。Co和Re含量分别降低1%和0.25%后合金在不同温度的层错能与初始成分合金的层错能对比如图4所示。可见,在100~1000℃之间,2种成分合金的层错能均随着温度的升高而增大,且2种合金的层错能差值基本保持不变,在800℃中温条件下的层错能之差约为17 mJ/m2,即少量降低Co和Re含量可明显增加合金的层错能,对合金的中温性能产生有益的影响。
图4
图4
优化成分与初始成分合金不同温度下层错能的热力学计算结果
Fig.4
Calculation results of stacking fault energies of single crystal superalloys with original and optimized compositions
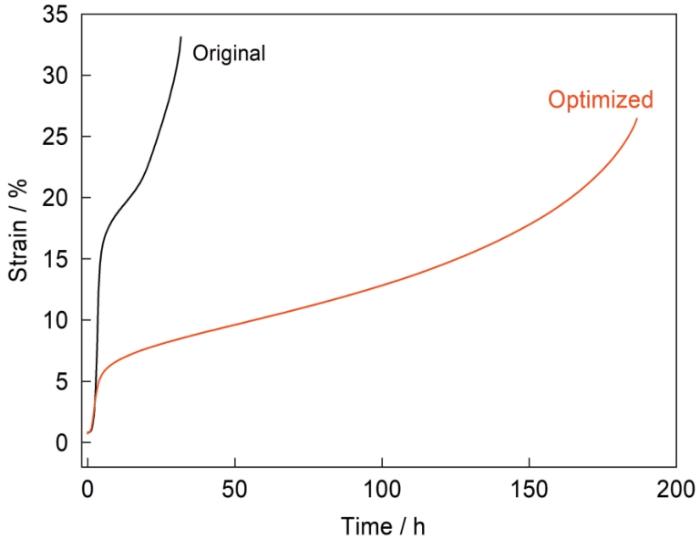
将初始合金及Co和Re含量分别降低1%和0.25%的单晶高温合金进行完全热处理后,在760℃、800 MPa条件下测定了合金的蠕变性能,蠕变曲线如图5所示。可见,初始成分的合金在760℃、800 MPa条件下的持久寿命约40 h,且蠕变第一阶段的变形量非常大,第一阶段结束时总应变约为15%。优化成分合金的蠕变寿命可达到150 h,且蠕变第一阶段的变形量显著降低,总应变约为5%。可见,成分调整显著改善了合金的中温性能。且合金在1120℃、135 MPa下的高温持久寿命仍可达到100 h。
图5
图5
初始成分与优化成分合金在760℃、800 MPa条件下的蠕变曲线
Fig.5
Creep curves under 760oC and 800 MPa of single crystal superalloys with original and optimized compositions
根据上述实验结果,将Al含量降低0.4%,Co和Re含量分别降低1%和0.25%确定为合金最佳成分。
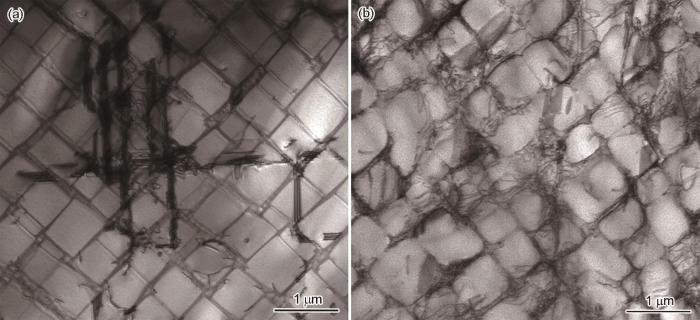
为了探明成分调整改善合金中温性能的机理,进行了760℃、800 MPa持续时间1 h的持久中断实验,初始成分与优化成分合金试样横截面内位错组态的TEM像如图6所示。可见,初始成分合金中位错分布非常集中,形成应变集中的滑移带,滑移带间的区域位错密度非常低,且有一个滑移带占主导地位,更重要的是γ'相形成大量层错,即位错切入γ'相是其主要的变形机制。而优化成分的合金中,位错在样品中分布均匀,且主要分布γ基体中,在γ'相中形成的层错数量极少,即位错在基体通道中弓出是其主要的变形机制。
图6
图6
初始成分与优化成分合金在760℃、800 MPa条件下蠕变1 h后位错组态的TEM像
Fig.6
TEM images showing dislocation configurations of single crystal superalloys with original (a) and optimized (b) compositions crept at 760oC and 800 MPa for 1 h (The incident beam along [001] orientation)
3 分析讨论
3.1 抑制TCP相析出的原因
研究[21,22]表明,当合金中难熔元素含量过高时,γ相中的难熔元素处于过饱和状态,在一定温度下保温时,TCP相即从γ相中形核析出。难熔元素的过饱和度越高,析出TCP相所需的时间越短而析出数量越多。由于第三代单晶高温合金中加入了较多的难熔元素,即使经过了长时间的固溶处理,也难以使合金成分完全均匀化,即使理想平衡态具有组织稳定性的合金也可能因为残余的枝晶偏析而析出少量TCP相。本研究的初始成分合金经过总计32 h的高温固溶处理,长期时效后仍然析出少量TCP相,只能通过成分调整来改善TCP相析出。抑制TCP相析出的直接途径就是降低TCP相主要形成元素Re含量,但ΔNv计算值和热力学计算表明,降低Al含量的间接途径抑制效果更为显著,根据热力学计算的相含量结果,通过Re含量与γ相质量分数的比值近似表征基体中的Re含量,可知Al含量降低0.4%后基体的Re含量为11.6%,而Re含量降低0.4%后基体的Re含量为13.0%,即在初始成分中降低同样质量分数的Al元素,可使γ'相含量减少,γ相含量增加,间接降低Re等TCP相形成元素的过饱和度,比直接降低Re含量更有利于抑制TCP相的析出。Al含量降低0.4%后的长期时效实验结果表明,在析出少量TCP相的合金中可通过少量降低Al的含量,抑制TCP相析出而改善合金的组织稳定性。
3.2 中温性能的影响因素
式中,G为剪切模量,ν为Poisson比,b为Burgers矢量模,d为γ'粒子的平均直径,ΓSF为γ'相层错能。可见,层错能越大,切入阻力也越大。通过降低Re和Co的含量,可使更有利于提高γ'相层错能的元素Mo、W、Ta等进入γ'相,从而增大了γ'的层错能,最终增大了1/3〈112〉位错切入γ'相的阻力,所以少量降低Re和Co含量可提高合金中温持久寿命。合金的层错能热力学计算结果表明成分优化后合金的层错能提高,且优化成分合金的实测持久寿命与预期结果相符,证实了成分优化方案的有效性。
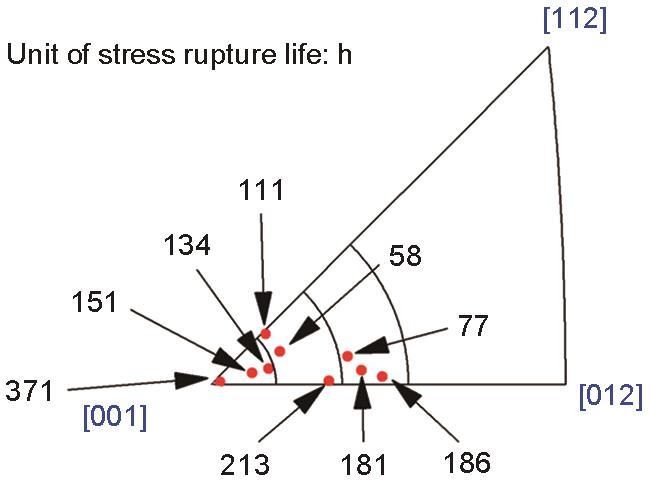
在760℃、800 MPa条件测定的多个试样的持久寿命呈现出明显的分散性,经过测定试样轴向的晶体取向,结果表明合金中温持久寿命与晶体取向密切相关,如图7所示(为反极图三角形的一部分),当样品轴向偏离[001]晶向的偏差角增大时,合金持久寿命显著降低。而且当偏差角相同时,合金持久寿命还受到偏离[001]-[011]边界的方位角的影响,当方位角越大即轴向投影点越靠近[001]-[111]边界时,合金持久寿命越低。
图7
图7
优化成分合金760℃、800 MPa的持久寿命与试样轴向取向的关系
Fig.7
Relation between stress rupture lives and orientations under 760oC and 800 MPa with optimized composition (Numbers denote the lives of corresponding dots in graph, the three arcs correspond to deviation angles 5°、10°, and 15°, respectively )
在本工作的试样取向所在的范围内(图7的取向三角形内),[001]-[111]边界为{111}<112>滑移系的单滑移区,[001]-[011]边界为{111}<112>滑移系的双滑移区。在蠕变过程中,由于晶格转动,试样的轴向投影点由初始位置向着双滑移区[001]-[011]边界移动,当达到或者非常接近此边界时次滑移系启动,与主滑移系交截产生硬化作用因而进入蠕变第二阶段。靠近[001]-[011]边界的试样达到双滑移区所需的晶格转动角度较小,因而更早进入蠕变第二阶段,此时第一阶段产生的应变更小因而有效应力更低,所以蠕变寿命更长。反之,取向靠近[001]-[111]边界的试样,需要更大的晶格转动角度才能启动次滑移系,两滑移系交截产生硬化作用,进入蠕变第二阶段时的应变更大,有效应力也更高,所以蠕变寿命更低[29]。
4 结论
(1) 电子空位数变化量计算表明,降低Al元素含量使单晶高温合金电子空位数降低的幅度最大,即Al是提高合金组织稳定性最有效的元素。Al含量降低0.4%可使合金在1100℃、1000 h长期时效后无TCP相析出。
(2) 降低Al元素含量改善单晶高温合金组织稳定性的原因是,Al含量的降低可增加γ相的体积分数,间接降低了TCP相形成元素在基体中的过饱和度,因而抑制了TCP相的析出。
(3) 在Al含量降低0.4%的基础上,通过将Re和Co含量分别降低0.25%和1%,可显著提高单晶高温合金在760℃、800 MPa中温条件下的持久寿命,原因在于增大了γ'相的层错能从而提高了1/3<112>位错切入γ'相的阻力。
(4) 单晶高温合金的中温持久寿命受到样品轴向晶体取向的显著影响,当样品轴向偏离[001]晶向相同偏差角时,投影点越靠近[001]-[011]边界时合金寿命越长,越靠近[001]-[111]边界时合金寿命越短。
参考文献
Joint development of a fourth generation single crystal superalloy
[A].
A 5th generation SC superalloy with balanced high temperature properties and processability
[A].
The development and application of CMSX®-10
[A].
René N6: Third generation single crystal superalloy
[A].
MC-NG: A 4th generation single-crystal superalloy for future aeronautical turbine blades and vanes
[A].
Development of AGAT, a third-generation nickel-based superalloy for single crystal turbine blade applications
[A].
Improvement of creep strength of a third generation, single-crystal Ni-base superalloy by solution heat treatment
[J].
Thermomechanical fatigue behavior of the third-generation, single-crystal superalloy TMS-75: Deformation structure
[J].
Third generation single crystal superalloy DD9
[J].
第三代单晶高温合金DD9
[J].
Microstructure and properties of third generation single crystal superalloy WZ30
[J].
一种新型第三代单晶高温合金WZ30组织与性能的研究
[J].
Segregation of elements in high refractory content single crystal nickel based superalloys
[A].
The effects of Re, W and Ru on microsegregation behaviour in single crystal superalloy systems
[A].
Solution heat treatment response of a third generation single crystal Ni-base superalloy
[J].
On the creep behavior at 1033K of new generation single-crystal superalloys
[J].
Formation and effect of topologically close-packed phases in nickel-base superalloys
[J].
TCP phase predictions in Ni-based superalloys: Structure maps revisited
[J].
Determination of γ/γ' lattice misfit in Ni-based single-crystal superalloys at high temperatures by neutron diffraction
[J].
The role of stacking fault shear in the primary creep of [001]-oriented single crystal superalloys at 750oC and 750 MPa
[J].
Development of γ phase stacking faults during high temperature creep of Ru-containing single crystal superalloys
[J].
Tuning planar fault energies of Ni3Al with substitutional alloying: First-principles description for guiding rational alloy design
[J].
Effect of minor additions on the formation of TCP phases in modified RR2086 SX superalloys
[J].
In situ TEM investigation on the precipitation behavior of μ phase in Ni-base single crystal superalloys
[J].
Superlattice intrinsic stacking faults in γ′ precipitates
[J].
The mechanisms and temperature dependence of superlattice stacking fault formation in the single-crystal superalloy PWA 1480
[J].
Superlattice stacking fault formation and twinning during creep in γ/γ' single crystal superalloy CMSX-4
[J].
Anisotropic creep in CMSX-4 in orientations distant from 〈001〉
[J].
Effects of sand blasting on surface integrity and high cycle fatigue properties of DD6 single crystal superalloy
[J].DD6 is a second generation single crystal superalloy independently developed in China, which offers advantages such as high-temperature strength, stable structure, and satisfactory casting process performance. Currently, it is being widely used in development of aviation engine turbine blades. Sand blasting can be performed for surface cleaning and adjusting surface roughness of single crystal turbine blades and is an essential process in manufacturing of single crystal blades. Although sand blasting has been widely used in the manufacturing process of DD6 alloy turbine blades, only few reports studied the impact of sand blasting on the surface integrity and fatigue performance of DD6 alloy. Therefore, research is required to provide a theoretical basis for the safe service of DD6 alloy turbine blades. In this work, several specimens after a standard heat treatment are blasted with white corundum sand with 150, 124, and 100 μm diameters at 0.5 MPa to study the effect of sand blasting on the surface integrity of DD6 alloy; the rotary bending high cycle fatigue properties of the specimens without and with sand blasting (blasting with white corundum sand with 150 μm diameter) were tested at 760 and 980oC, respectively, to study the effect of sand blasting on the alloy's fatigue property. The results show that sand blasting destroys the surface integrity of the single crystal superalloy, resulting in irregular pits on the surface caused by the cutting by sand particles while changing the surface morphology as well; the surface roughness and microhardness increase with sand particle size increase; after sand blasting, many dislocations slip in the γ phase, and the dislocation density near the surface is high. Additionally, many dislocations shear the γ′ phase, forming antiphase domain boundaries and stacking faults; sand blasting results in deformation strengthening and residual stress; blasting with 150 μm diameter sand at 0.5 MPa has a small effect on the rotary bending high cycle fatigue properties of DD6 alloy at 760oC, but it considerably reduces the alloy's fatigue properties at 980oC in the low stress amplitude region, decreasing the fatigue strength of the alloy by 7.3%. The combined action of the notch effect, oxidation damage, deformation strengthening, and residual compressive stress leads to the changes in fatigue life without and with sand blasting.
吹砂对DD6单晶高温合金表面完整性和高周疲劳强度的影响
[J].将标准热处理的试样分别采用粒径为150、124和100 μm白刚玉砂在0.5 MPa压力下吹砂,研究吹砂对第二代单晶高温合金DD6表面完整性的影响;对未吹砂和粒径150 μm吹砂试样分别进行760和980℃旋转弯曲高周疲劳性能测试,研究吹砂对DD6合金疲劳性能的影响。结果表明:吹砂会破坏单晶高温合金的表面完整性,使表面出现砂粒切削造成的不规则凹坑,改变表面形貌;砂粒粒径增加,表面粗糙度和显微硬度均增大;吹砂使大量位错在γ相通道中滑移,靠近表面区域位错密度较大;并且,大量位错剪切γ'相,形成反相畴界和层错;吹砂造成形变强化、引入残余应力;150 μm、0.5 MPa吹砂对DD6合金760℃旋转弯曲疲劳性能基本无影响,但会降低合金980℃疲劳性能,对低应力幅区疲劳寿命影响较大,使疲劳强度下降约7.3%。缺口效应、氧化损伤、形变强化和残余压应力的耦合作用导致吹砂与不吹砂试样疲劳寿命产生差异。
Some new aspects concerning particle hardening mechanisms in γ' precipitating Ni-base alloys—I. Theoretical concept
[J].
The influence of orientation on the stress rupture properties of nickel-base superalloy single crystals
[J].