节能减排已成为汽车工业发展中刻不容缓的核心问题,降低汽车车体重量实现汽车轻量化是节能减排最有效的措施之一。汽车车体重量约70%由钢铁材料构成,因此,开发应用高强度汽车用钢是降低汽车自重的有效途径[1 ,2 ] 。然而,汽车用钢在强度不断提高的同时,还需有良好的塑性和优良的凸缘拉延性能。以铁素体细晶强化为主要强化方式的汽车用钢,虽然凸缘性能优良,但抗拉强度往往在600 MPa以内,继续提高强度,需要更低的变形温度而无法在目前的工业生产线实现。具有铁素体+马氏体双相组织(DP)钢[3 ] 由于具有良好强塑性匹配,已在汽车用钢得到广泛应用,但是由于组织中的低温转变相与铁素体基体强度差异大,导致凸缘性能较差[4 ,5 ] ,加工成形性能不佳,需要采用新的组织设计理念来解决这个问题。
Funakawa等[6 ,7 ] 采用铁素体+纳米级析出物的组织调控方式在工业生产线开发出780 MPa级别高性能热轧汽车用钢,其典型组织为铁素体上分布着尺寸约3 nm的(Mo, Ti)C析出物,铁素体实现高塑性和高凸缘性能,纳米级析出物提供约300 MPa的强度贡献,细小弥散的析出粒子不容易引起应力集中,不会损害凸缘性能。由此可以看出,铁素体+纳米级析出的组织设计是同时提高强度和凸缘性能的有效方式,而如何大幅提高析出强化增量是研究重点。根据Orowan-Ashby析出强化机制[8 ] ,析出强化增量主要受析出粒子的尺寸和体积分数影响。析出粒子尺寸越细小,体积分数越高,则析出强化增量越大。在一定的体积分数的情况下,析出粒子越分散,析出粒子尺寸越细小,析出强化增量越大。20世纪70年代,Honeycombe等[9 ,10 ] 发现在γ →α 相变过程中,析出粒子呈平行排列称之为相间析出,析出粒子分散度大,可以在保证细小尺寸的情况下获得高的体积分数,Yen等[11 ] 研究表明,尺寸小于5 nm的TiC相间析出粒子可提供约400 MPa的强化增量,引起了国内外广泛关注。
采用复合微合金化技术可细化析出粒子尺寸和提高体积分数,进一步提高析出强化效果。Chen等[12 ] 和Jang等[13 ] 对比研究了Ti系、Ti-Nb系和Ti-Mo系热轧高强钢在相同工艺条件下的析出粒子尺寸d ,其大小满足d (Ti, Mo)C < d (Ti, Nb)C < d TiC ;Kamikawa等[14 ] 研究了TiC和(Ti, Mo)C在铁素体上的析出行为,Ti-Mo钢的析出强化能力远大于Ti钢;采用Ti-V成分设计[15 ] ,可实现与Ti-Mo同样的析出强化效果。Chen等[16 ] 对比研究了Mo对Ti-Nb系热轧高强钢在铁素体上的析出尺寸的影响规律,结果表明,含Mo型析出物尺寸为2.8 nm,而无Mo型为4.1 nm。由此可以看出,采用Ti-Mo复合的成分设计可很好地提高析出强化效果。通过工艺参数优化,亦可进一步提高析出强化增量,轧后采用超快速冷却[17 ] ,尺寸小于5 nm的析出粒子体积分数增加30%,析出强化增量提高30 MPa。Jha等[18 ] 和张可等[19 ,20 ] 分别采用复合添加大量的Ti、Nb、Mo、V的成分设计路线,结果表明经合适轧制工艺和卷取温度保温后,在铁素体基体上弥散析出多元复合第二相析出粒子,提供的析出强化增量可达到400 MPa级以上,但是为了使微合金元素充分固溶,需要进行较高的加热固溶温度。
除了微合金元素碳化物的相间析出之外,Cu也可发生相间析出,大幅提高析出强化效果。李闯等[21 ] 研究发现,在冷速低于5℃/s的连续冷却过程中可获得大量Cu的相间析出亚稳相。Dunne等[22 ,23 ] 将含Cu 1.1% (质量分数)的钢热轧后快速冷却至600℃进行等温时效,在铁素体中获得了大量的ε -Cu相间析出。因此,综合利用碳化物和Cu的共析出,大幅提高强度是一个可行的工艺方案。Gagliano和Fine[24 ] 对Cu-Nb钢中bcc-Cu和NbC共析出行为和析出动力学进行了研究,结果表明,NbC和bcc-Cu在铁素体中的析出形核和长大都是奥氏体化温度的函数,bcc-Cu的形核率比NbC高一个数量级,这就意味着bcc-Cu优先析出,然后是NbC析出。Chen等[25 ] 对TiC与ε -Cu共析出进行了探索,扫描透射电镜(STEM)结果显示,ε -Cu总是出现在具有相间析出的TiC相连位置处,故推测TiC优先析出,ε -Cu随后在TiC上形核长大,其析出次序与Gagliano结果[24 ] 相反。由此可见,关于Cu与碳化物的析出次序存在多种解释,甚至是矛盾之处,需要对其进行澄清与梳理。
本工作设计了低碳Ti-Mo与Cu共析出钢,通过等温热模拟实验和理论计算研究了不同等温温度下的析出行为和析出动力学,以期为共析出强化钢的析出次序、工艺优化和工业生产提供理论指导。
1 实验方法
实验用钢的化学成分(质量分数,%)为:C 0.06,Si 0.31,Mn 1.34,P 0.005,S 0.003,Ti 0.11,Mo 0.19,Cu 0.99,Alt 0.060,N 0.0041,Fe 余量。采用50 kg真空感应炉熔炼,锻造尺寸为100 mm × 100 mm × 300 mm钢坯,然后在中间部位加工成直径30 mm、高100 mm的圆柱形样坯,将其密封在充满Ar气保护的石英管中,随后放置在1200℃管式加热炉中保温72 h进行均质化处理,然后淬火至室温。从淬火样坯上切取直径3 mm、长10 mm圆柱形试样。将圆柱形试样以10℃/s的加热速率加热至1200℃保温180 s进行奥氏体化,然后以10℃/s的冷却速率冷却至600~660℃,并在此温度保温120 min发生铁素体相变,最后淬火至室温。
圆柱形试样沿中间刨开,经磨制抛光后,用体积分数为4%的硝酸酒精溶液腐蚀约15 s,然后利用DMRIM光学显微镜(OM)对显微组织进行观察。从圆柱形试样切取500 μm厚薄片观察不同等温温度下的析出行为,首先采用SiC砂纸研磨至约50 μm,然后采用Tenu-Pol-5电解双喷减薄仪在9% (体积分数)高氯酸酒精溶液进行双喷减薄,双喷电压为30~35 V,温度为-20℃,采用Tecnai G2 F20场发射透射电子显微镜(TEM)对析出粒子的尺寸、形貌及分布进行观察,采用Image J软件测量铁素体晶粒和析出粒子尺寸。
2 实验结果
2.1 显微组织
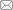
图1 为实验用钢不同等温温度下显微组织的OM像。从图1 a~c中可以看出,600~640℃等温时显微组织主要为铁素体为主,部分呈多边形、准多边形和针状形貌特征;当温度为660℃,显微组织为铁素体+未相变的奥氏体淬火过程中得到的贝氏体/马氏体(图1 d),说明在600~660℃等温,主要发生奥氏体→铁素体的相变,可获得高体积分数的铁素体组织。
图1
图1
实验用钢不同等温温度下显微组织的OM像
(a) 600o C (b) 620o C (c) 640o C (d) 660o C
Fig.1
OM images of experiment steel with different holding temperatures (F—ferrite, B—bainite, M—martensite)
2.2 析出行为
铁素体基体上的析出可以分为位错线上析出、过饱和析出和相间析出,而对于具有相间析出特征的TEM样品,通过倾转试样使得析出物的晶体学面的法线方向与透射电镜的电子束入射方向基本平行时,才能观察到相间析出特征[11 ] ,本实验采用此种手段来观察不同等温温度下的析出物是否具有相间析出特征。
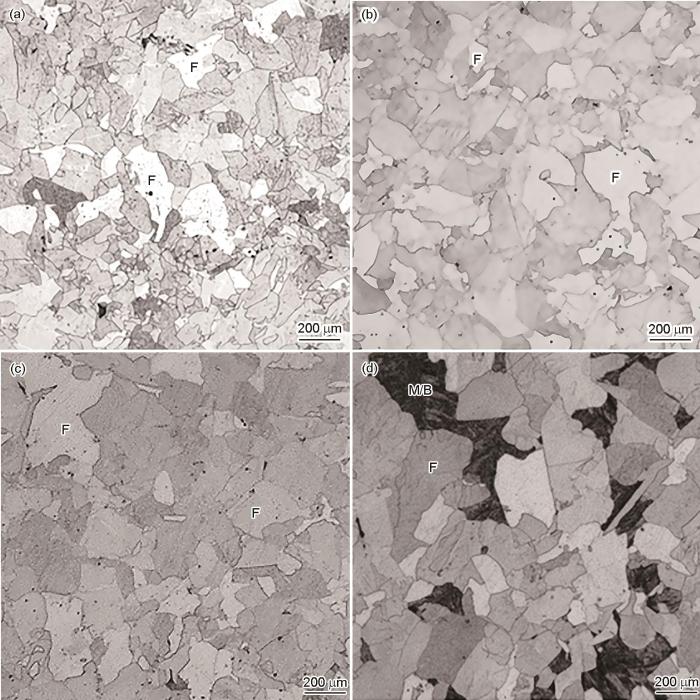
600℃等温条件下的析出物形貌和选区电子衍射(SAED)花样如图2 所示。从TEM结果可以看出,主要是以Cu的析出为主,碳化物析出量极少,未发现有碳化物的相间析出。Cu析出多呈椭圆形,平均半长轴为27.0 nm,展弦比为2.30,大量的Cu析出多出现在位错和铁素体晶界上,如图2 a和b箭头所示,铁素体晶粒内部存在大量的缠结位错,在靠近晶界位置,部分区域发现存在极少量的Cu的相间析出行为如图2 b所示,说明Cu以位错线上和基体2种方式形核,通过统计分析,位错线上析出与基体上析出比例约为4∶1。Cu的TEM明暗场和SAED花样如图2 c和d所示。由图可知,Cu析出物是具有fcc结构的ε -Cu,与铁素体基体满足Kurdjumov-Sachs (K-S)取向关系[22 ] :(1 ¯ 10 ) ferrite // ( 11 1 ¯ ) ε - C u [ 11 1 ¯ ] ferrite // [ 011 ] ε - C u d ( 11 1 ¯ ) aε- Cu
图2
图2
600℃等温后试样中的ε -Cu的TEM明场像和SAED花样
(a) at the dislocation (b) interphase precipitate near the grain boundary
(c) bright field image of Cu (d) dark field image of Cu and corresponding SAED pattern (inset)
Fig.2
TEM bright field images and SAED pattern of the interphase precipitate in speciments isothermally treated at 600o C (IP—interphase precipitation)
Goodman等[26 ] 发现当Cu析出物尺寸大于5 nm为非共格的fcc型ε -Cu,当尺寸超过10 nm时组分接近于纯Cu,而尺寸较小的析出物为共格bcc-Cu,根据析出物尺寸判断析出物基本为fcc型ε -Cu。Guo等[27 ] 发现Fe-1.67Cu-1.26Mn-1.43Ni合金在600℃等温18 h后,ε -Cu析出粒子尺寸为21.0 nm,显著小于本实验中结果。硬度测试表明,本工作中600℃等温过程中铁素体硬度均高于300 HV (如等温2 h对应的显微硬度为315 HV),显著高于Guo等[27 ] 研究中Cu析出前后的显微硬度(Cu析出前的显微硬度约为260 HV,18 h回火后约为230 HV),而且Kao[28 ] 采用类似成分与工艺获得的硬度结果与本实验相近(615℃等温30 min对应的显微硬度为303 HV)。由此可见,本实验中的铁素体基体具有更高的位错密度,而且较短时间的回火有利于位错密度的保留,Cu在位错通道的扩散促进了Cu的形核长大,这可能是本实验中Cu粒子尺寸较大的一个原因。因此在后续的动力学计算过程中忽略初期bcc-Cu形核,同时考虑ε -Cu在铁素体位错线和基体上的形核长大。
当温度升高到620℃时,如图3 a所示,在铁素体基体上出现大量具有相间析出特征的碳化物,其平均尺寸为4.1 nm,列间距为39.1 nm,同时伴随有ε -Cu的弥散析出,ε -Cu平均半长轴为33.3 nm,展弦比为2.33,与铁素体基体也满足K-S位相关系,无论ε -Cu析出尺寸多大,在相间析出列之间的位置没有单独的ε -Cu,这与Chen等[25 ] 的研究结果基本一致。当温度升高到640和660℃时,典型的TEM像如图3 b和c所示,基体上ε -Cu析出较少,只有在部分晶界位置出现,绝大多数为碳化物析出,且呈平直型相间析出分布,碳化物形貌多为圆形,在640℃时平均尺寸为5.6 nm,660℃为7.1 nm,相间析出列间距分别为42.7和98.5 nm。
图3
图3
620~660℃等温后试样中的相间析出碳化物的TEM像和SAED花样
Fig.3
TEM bright field images of the interphase precipitate in speciments isothermally treated at 620o C (a), 640o C (b), and 660o C (c), and dark filed image at 660o C and corresponding SAED pattern (inset) (d)
碳化物暗场像和SAED花样如图3 d所示,碳化物具有典型NaCl类型的晶体结构,与基体存在Nishiyama-Wassermann (N-W)位向关系: ( 2 ¯ 00 ) f e r r i t e ( 02 2 ¯ ) M C ferrite // [111]M C 。通过测量,可得到晶面间距d ( 02 2 ¯ ) aM C = 0.414 nm,明显小于TiC的晶格常数0.433 nm[29 ] 。Funakawa等[6 ] 通过X射线衍射(XRD)对具有NaCl型的复合碳化物(Ti, Mo)C进行了测量,晶格常数为0.433 nm。Yen等[11 ] 通过扫描透射电子显微镜高角环形暗场像(HAADF-STEM)研究发现,碳化物中含有大量的Ti和Mo,晶格常数范围为0.423~0.430 nm。Jang等[13 ] 通过对比研究0.04C-0.1Ti和0.04C-0.1Ti-0.2Mo模型合金,结果发现,与无Mo的碳化物TiC相比,Mo取代Ti形成的复合型碳化物(Ti, Mo)C,导致晶格常数由TiC的0.434 nm降低到(Ti, Mo)C的0.425 nm,缓解了碳化物和铁素体基体之间的晶格失配,促进了碳化物在铁素体基体上形核。由于本工作中的碳化物尺寸细小,EDX无法定量确定其组分,根据以上研究结果推测,碳化物为NaCl型(Ti, Mo)C,下文的析出动力学中估算其组分。综上可知,实验用钢中存在2种完全不同的析出物,分别为与铁素体基体保持K-S取向关系的ε -Cu和N-W取向关系的(Ti, Mo)C。
3 析出动力学
为考察实验用钢的共析出动力学,需分别计算复合型碳化物(Ti, Mo)C和ε -Cu析出的动力学。
3.1 热力学计算
为简化析出模型,根据TEM结果,ε -Cu以位错线上析出和基体上弥散析出2种方式同时形核析出,2者比例约为4∶1,而(Ti, Mo)C以基体上均匀析出方式形核长大。
根据复合析出相的固溶析出模型计算二元复合型碳化物(Ti, Mo)C析出动力学[30 ] ,假设条件如下:① 均热温度为1200℃,析出物完全溶解;② NaCl型TiC和MoC相互溶解,碳化物无间隙缺位,满足化学计量比,在复合碳化物中TiC的化学式系数x ,MoC的化学式系数为1- x ,复合碳化物记为Tix 1 - x
由于复合析出相在铁素体中满足平衡固溶的热力学平衡,同时处于析出态的Ti、Mo和C元素比满足化学计量比,可得到[30 ~32 ] :
l g [ T i ] [ C ] x = 4.40 - 9575 / T (1)
l g [ M o ] [ C ] 1 - x = 3.19 - 4649 / T (2)
( ω T i - [ T i ] ) / A T i x ⋅ ( ω C - [ C ] ) / A C = 1 (3)
( ω M o - [ M o ] ) / A M o ( 1 - x ) ⋅ ( ω C - [ C ] ) / A C = 1 (4)
式中,ωM 为实验用钢中元素M (M = Ti、Mo、C)的质量分数,%;AM 为元素M 的摩尔质量,g/mol;T 为热力学温度,K。方程(1)~(4)联立,求得实验用钢在不同温度下Ti、Mo和C元素在铁素体中的固溶量[Ti]、[Mo]、[C]和化学式系数x
Cu在铁素体中的固溶量需要满足固溶度积公式为[30 ] :
l g [ C u ] a = 2.983 - 3093 / T (5)
3.2 动力学计算
首先计算(Ti, Mo)C和ε -Cu的形核驱动力,即(Ti, Mo)C和ε -Cu在铁素体中析出的体积自由能(Δ G V ) 由其Gibbs摩尔自由能(Δ G m ) 和摩尔体积(V m )表示[30 ] :
Δ G V = Δ G m V m (6)
Δ G C u m = l n 10 ⋅ R T ( 2.938 - 3093 T ) -
l n 10 ⋅ R T ⋅ l g ω C u (7a)
Δ G M C m = l n 10 ⋅ R T ( A - B T ) -
l n 10 ⋅ R T ⋅ l g ( ω T i x ω M o 1 - x ω C ) (7b)
式中,Δ G M C m Δ G C u m ε -Cu不同温度析出时Gibbs摩尔自由能;A 和B 可由TiC和MoC的固溶度积系数联合化学式系数x 求得;(Ti, Mo)C的摩尔体积(V M C m ) 可由TiC和MoC的晶格常数及线膨胀系数通过线性内插法求得。
已知TiC、MoC和ε -Cu与铁素体之间半共格界面比界面能随温度变化的计算公式[30 ] :
σ T i C = 1.0687 - 0.3552 × 10 - 3 T (8)
σ M o C = 1.0046 - 0.3338 × 10 - 3 T (9)
σ C u = 0.3562 - 0.1270 × 10 - 3 T (10)
式中,σ TiC 、σ MoC 和σ Cu 分别为TiC、MoC和ε -Cu不同温度析出与铁素体基体的半共格界面比界面能,J/m2 。
球形(Ti, Mo)C在铁素体基体上形核时的自由能变化(Δ G M C ) 为[30 ] :
Δ G M C = 1 6 π d M C 3 Δ G M C V + π d M C 2 σ M C (11)
式中,dM C 为(Ti, Mo)C在基体上均匀形核的核胚直径;σM C 为(Ti, Mo)C与铁素体基体间的半共格界面比界面能,可由TiC和MoC的界面能结合化学式系数x 线性内插法求得。
ε -Cu在铁素体上形核的自由能Δ G C u m Δ G C u d i s Δ G C u m a t r i x ε -Cu的自由能变化为[30 ] :
Δ G C u m = 4 5 Δ G C u d i s + 1 5 Δ G C u m a t r i x (12)
ε -Cu在铁素体基体上形核时的自由能变化(Δ G C u m a t r i x ) 为[30 ] :
Δ G C u m a t r i x = 1 6 π d C u 3 Δ G C u V + π d C u 2 σ C u (13)
根据修正的Cahn位错形核理论[33 ,34 ] ,可得到球形ε -Cu在位错线上形核时的自由能变化Δ G C u d i s
Δ G C u d i s = 1 6 π d C u 3 Δ G C u V + π d C u 2 σ C u - L C u d C u (14)
L C u = G C u b C u 2 4 π ( e d g e d i s l o c a t i o n ) G C u b C u 2 4 π ( 1 - ν C u ) ( s c r e w d i s l o c a t i o n ) (15)
式中,d Cu 为ε -Cu新相沿位错线形成的核胚直径,L Cu 为单位长度的位错能量,G Cu 、b Cu 、v Cu 分别为Cu的切变模量、Burgers矢量模和Poisson比。由于刃型位错比螺型位错更适合析出物形核[30 ] ,所以只考虑形核位置为刃型位错的情况。
(Ti, Mo)C临界形核功(Δ G M C * ) 为[30 ] :
Δ G M C * = 16 π σ M C 3 3 ( Δ G M C V ) 2 (16)
ε -Cu均匀析出和在位错线上析出的临界形核功Δ G C u m a t r i x * Δ G C u d i s * [30 ] :
Δ G C u m a t r i x * = 16 π σ C u 3 3 ( Δ G C u V ) 2 (17)
Δ G C u d i s * = 16 π σ C u 3 3 ( Δ G C u V ) 2 ( 1 + β ) 3 / 2 (18)
β = L C u Δ G C u V 2 π σ C u 2 (19)
式中,β 为Cahn理论中的位错线形核参量[35 ] ,其值在-1~0之间。
(Ti, Mo)C和ε -Cu析出的相对开始时间分别为[30 ] :
l g t M C 0.05 t M C 0 = 2 5 [ - 1.28994 - 2 l g d M C * + 1 l n 10 ⋅
e x p ( Δ G M C * + 5 2 Q M C k T ) ] (20)
l g t C u 0.05 t C u 0 = 4 5 1 2 [ - 1.28994 - 2 l g d C u d * + 1 l n 10 ⋅ e x p ( Δ G C u d * + 5 3 Q C u k T ) ] + 1 5 2 5 [ - 1.28994 - 2 l g d C u m * + 1 l n 10 ⋅ e x p ( Δ G C u m * + 5 2 Q C u k T ) ] (21)
式中,t M C 0 t C u 0 M C和Cu析出的时间,t M C 0.05 t C u 0.05 M C和Cu析出5%时的时间,d M C * d C u * d C u m * ε -Cu在基体均匀析出和在位错线上析出的临界形核半径,QM C 和Q Cu 分别为复合碳化物形成元素Ti/Mo和Cu在铁素体基体上的扩散激活能,其中QM C 由Ti和Mo的扩散激活能结合化学式系数x 线性差值求得。
3.3 计算结果与讨论
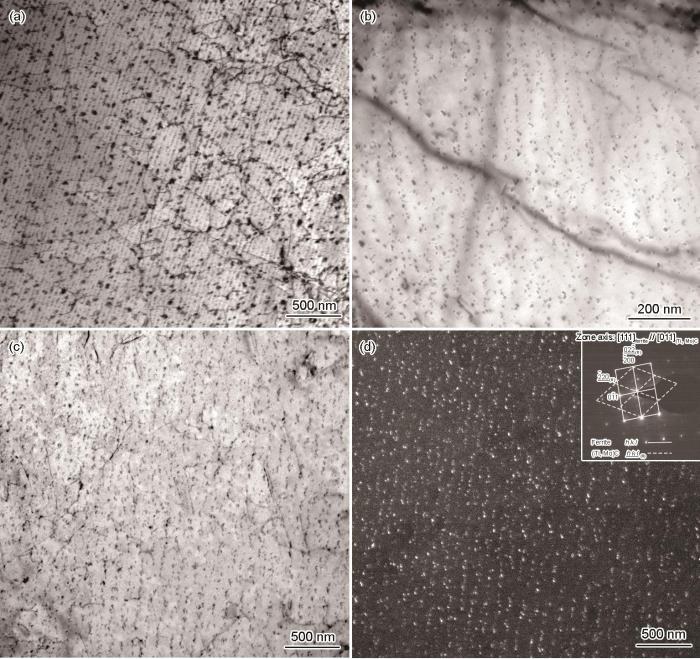
表1 [29 ,30 ,35 ~41 ] 为动力学计算中所使用的参数及其取值,析出动力学计算结果如图4 所示。复合碳化物(Ti, Mo)C在550~700℃保温区间,随温度的升高,化学式系数x 单调增加,如图4 a所示,即TiC在(Ti, Mo)C的占比由0.65增加到0.84,由此可得(Ti, Mo)C中Ti/Mo比由1.8增加到5.4。当温度为550~700℃时,随温度的升高,由于固溶度的增大,(Ti, Mo)C与ε -Cu的形核驱动力均单调减小,如图4 b所示,(Ti, Mo)C的驱动力的范围为4.88 × 109 ~4.41 × 109 J/m3 ,而ε -Cu的驱动力的范围为1.67 × 109 ~4.96 × 108 J/m3 ,2者之比由2.45扩大至8.88,可以看出,温度升高大幅降低了ε -Cu析出的驱动力,而(Ti, Mo)C的驱动力变化较小。(Ti, Mo)C与ε -Cu的析出相对开始时间即析出-温度-时间(PTT)曲线如图4 c所示,在550~700℃范围内,ε -Cu的PTT曲线呈典型C形状,鼻尖温度为586℃,当温度范围为550~586℃时,随温度的升高,ε -Cu的相对开始析出时间会越来越短,即孕育期越短;而温度范围为586~700℃时,随温度的升高,ε -Cu的相对开始析出时间会越来越长,即孕育期越长。而在550~700℃范围内,(Ti, Mo)C则呈单调下降趋势,即随温度的降低,(Ti, Mo)C的相对开始析出时间会越来越长,即孕育期越长。
图4
图4
不同温度下(Ti, Mo)C与ε -Cu在铁素体中析出热/动力学的计算结果
(a) Ti/Mo atomic ratio and x (b) driving force (c) PTT curves (d) solid solution content
Fig.4
Thermodynamics/kinetics calculation results of precipitation of (Ti, Mo)C and ε -Cu in ferrite at different temper-atures (PPT—precipitation-temperature-time, t 0 —the precipitation start time, t 0.05 —the time of pricipitates fraction of 5%)
(Ti, Mo)C中Ti/Mo原子比是探究Mo在复合碳化物作用的重要内容,也是化学成分设计的关键环节。Jang等[13 ] 对含Ti-Mo钢在630℃等温时效析出实验研究发现,碳化物中Ti/Mo比随析出物尺寸的增大而增加,当碳化物尺寸在5~14 nm内,(Ti, Mo)C析出物中Ti/Mo比为2.0~4.3。Wang等[42 ] 通过三维原子探针(APT)研究了Ti-Mo微合金钢在890℃进行热变形和不进行热变形时(Ti, Mo)C化学组分的演变规律,结果表明热变形对(Ti, Mo)C中的化学组分影响不大,热变形后并在650℃等温时Ti/Mo比为2.7,而不变形时为2.6。Dhara等[43 ] 采用APT和小角度中子散射(SANS)研究(Ti, Mo)C的组分变化,结果表明650℃形成的(Ti, Mo)C,当析出粒子尺寸的Guinier半径> 3 nm时,碳化物中的Ti/Mo比接近于平衡态的2.5,而Timokhina等[44 ] 研究发现,650℃保温1700 s后,(Ti, Mo)C的Ti/Mo比为3.3。综上可知,(Ti, Mo)C碳化物在630~650℃保温期间,Ti/Mo比基本在2.5~4.3范围内,在本实验600~660℃温度范围内,如图4 a所示,Ti/Mo比为2.5~4.5,基本与实验结果相近。当温度由600℃提高到660℃时,化学式系数x 单调增加,Ti/Mo比为由2.5增大到4.5,碳化物组成由Ti0.71 Mo0.29 C演变为Ti0.79 Mo0.21 C,也就是说MoC在低温时析出分数占比较高,而在高温时占比降低。这与组成复合碳化物的TiC和MoC的固溶度积有关,TiC的固溶度积比较小,为难固溶相,而MoC的固溶度积较大,为易固溶相。随着温度升高,2者的固溶度积均增大,固溶[Ti]和[Mo]均增大,但固溶[Mo]增加幅度更大,如图4 d所示,导致复合碳化物中MoC比例下降,Ti/Mo比增大。
第二相的析出次序问题一直是钢铁材料研究领域的重要问题,析出次序不仅与析出物在不同温度范围的热力学稳定性有关,同时也与析出反应的动力学有关。在本实验中,由于(Ti, Mo)C碳化物与ε -Cu析出物在铁素体上独立析出,因此可通过析出反应的动力学判断其析出次序。如图4 c所示,(Ti, Mo)C与ε -Cu的PTT曲线在616℃处相交,当温度低于616℃时,ε -Cu优先析出,然后是(Ti, Mo)C析出,而高于616℃时,(Ti, Mo)C优先析出,而后是ε -Cu。这与TEM中观察到的600℃出现单独ε -Cu析出,而在620℃发生ε -Cu与(Ti, Mo)C共析出,当温度为640~660℃时,以(Ti, Mo)C为主,ε -Cu很少的实验现象基本吻合。
根据动力学计算结果可知,在较低温度(如600℃)下,ε -Cu在铁素体中的位错线上和基体上优先于碳化物析出,大量析出的ε -Cu粒子将有效“钉扎”铁素体基体,阻碍位错运动而保证较高的位错密度,为后续碳化物的析出提供更多的形核地点。从这一角度考虑,ε -Cu的析出将促进碳化物的析出热/动力学。Guo等[27 ] 对比研究了含Cu钢、Nb钢和Nb-Cu钢的时效析出,从其对应的硬度变化趋势看,与含Nb钢相比,含Cu-Nb钢的时效析出硬度峰值前移至与Cu钢时效析出硬度峰值一致的时刻,这似乎可以反映出Cu的析出促进了NbC的析出。在较高温度(如620℃以上)下,碳化物将优先析出,亦会产生对位错的“钉扎”作用,但是温度较高,这种钉扎作用效果减弱,因此在实验结果中,在640~660℃较高温度下难以观察到ε -Cu的加速析出现象。但需要指出的是,2种析出之间的相互作用机制较为复杂,这其中可能涉及晶体学、热/动力学等多方面因素,有待进一步深入探索。
4 结论
(1) 低碳Ti-Mo与Cu共析出钢在温度为600℃时析出以ε -Cu为主,620℃发生(Ti, Mo)C与ε -Cu的共析出,在温度为640~660℃时以(Ti, Mo)C相间析出为主;TEM分析表明,(Ti, Mo)C与ε -Cu 2者独立析出,分别与铁素体呈N-W和K-S取向关系。
(2) 热/动力学计算表明,在600~660℃范围内,随温度提高,碳化物组成由Ti0.71 Mo0.29 C演变为Ti0.79 Mo0.21 C;(Ti, Mo)C与ε -Cu的PTT曲线在616℃处相交,当温度低于616℃时,ε -Cu优先析出,而后是(Ti, Mo)C析出,当温度高于616℃时,(Ti, Mo)C优先析出,而后是ε -Cu,很好地解释了实验结果。
参考文献
View Option
[1]
Takahashi M Development of high strength steels for automobiles
[R]. Nippon Steel Tech . Rep. No.88, 2003
[本文引用: 1]
[2]
Kashima T Hashimoto S Mukai Y 780 N/mm2 grade hot-rolled high-strength steel sheet for automotive suspension system
[J]. JSAE Rev. , 2003 , 24 : 81
[本文引用: 1]
[3]
Patel J Klinkenberg C Hulka K Hot rolled HSLA strip steels for automotive and construction applications
[A]. Niobium Science & Technology—Proceeding of the International Symposium Niobium 2001 [C]. Orlando, FL : Niobium 2001 Limited , 2001: 647
[本文引用: 1]
[4]
Morita M Kurosawa N Masui S et al Development of hot rolled high strength steels hardened by precipitation hardening with high stretch flanging
[A]. CAMP-ISIJ [C]. Tokyo : The Iron and Steel Institute of Japan , 1992 : 1863
[本文引用: 1]
[5]
Seto K Funakawa Y Kaneko S Hot rolled high strength steels for suspension and chassis parts “NANOHITEN” and “BHT® Steel
[R]. JFE Tech . Rep. No.10, 2007
[本文引用: 1]
[6]
Funakawa Y Shiozaki T Tomita K et al Development of high strength hot-rolled sheet steel consisting of ferrite and nanometer-sized carbides
[J]. ISIJ Int. , 2004 , 44 : 1945
[本文引用: 2]
[7]
Funakawa Y Seto K Stabilization in strength of hot-rolled sheet steel strengthened by nanometer-sized carbides
[J]. Tetsu Hagané , 2007 , 93 : 49
[本文引用: 1]
船川 義正 , 瀬戸 一洋 微細炭化物で析出強化した高強度熱延鋼板の強度安定化
[J]. 鐵と鋼 , 2007 , 93 : 49
[本文引用: 1]
[8]
Gladman T et al Structure-property relationships in high-strength microalloyed steels
[A]. Microalloying 75' [C]. New York : Union Carbide Corporation , 1977 : 32
[本文引用: 1]
[9]
Honeycombe R W K Mehl R F Transformation from austenite in alloy steels
[J]. Metall . Trans., 1976 , 7A : 915
[本文引用: 1]
[10]
Berry F G Honeycombe R W K Isothermal decomposition of austenite in Fe-Mo-C alloys
[J]. Metall . Trans., 1970 , 1B : 3279
[本文引用: 1]
[11]
Yen H W Chen P Y Huang C Y et al Interphase precipitation of nanometer-sized carbides in a titanium-molybdenum-bearing low-carbon steel
[J]. Acta Mater. , 2011 , 59 : 6264
[本文引用: 3]
[12]
Chen C Y Yen H W Kao F H et al Precipitation hardening of high-strength low-alloy steels by nanometer-sized carbides
[J]. Mater. Sci. Eng. , 2009 , A499 : 162
[本文引用: 1]
[13]
Jang J H Lee C H Heo Y U et al Stability of (Ti, M )C (M = Nb, V, Mo and W) carbide in steels using first-principles calculations
[J]. Acta Mater. , 2012 , 60 : 208
[本文引用: 3]
[14]
Kamikawa N Abe Y Miyamoto G et al Tensile behavior of Ti, Mo-added low carbon steels with interphase precipitation
[J]. ISIJ Int. , 2014 , 54 : 212
[本文引用: 1]
[15]
Chen J Lü M Y Tang S et al Microstructure, mechanical properties and interphase precipitation behaviors in V-Ti microalloyed steel
[J]. Acta Metall. Sin. , 2014 , 50 : 524
[本文引用: 1]
陈 俊 , 吕梦阳 , 唐 帅 等 V-Ti微合金钢的组织性能及相间析出行为
[J]. 金属学报 , 2014 , 50 : 524
[本文引用: 1]
[16]
Chen C Y Chen C C Yang J R Microstructure characterization of nanometer carbides heterogeneous precipitation in Ti-Nb and Ti-Nb-Mo steel
[J]. Mater. Charact. , 2014 , 88 : 69
[本文引用: 1]
[17]
Tang S Liu Z Y Wang G D et al Microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of high strength microalloyed steels: Ultra fast cooling (UFC) versus accelerated cooling (ACC)
[J]. Mater. Sci. Eng. , 2013 , A580 : 257
[本文引用: 1]
[18]
Jha G Das S Sinha S et al Design and development of precipitate strengthened advanced high strength steel for automotive application
[J]. Mater. Sci. Eng. , 2013 , A561 : 394
[本文引用: 1]
[19]
Zhang K Yong Q L Sun X J et al Effect of coiling temperature on microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti-V-Mo complex microalloyed ultra-high strength steel
[J]. Acta Metall. Sin. , 2016 , 52 : 529
[本文引用: 1]
张 可 , 雍岐龙 , 孙新军 等 卷取温度对Ti-V-Mo复合微合金化超高强度钢组织及力学性能的影响
[J]. 金属学报 , 2016 , 52 : 529
[本文引用: 1]
[20]
Zhang K Sun X J Zhang M Y et al Kinetics of (Ti, V, Mo) C precipitated in γ /α matrix of Ti-V-Mo complex microalloyed steel
[J]. Acta Metall. Sin. , 2018 , 54 : 1122
[本文引用: 1]
张 可 , 孙新军 , 张明亚 等 Ti-V-Mo复合微合金钢中(Ti, V, Mo)C在γ /α 中沉淀析出的动力学
[J]. 金属学报 , 2018 , 54 : 1122
[本文引用: 1]
[21]
Li C Wang X M Shang C J et al Study on precipitation behavior of phases containing Cu in the Cu-bearing steel in continuous cooling process
[J]. Acta Metall. Sin. , 2010 , 46 : 1488
[本文引用: 1]
李 闯 , 王学敏 , 尚成嘉 等 连续冷却过程中含Cu相在钢中析出行为的研究
[J]. 金属学报 , 2010 , 46 : 1488
[本文引用: 1]
[22]
Dunne D P Review: Interaction of precipitation with recrystallisation and phase transformation in low alloy steels
[J]. Mater. Sci. Technol. , 2010 , 26 : 410
[本文引用: 2]
[23]
Dunne D P Banadkouki S S G Yu D Isothermal transformation products in a Cu-bearing high strength low alloy steel
[J]. ISIJ Int. , 1996 , 36 : 324
[本文引用: 1]
[24]
Gagliano M S Fine M E Characterization of the nucleation and growth behavior of copper precipitates in low-carbon steels
[J]. Metall. Mater. Trans. , 2004 , 35A : 2323
[本文引用: 2]
[25]
Chen C Y Li C H Tsao T C et al A novel technique for developing a dual-phase steel with a lower strength difference between ferrite and martensite
[J]. Mater. Today Commun. , 2020 , 23 : 100895
[本文引用: 2]
[26]
Goodman S R Brenner S S Low J R An FIM-atom probe study of the precipitation of copper from iron-1.4 at. pct copper. Part I: Field-ion microscopy
[J]. Metall . Trans., 1973 , 4 : 2363
[本文引用: 1]
[27]
Guo H Cheng J J Yang S W et al Influence of combined Cu and Nb addition on the quenched microstructure and precipitation during tempering in ultra-low carbon steels
[J]. J. Alloys Compd. , 2013 , 577 : S619
[本文引用: 3]
[28]
Kao F Precipitation strengthening of nanometer-sized copper particles and alloy carbides in high strength low alloy steels
[D]. Taiwan University , 2008
[本文引用: 1]
[29]
Yang Y Lu H Yu C et al First-principles calculations of mechanical properties of TiC and TiN
[J]. J. Alloys Compd. , 2009 , 485 : 542
[本文引用: 5]
[30]
Yong Q L Secondary Phase in Steels [M]. Beijing : Metallurgical Industry Press , 2006 : 173
[本文引用: 17]
雍岐龙 钢铁材料中的第二相 [M]. 北京 : 冶金工业出版社 , 2006 : 173
[本文引用: 17]
[31]
Taylor K A Solubility products for titanium-, vanadium-, and niobium-carbide in ferrite
[J]. Scr. Metall. Mater. , 1995 , 32 : 7
[32]
Pavlina E J Speer J G van Tyne C J Equilibrium solubility products of molybdenum carbide and tungsten carbide in iron
[J]. Scr. Mater. , 2012 , 66 : 243
[本文引用: 1]
[33]
Cahn J W Nucleation on dislocations
[J]. Acta Metall. , 1957 , 5 : 169
[本文引用: 1]
[34]
Yong Q L Theory of nucleation on dislocations
[J]. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. , 1990 , 6 : 239
[本文引用: 1]
[35]
Willens R H Buehler E Matthias B T Superconductivity of the transition-metal carbides
[J]. Phys. Rev. , 1967 , 159 : 327
[本文引用: 5]
[36]
Straumanis M E Yu L S Lattice parameters, densities, expansion coefficients and perfection of structure of Cu and of Cu-In α phase
[J]. Acta Cryst. , 1969 , 25A : 676
[本文引用: 1]
[37]
Elliott R O Kempter C P Thermal expansion of some transition metal carbides
[J]. J. Phys. Chem. , 1958 , 62 : 630
[本文引用: 1]
[38]
Krasnenko V Brik M G First-principles calculations of hydrostatic pressure effects on the structural, elastic and thermodynamic properties of cubic monocarbides X C (X = Ti, V, Cr, Nb, Mo, Hf)
[J]. Solid State Sci. , 2012 , 14 : 1431
[本文引用: 1]
[39]
White G K Thermal expansion of reference materials: Copper, silica and silicon
[J]. J. Phys. , 1973 , 6D : 2070
[本文引用: 1]
[40]
Moll S H Ogilvie R E Solubility and diffusion of titanium in iron
[J]. Trans. Metall. Soc. AIME , 1959 , 215 : 613
[本文引用: 1]
[41]
Smithells C J Brandes E A Smithells Metals Reference Book [M]. Oxford : Butterworth-Heinemann , 1992 : 13
[本文引用: 7]
[42]
Wang J T Hodgson P D Bikmukhametov I et al Effects of hot-deformation on grain boundary precipitation and segregation in Ti-Mo microalloyed steels
[J]. Mater. Des. , 2018 , 141 : 48
[本文引用: 1]
[43]
Dhara S Marceau R K W Wood K et al Precipitation and clustering in a Ti-Mo steel investigated using atom probe tomography and small-angle neutron scattering
[J]. Mater. Sci. Eng. , 2018 , A718 : 74
[本文引用: 1]
[44]
Timokhina I Miller M K Wang J T et al On the Ti-Mo-Fe-C atomic clustering during interphase precipitation in the Ti-Mo steel studied by advanced microscopic techniques
[J]. Mater. Des. , 2016 , 111 : 222
[本文引用: 1]
Development of high strength steels for automobiles
1
2003
... 节能减排已成为汽车工业发展中刻不容缓的核心问题,降低汽车车体重量实现汽车轻量化是节能减排最有效的措施之一.汽车车体重量约70%由钢铁材料构成,因此,开发应用高强度汽车用钢是降低汽车自重的有效途径[1 ,2 ] .然而,汽车用钢在强度不断提高的同时,还需有良好的塑性和优良的凸缘拉延性能.以铁素体细晶强化为主要强化方式的汽车用钢,虽然凸缘性能优良,但抗拉强度往往在600 MPa以内,继续提高强度,需要更低的变形温度而无法在目前的工业生产线实现.具有铁素体+马氏体双相组织(DP)钢[3 ] 由于具有良好强塑性匹配,已在汽车用钢得到广泛应用,但是由于组织中的低温转变相与铁素体基体强度差异大,导致凸缘性能较差[4 ,5 ] ,加工成形性能不佳,需要采用新的组织设计理念来解决这个问题. ...
780 N/mm2 grade hot-rolled high-strength steel sheet for automotive suspension system
1
2003
... 节能减排已成为汽车工业发展中刻不容缓的核心问题,降低汽车车体重量实现汽车轻量化是节能减排最有效的措施之一.汽车车体重量约70%由钢铁材料构成,因此,开发应用高强度汽车用钢是降低汽车自重的有效途径[1 ,2 ] .然而,汽车用钢在强度不断提高的同时,还需有良好的塑性和优良的凸缘拉延性能.以铁素体细晶强化为主要强化方式的汽车用钢,虽然凸缘性能优良,但抗拉强度往往在600 MPa以内,继续提高强度,需要更低的变形温度而无法在目前的工业生产线实现.具有铁素体+马氏体双相组织(DP)钢[3 ] 由于具有良好强塑性匹配,已在汽车用钢得到广泛应用,但是由于组织中的低温转变相与铁素体基体强度差异大,导致凸缘性能较差[4 ,5 ] ,加工成形性能不佳,需要采用新的组织设计理念来解决这个问题. ...
Hot rolled HSLA strip steels for automotive and construction applications
1
2001
... 节能减排已成为汽车工业发展中刻不容缓的核心问题,降低汽车车体重量实现汽车轻量化是节能减排最有效的措施之一.汽车车体重量约70%由钢铁材料构成,因此,开发应用高强度汽车用钢是降低汽车自重的有效途径[1 ,2 ] .然而,汽车用钢在强度不断提高的同时,还需有良好的塑性和优良的凸缘拉延性能.以铁素体细晶强化为主要强化方式的汽车用钢,虽然凸缘性能优良,但抗拉强度往往在600 MPa以内,继续提高强度,需要更低的变形温度而无法在目前的工业生产线实现.具有铁素体+马氏体双相组织(DP)钢[3 ] 由于具有良好强塑性匹配,已在汽车用钢得到广泛应用,但是由于组织中的低温转变相与铁素体基体强度差异大,导致凸缘性能较差[4 ,5 ] ,加工成形性能不佳,需要采用新的组织设计理念来解决这个问题. ...
Development of hot rolled high strength steels hardened by precipitation hardening with high stretch flanging
1
1992
... 节能减排已成为汽车工业发展中刻不容缓的核心问题,降低汽车车体重量实现汽车轻量化是节能减排最有效的措施之一.汽车车体重量约70%由钢铁材料构成,因此,开发应用高强度汽车用钢是降低汽车自重的有效途径[1 ,2 ] .然而,汽车用钢在强度不断提高的同时,还需有良好的塑性和优良的凸缘拉延性能.以铁素体细晶强化为主要强化方式的汽车用钢,虽然凸缘性能优良,但抗拉强度往往在600 MPa以内,继续提高强度,需要更低的变形温度而无法在目前的工业生产线实现.具有铁素体+马氏体双相组织(DP)钢[3 ] 由于具有良好强塑性匹配,已在汽车用钢得到广泛应用,但是由于组织中的低温转变相与铁素体基体强度差异大,导致凸缘性能较差[4 ,5 ] ,加工成形性能不佳,需要采用新的组织设计理念来解决这个问题. ...
Hot rolled high strength steels for suspension and chassis parts “NANOHITEN” and “BHT? Steel
1
2007
... 节能减排已成为汽车工业发展中刻不容缓的核心问题,降低汽车车体重量实现汽车轻量化是节能减排最有效的措施之一.汽车车体重量约70%由钢铁材料构成,因此,开发应用高强度汽车用钢是降低汽车自重的有效途径[1 ,2 ] .然而,汽车用钢在强度不断提高的同时,还需有良好的塑性和优良的凸缘拉延性能.以铁素体细晶强化为主要强化方式的汽车用钢,虽然凸缘性能优良,但抗拉强度往往在600 MPa以内,继续提高强度,需要更低的变形温度而无法在目前的工业生产线实现.具有铁素体+马氏体双相组织(DP)钢[3 ] 由于具有良好强塑性匹配,已在汽车用钢得到广泛应用,但是由于组织中的低温转变相与铁素体基体强度差异大,导致凸缘性能较差[4 ,5 ] ,加工成形性能不佳,需要采用新的组织设计理念来解决这个问题. ...
Development of high strength hot-rolled sheet steel consisting of ferrite and nanometer-sized carbides
2
2004
... Funakawa等[6 ,7 ] 采用铁素体+纳米级析出物的组织调控方式在工业生产线开发出780 MPa级别高性能热轧汽车用钢,其典型组织为铁素体上分布着尺寸约3 nm的(Mo, Ti)C析出物,铁素体实现高塑性和高凸缘性能,纳米级析出物提供约300 MPa的强度贡献,细小弥散的析出粒子不容易引起应力集中,不会损害凸缘性能.由此可以看出,铁素体+纳米级析出的组织设计是同时提高强度和凸缘性能的有效方式,而如何大幅提高析出强化增量是研究重点.根据Orowan-Ashby析出强化机制[8 ] ,析出强化增量主要受析出粒子的尺寸和体积分数影响.析出粒子尺寸越细小,体积分数越高,则析出强化增量越大.在一定的体积分数的情况下,析出粒子越分散,析出粒子尺寸越细小,析出强化增量越大.20世纪70年代,Honeycombe等[9 ,10 ] 发现在γ →α 相变过程中,析出粒子呈平行排列称之为相间析出,析出粒子分散度大,可以在保证细小尺寸的情况下获得高的体积分数,Yen等[11 ] 研究表明,尺寸小于5 nm的TiC相间析出粒子可提供约400 MPa的强化增量,引起了国内外广泛关注. ...
... 碳化物暗场像和SAED花样如图3 d所示,碳化物具有典型NaCl类型的晶体结构,与基体存在Nishiyama-Wassermann (N-W)位向关系: ( 2 ¯ 00 ) f e r r i t e ( 02 2 ¯ ) M C ferrite // [111]M C .通过测量,可得到晶面间距d ( 02 2 ¯ ) aM C = 0.414 nm,明显小于TiC的晶格常数0.433 nm[29 ] .Funakawa等[6 ] 通过X射线衍射(XRD)对具有NaCl型的复合碳化物(Ti, Mo)C进行了测量,晶格常数为0.433 nm.Yen等[11 ] 通过扫描透射电子显微镜高角环形暗场像(HAADF-STEM)研究发现,碳化物中含有大量的Ti和Mo,晶格常数范围为0.423~0.430 nm.Jang等[13 ] 通过对比研究0.04C-0.1Ti和0.04C-0.1Ti-0.2Mo模型合金,结果发现,与无Mo的碳化物TiC相比,Mo取代Ti形成的复合型碳化物(Ti, Mo)C,导致晶格常数由TiC的0.434 nm降低到(Ti, Mo)C的0.425 nm,缓解了碳化物和铁素体基体之间的晶格失配,促进了碳化物在铁素体基体上形核.由于本工作中的碳化物尺寸细小,EDX无法定量确定其组分,根据以上研究结果推测,碳化物为NaCl型(Ti, Mo)C,下文的析出动力学中估算其组分.综上可知,实验用钢中存在2种完全不同的析出物,分别为与铁素体基体保持K-S取向关系的ε -Cu和N-W取向关系的(Ti, Mo)C. ...
微細炭化物で析出強化した高強度熱延鋼板の強度安定化
1
2007
... Funakawa等[6 ,7 ] 采用铁素体+纳米级析出物的组织调控方式在工业生产线开发出780 MPa级别高性能热轧汽车用钢,其典型组织为铁素体上分布着尺寸约3 nm的(Mo, Ti)C析出物,铁素体实现高塑性和高凸缘性能,纳米级析出物提供约300 MPa的强度贡献,细小弥散的析出粒子不容易引起应力集中,不会损害凸缘性能.由此可以看出,铁素体+纳米级析出的组织设计是同时提高强度和凸缘性能的有效方式,而如何大幅提高析出强化增量是研究重点.根据Orowan-Ashby析出强化机制[8 ] ,析出强化增量主要受析出粒子的尺寸和体积分数影响.析出粒子尺寸越细小,体积分数越高,则析出强化增量越大.在一定的体积分数的情况下,析出粒子越分散,析出粒子尺寸越细小,析出强化增量越大.20世纪70年代,Honeycombe等[9 ,10 ] 发现在γ →α 相变过程中,析出粒子呈平行排列称之为相间析出,析出粒子分散度大,可以在保证细小尺寸的情况下获得高的体积分数,Yen等[11 ] 研究表明,尺寸小于5 nm的TiC相间析出粒子可提供约400 MPa的强化增量,引起了国内外广泛关注. ...
微細炭化物で析出強化した高強度熱延鋼板の強度安定化
1
2007
... Funakawa等[6 ,7 ] 采用铁素体+纳米级析出物的组织调控方式在工业生产线开发出780 MPa级别高性能热轧汽车用钢,其典型组织为铁素体上分布着尺寸约3 nm的(Mo, Ti)C析出物,铁素体实现高塑性和高凸缘性能,纳米级析出物提供约300 MPa的强度贡献,细小弥散的析出粒子不容易引起应力集中,不会损害凸缘性能.由此可以看出,铁素体+纳米级析出的组织设计是同时提高强度和凸缘性能的有效方式,而如何大幅提高析出强化增量是研究重点.根据Orowan-Ashby析出强化机制[8 ] ,析出强化增量主要受析出粒子的尺寸和体积分数影响.析出粒子尺寸越细小,体积分数越高,则析出强化增量越大.在一定的体积分数的情况下,析出粒子越分散,析出粒子尺寸越细小,析出强化增量越大.20世纪70年代,Honeycombe等[9 ,10 ] 发现在γ →α 相变过程中,析出粒子呈平行排列称之为相间析出,析出粒子分散度大,可以在保证细小尺寸的情况下获得高的体积分数,Yen等[11 ] 研究表明,尺寸小于5 nm的TiC相间析出粒子可提供约400 MPa的强化增量,引起了国内外广泛关注. ...
Structure-property relationships in high-strength microalloyed steels
1
1977
... Funakawa等[6 ,7 ] 采用铁素体+纳米级析出物的组织调控方式在工业生产线开发出780 MPa级别高性能热轧汽车用钢,其典型组织为铁素体上分布着尺寸约3 nm的(Mo, Ti)C析出物,铁素体实现高塑性和高凸缘性能,纳米级析出物提供约300 MPa的强度贡献,细小弥散的析出粒子不容易引起应力集中,不会损害凸缘性能.由此可以看出,铁素体+纳米级析出的组织设计是同时提高强度和凸缘性能的有效方式,而如何大幅提高析出强化增量是研究重点.根据Orowan-Ashby析出强化机制[8 ] ,析出强化增量主要受析出粒子的尺寸和体积分数影响.析出粒子尺寸越细小,体积分数越高,则析出强化增量越大.在一定的体积分数的情况下,析出粒子越分散,析出粒子尺寸越细小,析出强化增量越大.20世纪70年代,Honeycombe等[9 ,10 ] 发现在γ →α 相变过程中,析出粒子呈平行排列称之为相间析出,析出粒子分散度大,可以在保证细小尺寸的情况下获得高的体积分数,Yen等[11 ] 研究表明,尺寸小于5 nm的TiC相间析出粒子可提供约400 MPa的强化增量,引起了国内外广泛关注. ...
Transformation from austenite in alloy steels
1
1976
... Funakawa等[6 ,7 ] 采用铁素体+纳米级析出物的组织调控方式在工业生产线开发出780 MPa级别高性能热轧汽车用钢,其典型组织为铁素体上分布着尺寸约3 nm的(Mo, Ti)C析出物,铁素体实现高塑性和高凸缘性能,纳米级析出物提供约300 MPa的强度贡献,细小弥散的析出粒子不容易引起应力集中,不会损害凸缘性能.由此可以看出,铁素体+纳米级析出的组织设计是同时提高强度和凸缘性能的有效方式,而如何大幅提高析出强化增量是研究重点.根据Orowan-Ashby析出强化机制[8 ] ,析出强化增量主要受析出粒子的尺寸和体积分数影响.析出粒子尺寸越细小,体积分数越高,则析出强化增量越大.在一定的体积分数的情况下,析出粒子越分散,析出粒子尺寸越细小,析出强化增量越大.20世纪70年代,Honeycombe等[9 ,10 ] 发现在γ →α 相变过程中,析出粒子呈平行排列称之为相间析出,析出粒子分散度大,可以在保证细小尺寸的情况下获得高的体积分数,Yen等[11 ] 研究表明,尺寸小于5 nm的TiC相间析出粒子可提供约400 MPa的强化增量,引起了国内外广泛关注. ...
Isothermal decomposition of austenite in Fe-Mo-C alloys
1
1970
... Funakawa等[6 ,7 ] 采用铁素体+纳米级析出物的组织调控方式在工业生产线开发出780 MPa级别高性能热轧汽车用钢,其典型组织为铁素体上分布着尺寸约3 nm的(Mo, Ti)C析出物,铁素体实现高塑性和高凸缘性能,纳米级析出物提供约300 MPa的强度贡献,细小弥散的析出粒子不容易引起应力集中,不会损害凸缘性能.由此可以看出,铁素体+纳米级析出的组织设计是同时提高强度和凸缘性能的有效方式,而如何大幅提高析出强化增量是研究重点.根据Orowan-Ashby析出强化机制[8 ] ,析出强化增量主要受析出粒子的尺寸和体积分数影响.析出粒子尺寸越细小,体积分数越高,则析出强化增量越大.在一定的体积分数的情况下,析出粒子越分散,析出粒子尺寸越细小,析出强化增量越大.20世纪70年代,Honeycombe等[9 ,10 ] 发现在γ →α 相变过程中,析出粒子呈平行排列称之为相间析出,析出粒子分散度大,可以在保证细小尺寸的情况下获得高的体积分数,Yen等[11 ] 研究表明,尺寸小于5 nm的TiC相间析出粒子可提供约400 MPa的强化增量,引起了国内外广泛关注. ...
Interphase precipitation of nanometer-sized carbides in a titanium-molybdenum-bearing low-carbon steel
3
2011
... Funakawa等[6 ,7 ] 采用铁素体+纳米级析出物的组织调控方式在工业生产线开发出780 MPa级别高性能热轧汽车用钢,其典型组织为铁素体上分布着尺寸约3 nm的(Mo, Ti)C析出物,铁素体实现高塑性和高凸缘性能,纳米级析出物提供约300 MPa的强度贡献,细小弥散的析出粒子不容易引起应力集中,不会损害凸缘性能.由此可以看出,铁素体+纳米级析出的组织设计是同时提高强度和凸缘性能的有效方式,而如何大幅提高析出强化增量是研究重点.根据Orowan-Ashby析出强化机制[8 ] ,析出强化增量主要受析出粒子的尺寸和体积分数影响.析出粒子尺寸越细小,体积分数越高,则析出强化增量越大.在一定的体积分数的情况下,析出粒子越分散,析出粒子尺寸越细小,析出强化增量越大.20世纪70年代,Honeycombe等[9 ,10 ] 发现在γ →α 相变过程中,析出粒子呈平行排列称之为相间析出,析出粒子分散度大,可以在保证细小尺寸的情况下获得高的体积分数,Yen等[11 ] 研究表明,尺寸小于5 nm的TiC相间析出粒子可提供约400 MPa的强化增量,引起了国内外广泛关注. ...
... 铁素体基体上的析出可以分为位错线上析出、过饱和析出和相间析出,而对于具有相间析出特征的TEM样品,通过倾转试样使得析出物的晶体学面的法线方向与透射电镜的电子束入射方向基本平行时,才能观察到相间析出特征[11 ] ,本实验采用此种手段来观察不同等温温度下的析出物是否具有相间析出特征. ...
... 碳化物暗场像和SAED花样如图3 d所示,碳化物具有典型NaCl类型的晶体结构,与基体存在Nishiyama-Wassermann (N-W)位向关系: ( 2 ¯ 00 ) f e r r i t e ( 02 2 ¯ ) M C ferrite // [111]M C .通过测量,可得到晶面间距d ( 02 2 ¯ ) aM C = 0.414 nm,明显小于TiC的晶格常数0.433 nm[29 ] .Funakawa等[6 ] 通过X射线衍射(XRD)对具有NaCl型的复合碳化物(Ti, Mo)C进行了测量,晶格常数为0.433 nm.Yen等[11 ] 通过扫描透射电子显微镜高角环形暗场像(HAADF-STEM)研究发现,碳化物中含有大量的Ti和Mo,晶格常数范围为0.423~0.430 nm.Jang等[13 ] 通过对比研究0.04C-0.1Ti和0.04C-0.1Ti-0.2Mo模型合金,结果发现,与无Mo的碳化物TiC相比,Mo取代Ti形成的复合型碳化物(Ti, Mo)C,导致晶格常数由TiC的0.434 nm降低到(Ti, Mo)C的0.425 nm,缓解了碳化物和铁素体基体之间的晶格失配,促进了碳化物在铁素体基体上形核.由于本工作中的碳化物尺寸细小,EDX无法定量确定其组分,根据以上研究结果推测,碳化物为NaCl型(Ti, Mo)C,下文的析出动力学中估算其组分.综上可知,实验用钢中存在2种完全不同的析出物,分别为与铁素体基体保持K-S取向关系的ε -Cu和N-W取向关系的(Ti, Mo)C. ...
Precipitation hardening of high-strength low-alloy steels by nanometer-sized carbides
1
2009
... 采用复合微合金化技术可细化析出粒子尺寸和提高体积分数,进一步提高析出强化效果.Chen等[12 ] 和Jang等[13 ] 对比研究了Ti系、Ti-Nb系和Ti-Mo系热轧高强钢在相同工艺条件下的析出粒子尺寸d ,其大小满足d (Ti, Mo)C < d (Ti, Nb)C < d TiC ;Kamikawa等[14 ] 研究了TiC和(Ti, Mo)C在铁素体上的析出行为,Ti-Mo钢的析出强化能力远大于Ti钢;采用Ti-V成分设计[15 ] ,可实现与Ti-Mo同样的析出强化效果.Chen等[16 ] 对比研究了Mo对Ti-Nb系热轧高强钢在铁素体上的析出尺寸的影响规律,结果表明,含Mo型析出物尺寸为2.8 nm,而无Mo型为4.1 nm.由此可以看出,采用Ti-Mo复合的成分设计可很好地提高析出强化效果.通过工艺参数优化,亦可进一步提高析出强化增量,轧后采用超快速冷却[17 ] ,尺寸小于5 nm的析出粒子体积分数增加30%,析出强化增量提高30 MPa.Jha等[18 ] 和张可等[19 ,20 ] 分别采用复合添加大量的Ti、Nb、Mo、V的成分设计路线,结果表明经合适轧制工艺和卷取温度保温后,在铁素体基体上弥散析出多元复合第二相析出粒子,提供的析出强化增量可达到400 MPa级以上,但是为了使微合金元素充分固溶,需要进行较高的加热固溶温度. ...
Stability of (Ti, M )C (M = Nb, V, Mo and W) carbide in steels using first-principles calculations
3
2012
... 采用复合微合金化技术可细化析出粒子尺寸和提高体积分数,进一步提高析出强化效果.Chen等[12 ] 和Jang等[13 ] 对比研究了Ti系、Ti-Nb系和Ti-Mo系热轧高强钢在相同工艺条件下的析出粒子尺寸d ,其大小满足d (Ti, Mo)C < d (Ti, Nb)C < d TiC ;Kamikawa等[14 ] 研究了TiC和(Ti, Mo)C在铁素体上的析出行为,Ti-Mo钢的析出强化能力远大于Ti钢;采用Ti-V成分设计[15 ] ,可实现与Ti-Mo同样的析出强化效果.Chen等[16 ] 对比研究了Mo对Ti-Nb系热轧高强钢在铁素体上的析出尺寸的影响规律,结果表明,含Mo型析出物尺寸为2.8 nm,而无Mo型为4.1 nm.由此可以看出,采用Ti-Mo复合的成分设计可很好地提高析出强化效果.通过工艺参数优化,亦可进一步提高析出强化增量,轧后采用超快速冷却[17 ] ,尺寸小于5 nm的析出粒子体积分数增加30%,析出强化增量提高30 MPa.Jha等[18 ] 和张可等[19 ,20 ] 分别采用复合添加大量的Ti、Nb、Mo、V的成分设计路线,结果表明经合适轧制工艺和卷取温度保温后,在铁素体基体上弥散析出多元复合第二相析出粒子,提供的析出强化增量可达到400 MPa级以上,但是为了使微合金元素充分固溶,需要进行较高的加热固溶温度. ...
... 碳化物暗场像和SAED花样如图3 d所示,碳化物具有典型NaCl类型的晶体结构,与基体存在Nishiyama-Wassermann (N-W)位向关系: ( 2 ¯ 00 ) f e r r i t e ( 02 2 ¯ ) M C ferrite // [111]M C .通过测量,可得到晶面间距d ( 02 2 ¯ ) aM C = 0.414 nm,明显小于TiC的晶格常数0.433 nm[29 ] .Funakawa等[6 ] 通过X射线衍射(XRD)对具有NaCl型的复合碳化物(Ti, Mo)C进行了测量,晶格常数为0.433 nm.Yen等[11 ] 通过扫描透射电子显微镜高角环形暗场像(HAADF-STEM)研究发现,碳化物中含有大量的Ti和Mo,晶格常数范围为0.423~0.430 nm.Jang等[13 ] 通过对比研究0.04C-0.1Ti和0.04C-0.1Ti-0.2Mo模型合金,结果发现,与无Mo的碳化物TiC相比,Mo取代Ti形成的复合型碳化物(Ti, Mo)C,导致晶格常数由TiC的0.434 nm降低到(Ti, Mo)C的0.425 nm,缓解了碳化物和铁素体基体之间的晶格失配,促进了碳化物在铁素体基体上形核.由于本工作中的碳化物尺寸细小,EDX无法定量确定其组分,根据以上研究结果推测,碳化物为NaCl型(Ti, Mo)C,下文的析出动力学中估算其组分.综上可知,实验用钢中存在2种完全不同的析出物,分别为与铁素体基体保持K-S取向关系的ε -Cu和N-W取向关系的(Ti, Mo)C. ...
... (Ti, Mo)C中Ti/Mo原子比是探究Mo在复合碳化物作用的重要内容,也是化学成分设计的关键环节.Jang等[13 ] 对含Ti-Mo钢在630℃等温时效析出实验研究发现,碳化物中Ti/Mo比随析出物尺寸的增大而增加,当碳化物尺寸在5~14 nm内,(Ti, Mo)C析出物中Ti/Mo比为2.0~4.3.Wang等[42 ] 通过三维原子探针(APT)研究了Ti-Mo微合金钢在890℃进行热变形和不进行热变形时(Ti, Mo)C化学组分的演变规律,结果表明热变形对(Ti, Mo)C中的化学组分影响不大,热变形后并在650℃等温时Ti/Mo比为2.7,而不变形时为2.6.Dhara等[43 ] 采用APT和小角度中子散射(SANS)研究(Ti, Mo)C的组分变化,结果表明650℃形成的(Ti, Mo)C,当析出粒子尺寸的Guinier半径> 3 nm时,碳化物中的Ti/Mo比接近于平衡态的2.5,而Timokhina等[44 ] 研究发现,650℃保温1700 s后,(Ti, Mo)C的Ti/Mo比为3.3.综上可知,(Ti, Mo)C碳化物在630~650℃保温期间,Ti/Mo比基本在2.5~4.3范围内,在本实验600~660℃温度范围内,如图4 a所示,Ti/Mo比为2.5~4.5,基本与实验结果相近.当温度由600℃提高到660℃时,化学式系数x 单调增加,Ti/Mo比为由2.5增大到4.5,碳化物组成由Ti0.71 Mo0.29 C演变为Ti0.79 Mo0.21 C,也就是说MoC在低温时析出分数占比较高,而在高温时占比降低.这与组成复合碳化物的TiC和MoC的固溶度积有关,TiC的固溶度积比较小,为难固溶相,而MoC的固溶度积较大,为易固溶相.随着温度升高,2者的固溶度积均增大,固溶[Ti]和[Mo]均增大,但固溶[Mo]增加幅度更大,如图4 d所示,导致复合碳化物中MoC比例下降,Ti/Mo比增大. ...
Tensile behavior of Ti, Mo-added low carbon steels with interphase precipitation
1
2014
... 采用复合微合金化技术可细化析出粒子尺寸和提高体积分数,进一步提高析出强化效果.Chen等[12 ] 和Jang等[13 ] 对比研究了Ti系、Ti-Nb系和Ti-Mo系热轧高强钢在相同工艺条件下的析出粒子尺寸d ,其大小满足d (Ti, Mo)C < d (Ti, Nb)C < d TiC ;Kamikawa等[14 ] 研究了TiC和(Ti, Mo)C在铁素体上的析出行为,Ti-Mo钢的析出强化能力远大于Ti钢;采用Ti-V成分设计[15 ] ,可实现与Ti-Mo同样的析出强化效果.Chen等[16 ] 对比研究了Mo对Ti-Nb系热轧高强钢在铁素体上的析出尺寸的影响规律,结果表明,含Mo型析出物尺寸为2.8 nm,而无Mo型为4.1 nm.由此可以看出,采用Ti-Mo复合的成分设计可很好地提高析出强化效果.通过工艺参数优化,亦可进一步提高析出强化增量,轧后采用超快速冷却[17 ] ,尺寸小于5 nm的析出粒子体积分数增加30%,析出强化增量提高30 MPa.Jha等[18 ] 和张可等[19 ,20 ] 分别采用复合添加大量的Ti、Nb、Mo、V的成分设计路线,结果表明经合适轧制工艺和卷取温度保温后,在铁素体基体上弥散析出多元复合第二相析出粒子,提供的析出强化增量可达到400 MPa级以上,但是为了使微合金元素充分固溶,需要进行较高的加热固溶温度. ...
V-Ti微合金钢的组织性能及相间析出行为
1
2014
... 采用复合微合金化技术可细化析出粒子尺寸和提高体积分数,进一步提高析出强化效果.Chen等[12 ] 和Jang等[13 ] 对比研究了Ti系、Ti-Nb系和Ti-Mo系热轧高强钢在相同工艺条件下的析出粒子尺寸d ,其大小满足d (Ti, Mo)C < d (Ti, Nb)C < d TiC ;Kamikawa等[14 ] 研究了TiC和(Ti, Mo)C在铁素体上的析出行为,Ti-Mo钢的析出强化能力远大于Ti钢;采用Ti-V成分设计[15 ] ,可实现与Ti-Mo同样的析出强化效果.Chen等[16 ] 对比研究了Mo对Ti-Nb系热轧高强钢在铁素体上的析出尺寸的影响规律,结果表明,含Mo型析出物尺寸为2.8 nm,而无Mo型为4.1 nm.由此可以看出,采用Ti-Mo复合的成分设计可很好地提高析出强化效果.通过工艺参数优化,亦可进一步提高析出强化增量,轧后采用超快速冷却[17 ] ,尺寸小于5 nm的析出粒子体积分数增加30%,析出强化增量提高30 MPa.Jha等[18 ] 和张可等[19 ,20 ] 分别采用复合添加大量的Ti、Nb、Mo、V的成分设计路线,结果表明经合适轧制工艺和卷取温度保温后,在铁素体基体上弥散析出多元复合第二相析出粒子,提供的析出强化增量可达到400 MPa级以上,但是为了使微合金元素充分固溶,需要进行较高的加热固溶温度. ...
V-Ti微合金钢的组织性能及相间析出行为
1
2014
... 采用复合微合金化技术可细化析出粒子尺寸和提高体积分数,进一步提高析出强化效果.Chen等[12 ] 和Jang等[13 ] 对比研究了Ti系、Ti-Nb系和Ti-Mo系热轧高强钢在相同工艺条件下的析出粒子尺寸d ,其大小满足d (Ti, Mo)C < d (Ti, Nb)C < d TiC ;Kamikawa等[14 ] 研究了TiC和(Ti, Mo)C在铁素体上的析出行为,Ti-Mo钢的析出强化能力远大于Ti钢;采用Ti-V成分设计[15 ] ,可实现与Ti-Mo同样的析出强化效果.Chen等[16 ] 对比研究了Mo对Ti-Nb系热轧高强钢在铁素体上的析出尺寸的影响规律,结果表明,含Mo型析出物尺寸为2.8 nm,而无Mo型为4.1 nm.由此可以看出,采用Ti-Mo复合的成分设计可很好地提高析出强化效果.通过工艺参数优化,亦可进一步提高析出强化增量,轧后采用超快速冷却[17 ] ,尺寸小于5 nm的析出粒子体积分数增加30%,析出强化增量提高30 MPa.Jha等[18 ] 和张可等[19 ,20 ] 分别采用复合添加大量的Ti、Nb、Mo、V的成分设计路线,结果表明经合适轧制工艺和卷取温度保温后,在铁素体基体上弥散析出多元复合第二相析出粒子,提供的析出强化增量可达到400 MPa级以上,但是为了使微合金元素充分固溶,需要进行较高的加热固溶温度. ...
Microstructure characterization of nanometer carbides heterogeneous precipitation in Ti-Nb and Ti-Nb-Mo steel
1
2014
... 采用复合微合金化技术可细化析出粒子尺寸和提高体积分数,进一步提高析出强化效果.Chen等[12 ] 和Jang等[13 ] 对比研究了Ti系、Ti-Nb系和Ti-Mo系热轧高强钢在相同工艺条件下的析出粒子尺寸d ,其大小满足d (Ti, Mo)C < d (Ti, Nb)C < d TiC ;Kamikawa等[14 ] 研究了TiC和(Ti, Mo)C在铁素体上的析出行为,Ti-Mo钢的析出强化能力远大于Ti钢;采用Ti-V成分设计[15 ] ,可实现与Ti-Mo同样的析出强化效果.Chen等[16 ] 对比研究了Mo对Ti-Nb系热轧高强钢在铁素体上的析出尺寸的影响规律,结果表明,含Mo型析出物尺寸为2.8 nm,而无Mo型为4.1 nm.由此可以看出,采用Ti-Mo复合的成分设计可很好地提高析出强化效果.通过工艺参数优化,亦可进一步提高析出强化增量,轧后采用超快速冷却[17 ] ,尺寸小于5 nm的析出粒子体积分数增加30%,析出强化增量提高30 MPa.Jha等[18 ] 和张可等[19 ,20 ] 分别采用复合添加大量的Ti、Nb、Mo、V的成分设计路线,结果表明经合适轧制工艺和卷取温度保温后,在铁素体基体上弥散析出多元复合第二相析出粒子,提供的析出强化增量可达到400 MPa级以上,但是为了使微合金元素充分固溶,需要进行较高的加热固溶温度. ...
Microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of high strength microalloyed steels: Ultra fast cooling (UFC) versus accelerated cooling (ACC)
1
2013
... 采用复合微合金化技术可细化析出粒子尺寸和提高体积分数,进一步提高析出强化效果.Chen等[12 ] 和Jang等[13 ] 对比研究了Ti系、Ti-Nb系和Ti-Mo系热轧高强钢在相同工艺条件下的析出粒子尺寸d ,其大小满足d (Ti, Mo)C < d (Ti, Nb)C < d TiC ;Kamikawa等[14 ] 研究了TiC和(Ti, Mo)C在铁素体上的析出行为,Ti-Mo钢的析出强化能力远大于Ti钢;采用Ti-V成分设计[15 ] ,可实现与Ti-Mo同样的析出强化效果.Chen等[16 ] 对比研究了Mo对Ti-Nb系热轧高强钢在铁素体上的析出尺寸的影响规律,结果表明,含Mo型析出物尺寸为2.8 nm,而无Mo型为4.1 nm.由此可以看出,采用Ti-Mo复合的成分设计可很好地提高析出强化效果.通过工艺参数优化,亦可进一步提高析出强化增量,轧后采用超快速冷却[17 ] ,尺寸小于5 nm的析出粒子体积分数增加30%,析出强化增量提高30 MPa.Jha等[18 ] 和张可等[19 ,20 ] 分别采用复合添加大量的Ti、Nb、Mo、V的成分设计路线,结果表明经合适轧制工艺和卷取温度保温后,在铁素体基体上弥散析出多元复合第二相析出粒子,提供的析出强化增量可达到400 MPa级以上,但是为了使微合金元素充分固溶,需要进行较高的加热固溶温度. ...
Design and development of precipitate strengthened advanced high strength steel for automotive application
1
2013
... 采用复合微合金化技术可细化析出粒子尺寸和提高体积分数,进一步提高析出强化效果.Chen等[12 ] 和Jang等[13 ] 对比研究了Ti系、Ti-Nb系和Ti-Mo系热轧高强钢在相同工艺条件下的析出粒子尺寸d ,其大小满足d (Ti, Mo)C < d (Ti, Nb)C < d TiC ;Kamikawa等[14 ] 研究了TiC和(Ti, Mo)C在铁素体上的析出行为,Ti-Mo钢的析出强化能力远大于Ti钢;采用Ti-V成分设计[15 ] ,可实现与Ti-Mo同样的析出强化效果.Chen等[16 ] 对比研究了Mo对Ti-Nb系热轧高强钢在铁素体上的析出尺寸的影响规律,结果表明,含Mo型析出物尺寸为2.8 nm,而无Mo型为4.1 nm.由此可以看出,采用Ti-Mo复合的成分设计可很好地提高析出强化效果.通过工艺参数优化,亦可进一步提高析出强化增量,轧后采用超快速冷却[17 ] ,尺寸小于5 nm的析出粒子体积分数增加30%,析出强化增量提高30 MPa.Jha等[18 ] 和张可等[19 ,20 ] 分别采用复合添加大量的Ti、Nb、Mo、V的成分设计路线,结果表明经合适轧制工艺和卷取温度保温后,在铁素体基体上弥散析出多元复合第二相析出粒子,提供的析出强化增量可达到400 MPa级以上,但是为了使微合金元素充分固溶,需要进行较高的加热固溶温度. ...
卷取温度对Ti-V-Mo复合微合金化超高强度钢组织及力学性能的影响
1
2016
... 采用复合微合金化技术可细化析出粒子尺寸和提高体积分数,进一步提高析出强化效果.Chen等[12 ] 和Jang等[13 ] 对比研究了Ti系、Ti-Nb系和Ti-Mo系热轧高强钢在相同工艺条件下的析出粒子尺寸d ,其大小满足d (Ti, Mo)C < d (Ti, Nb)C < d TiC ;Kamikawa等[14 ] 研究了TiC和(Ti, Mo)C在铁素体上的析出行为,Ti-Mo钢的析出强化能力远大于Ti钢;采用Ti-V成分设计[15 ] ,可实现与Ti-Mo同样的析出强化效果.Chen等[16 ] 对比研究了Mo对Ti-Nb系热轧高强钢在铁素体上的析出尺寸的影响规律,结果表明,含Mo型析出物尺寸为2.8 nm,而无Mo型为4.1 nm.由此可以看出,采用Ti-Mo复合的成分设计可很好地提高析出强化效果.通过工艺参数优化,亦可进一步提高析出强化增量,轧后采用超快速冷却[17 ] ,尺寸小于5 nm的析出粒子体积分数增加30%,析出强化增量提高30 MPa.Jha等[18 ] 和张可等[19 ,20 ] 分别采用复合添加大量的Ti、Nb、Mo、V的成分设计路线,结果表明经合适轧制工艺和卷取温度保温后,在铁素体基体上弥散析出多元复合第二相析出粒子,提供的析出强化增量可达到400 MPa级以上,但是为了使微合金元素充分固溶,需要进行较高的加热固溶温度. ...
卷取温度对Ti-V-Mo复合微合金化超高强度钢组织及力学性能的影响
1
2016
... 采用复合微合金化技术可细化析出粒子尺寸和提高体积分数,进一步提高析出强化效果.Chen等[12 ] 和Jang等[13 ] 对比研究了Ti系、Ti-Nb系和Ti-Mo系热轧高强钢在相同工艺条件下的析出粒子尺寸d ,其大小满足d (Ti, Mo)C < d (Ti, Nb)C < d TiC ;Kamikawa等[14 ] 研究了TiC和(Ti, Mo)C在铁素体上的析出行为,Ti-Mo钢的析出强化能力远大于Ti钢;采用Ti-V成分设计[15 ] ,可实现与Ti-Mo同样的析出强化效果.Chen等[16 ] 对比研究了Mo对Ti-Nb系热轧高强钢在铁素体上的析出尺寸的影响规律,结果表明,含Mo型析出物尺寸为2.8 nm,而无Mo型为4.1 nm.由此可以看出,采用Ti-Mo复合的成分设计可很好地提高析出强化效果.通过工艺参数优化,亦可进一步提高析出强化增量,轧后采用超快速冷却[17 ] ,尺寸小于5 nm的析出粒子体积分数增加30%,析出强化增量提高30 MPa.Jha等[18 ] 和张可等[19 ,20 ] 分别采用复合添加大量的Ti、Nb、Mo、V的成分设计路线,结果表明经合适轧制工艺和卷取温度保温后,在铁素体基体上弥散析出多元复合第二相析出粒子,提供的析出强化增量可达到400 MPa级以上,但是为了使微合金元素充分固溶,需要进行较高的加热固溶温度. ...
Ti-V-Mo复合微合金钢中(Ti, V, Mo)C在γ /α 中沉淀析出的动力学
1
2018
... 采用复合微合金化技术可细化析出粒子尺寸和提高体积分数,进一步提高析出强化效果.Chen等[12 ] 和Jang等[13 ] 对比研究了Ti系、Ti-Nb系和Ti-Mo系热轧高强钢在相同工艺条件下的析出粒子尺寸d ,其大小满足d (Ti, Mo)C < d (Ti, Nb)C < d TiC ;Kamikawa等[14 ] 研究了TiC和(Ti, Mo)C在铁素体上的析出行为,Ti-Mo钢的析出强化能力远大于Ti钢;采用Ti-V成分设计[15 ] ,可实现与Ti-Mo同样的析出强化效果.Chen等[16 ] 对比研究了Mo对Ti-Nb系热轧高强钢在铁素体上的析出尺寸的影响规律,结果表明,含Mo型析出物尺寸为2.8 nm,而无Mo型为4.1 nm.由此可以看出,采用Ti-Mo复合的成分设计可很好地提高析出强化效果.通过工艺参数优化,亦可进一步提高析出强化增量,轧后采用超快速冷却[17 ] ,尺寸小于5 nm的析出粒子体积分数增加30%,析出强化增量提高30 MPa.Jha等[18 ] 和张可等[19 ,20 ] 分别采用复合添加大量的Ti、Nb、Mo、V的成分设计路线,结果表明经合适轧制工艺和卷取温度保温后,在铁素体基体上弥散析出多元复合第二相析出粒子,提供的析出强化增量可达到400 MPa级以上,但是为了使微合金元素充分固溶,需要进行较高的加热固溶温度. ...
Ti-V-Mo复合微合金钢中(Ti, V, Mo)C在γ /α 中沉淀析出的动力学
1
2018
... 采用复合微合金化技术可细化析出粒子尺寸和提高体积分数,进一步提高析出强化效果.Chen等[12 ] 和Jang等[13 ] 对比研究了Ti系、Ti-Nb系和Ti-Mo系热轧高强钢在相同工艺条件下的析出粒子尺寸d ,其大小满足d (Ti, Mo)C < d (Ti, Nb)C < d TiC ;Kamikawa等[14 ] 研究了TiC和(Ti, Mo)C在铁素体上的析出行为,Ti-Mo钢的析出强化能力远大于Ti钢;采用Ti-V成分设计[15 ] ,可实现与Ti-Mo同样的析出强化效果.Chen等[16 ] 对比研究了Mo对Ti-Nb系热轧高强钢在铁素体上的析出尺寸的影响规律,结果表明,含Mo型析出物尺寸为2.8 nm,而无Mo型为4.1 nm.由此可以看出,采用Ti-Mo复合的成分设计可很好地提高析出强化效果.通过工艺参数优化,亦可进一步提高析出强化增量,轧后采用超快速冷却[17 ] ,尺寸小于5 nm的析出粒子体积分数增加30%,析出强化增量提高30 MPa.Jha等[18 ] 和张可等[19 ,20 ] 分别采用复合添加大量的Ti、Nb、Mo、V的成分设计路线,结果表明经合适轧制工艺和卷取温度保温后,在铁素体基体上弥散析出多元复合第二相析出粒子,提供的析出强化增量可达到400 MPa级以上,但是为了使微合金元素充分固溶,需要进行较高的加热固溶温度. ...
连续冷却过程中含Cu相在钢中析出行为的研究
1
2010
... 除了微合金元素碳化物的相间析出之外,Cu也可发生相间析出,大幅提高析出强化效果.李闯等[21 ] 研究发现,在冷速低于5℃/s的连续冷却过程中可获得大量Cu的相间析出亚稳相.Dunne等[22 ,23 ] 将含Cu 1.1% (质量分数)的钢热轧后快速冷却至600℃进行等温时效,在铁素体中获得了大量的ε -Cu相间析出.因此,综合利用碳化物和Cu的共析出,大幅提高强度是一个可行的工艺方案.Gagliano和Fine[24 ] 对Cu-Nb钢中bcc-Cu和NbC共析出行为和析出动力学进行了研究,结果表明,NbC和bcc-Cu在铁素体中的析出形核和长大都是奥氏体化温度的函数,bcc-Cu的形核率比NbC高一个数量级,这就意味着bcc-Cu优先析出,然后是NbC析出.Chen等[25 ] 对TiC与ε -Cu共析出进行了探索,扫描透射电镜(STEM)结果显示,ε -Cu总是出现在具有相间析出的TiC相连位置处,故推测TiC优先析出,ε -Cu随后在TiC上形核长大,其析出次序与Gagliano结果[24 ] 相反.由此可见,关于Cu与碳化物的析出次序存在多种解释,甚至是矛盾之处,需要对其进行澄清与梳理. ...
连续冷却过程中含Cu相在钢中析出行为的研究
1
2010
... 除了微合金元素碳化物的相间析出之外,Cu也可发生相间析出,大幅提高析出强化效果.李闯等[21 ] 研究发现,在冷速低于5℃/s的连续冷却过程中可获得大量Cu的相间析出亚稳相.Dunne等[22 ,23 ] 将含Cu 1.1% (质量分数)的钢热轧后快速冷却至600℃进行等温时效,在铁素体中获得了大量的ε -Cu相间析出.因此,综合利用碳化物和Cu的共析出,大幅提高强度是一个可行的工艺方案.Gagliano和Fine[24 ] 对Cu-Nb钢中bcc-Cu和NbC共析出行为和析出动力学进行了研究,结果表明,NbC和bcc-Cu在铁素体中的析出形核和长大都是奥氏体化温度的函数,bcc-Cu的形核率比NbC高一个数量级,这就意味着bcc-Cu优先析出,然后是NbC析出.Chen等[25 ] 对TiC与ε -Cu共析出进行了探索,扫描透射电镜(STEM)结果显示,ε -Cu总是出现在具有相间析出的TiC相连位置处,故推测TiC优先析出,ε -Cu随后在TiC上形核长大,其析出次序与Gagliano结果[24 ] 相反.由此可见,关于Cu与碳化物的析出次序存在多种解释,甚至是矛盾之处,需要对其进行澄清与梳理. ...
Review: Interaction of precipitation with recrystallisation and phase transformation in low alloy steels
2
2010
... 除了微合金元素碳化物的相间析出之外,Cu也可发生相间析出,大幅提高析出强化效果.李闯等[21 ] 研究发现,在冷速低于5℃/s的连续冷却过程中可获得大量Cu的相间析出亚稳相.Dunne等[22 ,23 ] 将含Cu 1.1% (质量分数)的钢热轧后快速冷却至600℃进行等温时效,在铁素体中获得了大量的ε -Cu相间析出.因此,综合利用碳化物和Cu的共析出,大幅提高强度是一个可行的工艺方案.Gagliano和Fine[24 ] 对Cu-Nb钢中bcc-Cu和NbC共析出行为和析出动力学进行了研究,结果表明,NbC和bcc-Cu在铁素体中的析出形核和长大都是奥氏体化温度的函数,bcc-Cu的形核率比NbC高一个数量级,这就意味着bcc-Cu优先析出,然后是NbC析出.Chen等[25 ] 对TiC与ε -Cu共析出进行了探索,扫描透射电镜(STEM)结果显示,ε -Cu总是出现在具有相间析出的TiC相连位置处,故推测TiC优先析出,ε -Cu随后在TiC上形核长大,其析出次序与Gagliano结果[24 ] 相反.由此可见,关于Cu与碳化物的析出次序存在多种解释,甚至是矛盾之处,需要对其进行澄清与梳理. ...
... 600℃等温条件下的析出物形貌和选区电子衍射(SAED)花样如图2 所示.从TEM结果可以看出,主要是以Cu的析出为主,碳化物析出量极少,未发现有碳化物的相间析出.Cu析出多呈椭圆形,平均半长轴为27.0 nm,展弦比为2.30,大量的Cu析出多出现在位错和铁素体晶界上,如图2 a和b箭头所示,铁素体晶粒内部存在大量的缠结位错,在靠近晶界位置,部分区域发现存在极少量的Cu的相间析出行为如图2 b所示,说明Cu以位错线上和基体2种方式形核,通过统计分析,位错线上析出与基体上析出比例约为4∶1.Cu的TEM明暗场和SAED花样如图2 c和d所示.由图可知,Cu析出物是具有fcc结构的ε -Cu,与铁素体基体满足Kurdjumov-Sachs (K-S)取向关系[22 ] :(1 ¯ 10 ) ferrite // ( 11 1 ¯ ) ε - C u [ 11 1 ¯ ] ferrite // [ 011 ] ε - C u d ( 11 1 ¯ ) aε- Cu
Isothermal transformation products in a Cu-bearing high strength low alloy steel
1
1996
... 除了微合金元素碳化物的相间析出之外,Cu也可发生相间析出,大幅提高析出强化效果.李闯等[21 ] 研究发现,在冷速低于5℃/s的连续冷却过程中可获得大量Cu的相间析出亚稳相.Dunne等[22 ,23 ] 将含Cu 1.1% (质量分数)的钢热轧后快速冷却至600℃进行等温时效,在铁素体中获得了大量的ε -Cu相间析出.因此,综合利用碳化物和Cu的共析出,大幅提高强度是一个可行的工艺方案.Gagliano和Fine[24 ] 对Cu-Nb钢中bcc-Cu和NbC共析出行为和析出动力学进行了研究,结果表明,NbC和bcc-Cu在铁素体中的析出形核和长大都是奥氏体化温度的函数,bcc-Cu的形核率比NbC高一个数量级,这就意味着bcc-Cu优先析出,然后是NbC析出.Chen等[25 ] 对TiC与ε -Cu共析出进行了探索,扫描透射电镜(STEM)结果显示,ε -Cu总是出现在具有相间析出的TiC相连位置处,故推测TiC优先析出,ε -Cu随后在TiC上形核长大,其析出次序与Gagliano结果[24 ] 相反.由此可见,关于Cu与碳化物的析出次序存在多种解释,甚至是矛盾之处,需要对其进行澄清与梳理. ...
Characterization of the nucleation and growth behavior of copper precipitates in low-carbon steels
2
2004
... 除了微合金元素碳化物的相间析出之外,Cu也可发生相间析出,大幅提高析出强化效果.李闯等[21 ] 研究发现,在冷速低于5℃/s的连续冷却过程中可获得大量Cu的相间析出亚稳相.Dunne等[22 ,23 ] 将含Cu 1.1% (质量分数)的钢热轧后快速冷却至600℃进行等温时效,在铁素体中获得了大量的ε -Cu相间析出.因此,综合利用碳化物和Cu的共析出,大幅提高强度是一个可行的工艺方案.Gagliano和Fine[24 ] 对Cu-Nb钢中bcc-Cu和NbC共析出行为和析出动力学进行了研究,结果表明,NbC和bcc-Cu在铁素体中的析出形核和长大都是奥氏体化温度的函数,bcc-Cu的形核率比NbC高一个数量级,这就意味着bcc-Cu优先析出,然后是NbC析出.Chen等[25 ] 对TiC与ε -Cu共析出进行了探索,扫描透射电镜(STEM)结果显示,ε -Cu总是出现在具有相间析出的TiC相连位置处,故推测TiC优先析出,ε -Cu随后在TiC上形核长大,其析出次序与Gagliano结果[24 ] 相反.由此可见,关于Cu与碳化物的析出次序存在多种解释,甚至是矛盾之处,需要对其进行澄清与梳理. ...
... [24 ]相反.由此可见,关于Cu与碳化物的析出次序存在多种解释,甚至是矛盾之处,需要对其进行澄清与梳理. ...
A novel technique for developing a dual-phase steel with a lower strength difference between ferrite and martensite
2
2020
... 除了微合金元素碳化物的相间析出之外,Cu也可发生相间析出,大幅提高析出强化效果.李闯等[21 ] 研究发现,在冷速低于5℃/s的连续冷却过程中可获得大量Cu的相间析出亚稳相.Dunne等[22 ,23 ] 将含Cu 1.1% (质量分数)的钢热轧后快速冷却至600℃进行等温时效,在铁素体中获得了大量的ε -Cu相间析出.因此,综合利用碳化物和Cu的共析出,大幅提高强度是一个可行的工艺方案.Gagliano和Fine[24 ] 对Cu-Nb钢中bcc-Cu和NbC共析出行为和析出动力学进行了研究,结果表明,NbC和bcc-Cu在铁素体中的析出形核和长大都是奥氏体化温度的函数,bcc-Cu的形核率比NbC高一个数量级,这就意味着bcc-Cu优先析出,然后是NbC析出.Chen等[25 ] 对TiC与ε -Cu共析出进行了探索,扫描透射电镜(STEM)结果显示,ε -Cu总是出现在具有相间析出的TiC相连位置处,故推测TiC优先析出,ε -Cu随后在TiC上形核长大,其析出次序与Gagliano结果[24 ] 相反.由此可见,关于Cu与碳化物的析出次序存在多种解释,甚至是矛盾之处,需要对其进行澄清与梳理. ...
... 当温度升高到620℃时,如图3 a所示,在铁素体基体上出现大量具有相间析出特征的碳化物,其平均尺寸为4.1 nm,列间距为39.1 nm,同时伴随有ε -Cu的弥散析出,ε -Cu平均半长轴为33.3 nm,展弦比为2.33,与铁素体基体也满足K-S位相关系,无论ε -Cu析出尺寸多大,在相间析出列之间的位置没有单独的ε -Cu,这与Chen等[25 ] 的研究结果基本一致.当温度升高到640和660℃时,典型的TEM像如图3 b和c所示,基体上ε -Cu析出较少,只有在部分晶界位置出现,绝大多数为碳化物析出,且呈平直型相间析出分布,碳化物形貌多为圆形,在640℃时平均尺寸为5.6 nm,660℃为7.1 nm,相间析出列间距分别为42.7和98.5 nm. ...
An FIM-atom probe study of the precipitation of copper from iron-1.4 at. pct copper. Part I: Field-ion microscopy
1
1973
... Goodman等[26 ] 发现当Cu析出物尺寸大于5 nm为非共格的fcc型ε -Cu,当尺寸超过10 nm时组分接近于纯Cu,而尺寸较小的析出物为共格bcc-Cu,根据析出物尺寸判断析出物基本为fcc型ε -Cu.Guo等[27 ] 发现Fe-1.67Cu-1.26Mn-1.43Ni合金在600℃等温18 h后,ε -Cu析出粒子尺寸为21.0 nm,显著小于本实验中结果.硬度测试表明,本工作中600℃等温过程中铁素体硬度均高于300 HV (如等温2 h对应的显微硬度为315 HV),显著高于Guo等[27 ] 研究中Cu析出前后的显微硬度(Cu析出前的显微硬度约为260 HV,18 h回火后约为230 HV),而且Kao[28 ] 采用类似成分与工艺获得的硬度结果与本实验相近(615℃等温30 min对应的显微硬度为303 HV).由此可见,本实验中的铁素体基体具有更高的位错密度,而且较短时间的回火有利于位错密度的保留,Cu在位错通道的扩散促进了Cu的形核长大,这可能是本实验中Cu粒子尺寸较大的一个原因.因此在后续的动力学计算过程中忽略初期bcc-Cu形核,同时考虑ε -Cu在铁素体位错线和基体上的形核长大. ...
Influence of combined Cu and Nb addition on the quenched microstructure and precipitation during tempering in ultra-low carbon steels
3
2013
... Goodman等[26 ] 发现当Cu析出物尺寸大于5 nm为非共格的fcc型ε -Cu,当尺寸超过10 nm时组分接近于纯Cu,而尺寸较小的析出物为共格bcc-Cu,根据析出物尺寸判断析出物基本为fcc型ε -Cu.Guo等[27 ] 发现Fe-1.67Cu-1.26Mn-1.43Ni合金在600℃等温18 h后,ε -Cu析出粒子尺寸为21.0 nm,显著小于本实验中结果.硬度测试表明,本工作中600℃等温过程中铁素体硬度均高于300 HV (如等温2 h对应的显微硬度为315 HV),显著高于Guo等[27 ] 研究中Cu析出前后的显微硬度(Cu析出前的显微硬度约为260 HV,18 h回火后约为230 HV),而且Kao[28 ] 采用类似成分与工艺获得的硬度结果与本实验相近(615℃等温30 min对应的显微硬度为303 HV).由此可见,本实验中的铁素体基体具有更高的位错密度,而且较短时间的回火有利于位错密度的保留,Cu在位错通道的扩散促进了Cu的形核长大,这可能是本实验中Cu粒子尺寸较大的一个原因.因此在后续的动力学计算过程中忽略初期bcc-Cu形核,同时考虑ε -Cu在铁素体位错线和基体上的形核长大. ...
... [27 ]研究中Cu析出前后的显微硬度(Cu析出前的显微硬度约为260 HV,18 h回火后约为230 HV),而且Kao[28 ] 采用类似成分与工艺获得的硬度结果与本实验相近(615℃等温30 min对应的显微硬度为303 HV).由此可见,本实验中的铁素体基体具有更高的位错密度,而且较短时间的回火有利于位错密度的保留,Cu在位错通道的扩散促进了Cu的形核长大,这可能是本实验中Cu粒子尺寸较大的一个原因.因此在后续的动力学计算过程中忽略初期bcc-Cu形核,同时考虑ε -Cu在铁素体位错线和基体上的形核长大. ...
... 根据动力学计算结果可知,在较低温度(如600℃)下,ε -Cu在铁素体中的位错线上和基体上优先于碳化物析出,大量析出的ε -Cu粒子将有效“钉扎”铁素体基体,阻碍位错运动而保证较高的位错密度,为后续碳化物的析出提供更多的形核地点.从这一角度考虑,ε -Cu的析出将促进碳化物的析出热/动力学.Guo等[27 ] 对比研究了含Cu钢、Nb钢和Nb-Cu钢的时效析出,从其对应的硬度变化趋势看,与含Nb钢相比,含Cu-Nb钢的时效析出硬度峰值前移至与Cu钢时效析出硬度峰值一致的时刻,这似乎可以反映出Cu的析出促进了NbC的析出.在较高温度(如620℃以上)下,碳化物将优先析出,亦会产生对位错的“钉扎”作用,但是温度较高,这种钉扎作用效果减弱,因此在实验结果中,在640~660℃较高温度下难以观察到ε -Cu的加速析出现象.但需要指出的是,2种析出之间的相互作用机制较为复杂,这其中可能涉及晶体学、热/动力学等多方面因素,有待进一步深入探索. ...
Precipitation strengthening of nanometer-sized copper particles and alloy carbides in high strength low alloy steels
1
2008
... Goodman等[26 ] 发现当Cu析出物尺寸大于5 nm为非共格的fcc型ε -Cu,当尺寸超过10 nm时组分接近于纯Cu,而尺寸较小的析出物为共格bcc-Cu,根据析出物尺寸判断析出物基本为fcc型ε -Cu.Guo等[27 ] 发现Fe-1.67Cu-1.26Mn-1.43Ni合金在600℃等温18 h后,ε -Cu析出粒子尺寸为21.0 nm,显著小于本实验中结果.硬度测试表明,本工作中600℃等温过程中铁素体硬度均高于300 HV (如等温2 h对应的显微硬度为315 HV),显著高于Guo等[27 ] 研究中Cu析出前后的显微硬度(Cu析出前的显微硬度约为260 HV,18 h回火后约为230 HV),而且Kao[28 ] 采用类似成分与工艺获得的硬度结果与本实验相近(615℃等温30 min对应的显微硬度为303 HV).由此可见,本实验中的铁素体基体具有更高的位错密度,而且较短时间的回火有利于位错密度的保留,Cu在位错通道的扩散促进了Cu的形核长大,这可能是本实验中Cu粒子尺寸较大的一个原因.因此在后续的动力学计算过程中忽略初期bcc-Cu形核,同时考虑ε -Cu在铁素体位错线和基体上的形核长大. ...
First-principles calculations of mechanical properties of TiC and TiN
5
2009
... 碳化物暗场像和SAED花样如图3 d所示,碳化物具有典型NaCl类型的晶体结构,与基体存在Nishiyama-Wassermann (N-W)位向关系: ( 2 ¯ 00 ) f e r r i t e ( 02 2 ¯ ) M C ferrite // [111]M C .通过测量,可得到晶面间距d ( 02 2 ¯ ) aM C = 0.414 nm,明显小于TiC的晶格常数0.433 nm[29 ] .Funakawa等[6 ] 通过X射线衍射(XRD)对具有NaCl型的复合碳化物(Ti, Mo)C进行了测量,晶格常数为0.433 nm.Yen等[11 ] 通过扫描透射电子显微镜高角环形暗场像(HAADF-STEM)研究发现,碳化物中含有大量的Ti和Mo,晶格常数范围为0.423~0.430 nm.Jang等[13 ] 通过对比研究0.04C-0.1Ti和0.04C-0.1Ti-0.2Mo模型合金,结果发现,与无Mo的碳化物TiC相比,Mo取代Ti形成的复合型碳化物(Ti, Mo)C,导致晶格常数由TiC的0.434 nm降低到(Ti, Mo)C的0.425 nm,缓解了碳化物和铁素体基体之间的晶格失配,促进了碳化物在铁素体基体上形核.由于本工作中的碳化物尺寸细小,EDX无法定量确定其组分,根据以上研究结果推测,碳化物为NaCl型(Ti, Mo)C,下文的析出动力学中估算其组分.综上可知,实验用钢中存在2种完全不同的析出物,分别为与铁素体基体保持K-S取向关系的ε -Cu和N-W取向关系的(Ti, Mo)C. ...
... 表1 [29 ,30 ,35 ~41 ] 为动力学计算中所使用的参数及其取值,析出动力学计算结果如图4 所示.复合碳化物(Ti, Mo)C在550~700℃保温区间,随温度的升高,化学式系数x 单调增加,如图4 a所示,即TiC在(Ti, Mo)C的占比由0.65增加到0.84,由此可得(Ti, Mo)C中Ti/Mo比由1.8增加到5.4.当温度为550~700℃时,随温度的升高,由于固溶度的增大,(Ti, Mo)C与ε -Cu的形核驱动力均单调减小,如图4 b所示,(Ti, Mo)C的驱动力的范围为4.88 × 109 ~4.41 × 109 J/m3 ,而ε -Cu的驱动力的范围为1.67 × 109 ~4.96 × 108 J/m3 ,2者之比由2.45扩大至8.88,可以看出,温度升高大幅降低了ε -Cu析出的驱动力,而(Ti, Mo)C的驱动力变化较小.(Ti, Mo)C与ε -Cu的析出相对开始时间即析出-温度-时间(PTT)曲线如图4 c所示,在550~700℃范围内,ε -Cu的PTT曲线呈典型C形状,鼻尖温度为586℃,当温度范围为550~586℃时,随温度的升高,ε -Cu的相对开始析出时间会越来越短,即孕育期越短;而温度范围为586~700℃时,随温度的升高,ε -Cu的相对开始析出时间会越来越长,即孕育期越长.而在550~700℃范围内,(Ti, Mo)C则呈单调下降趋势,即随温度的降低,(Ti, Mo)C的相对开始析出时间会越来越长,即孕育期越长. ...
... 计算中使用的参数[29 ,30 ,35 ~41 ] ...
... Parameters used in calculations[29 ,30 ,35 -41 ] ...
... [
29 ]
a MoC Lattice constant of MoC at room temperature 0.428 nm [35 ] a Cu Lattice constant of ε -Cu at room temperature 0.362 nm [36 ] a Fe Lattice constant of α -Fe at room temperature 0.287 nm α TiC Linear expansion coefficient of TiC 7.86 × 10-6 K-1 [37 ] α MoC Linear expansion coefficient of MoC 6.88 × 10-6 K-1 [38 ] α Cu Linear expansion coefficient of Cu 16.5 × 10-6 K-1 [39 ] Q Ti Activation energy of Ti in α -Fe 248 kJ·mol-1 [40 ] Q Mo Activation energy of Mo in α -Fe 229 kJ·mol-1 [41 ] Q Cu Activation energy of Cu in α -Fe 284 kJ·mol-1 [41 ] v Fe Poisson ratio of Fe 0.291 [41 ] v Cu Poisson ratio of Cu 0.345 [41 ] G Fe Shear modulus of Fe 89334 - 29.688T GPa [30 ] G Cu Shear modulus of Cu 44689 - 15.936T GPa [30 ] k Boltzmann constant 1.38 × 10-23 J·K-1 图4 不同温度下(Ti, Mo)C与<i>ε</i>-Cu在铁素体中析出热/动力学的计算结果 (a) Ti/Mo atomic ratio and x (b) driving force (c) PTT curves (d) solid solution content ...
17
2006
... 根据复合析出相的固溶析出模型计算二元复合型碳化物(Ti, Mo)C析出动力学[30 ] ,假设条件如下:① 均热温度为1200℃,析出物完全溶解;② NaCl型TiC和MoC相互溶解,碳化物无间隙缺位,满足化学计量比,在复合碳化物中TiC的化学式系数x ,MoC的化学式系数为1- x ,复合碳化物记为Tix 1 - x
... 由于复合析出相在铁素体中满足平衡固溶的热力学平衡,同时处于析出态的Ti、Mo和C元素比满足化学计量比,可得到[30 ~32 ] : ...
... Cu在铁素体中的固溶量需要满足固溶度积公式为[30 ] : ...
... 首先计算(Ti, Mo)C和ε -Cu的形核驱动力,即(Ti, Mo)C和ε -Cu在铁素体中析出的体积自由能(Δ G V ) 由其Gibbs摩尔自由能(Δ G m ) 和摩尔体积(V m )表示[30 ] : ...
... 已知TiC、MoC和ε -Cu与铁素体之间半共格界面比界面能随温度变化的计算公式[30 ] : ...
... 球形(Ti, Mo)C在铁素体基体上形核时的自由能变化(Δ G M C ) 为[30 ] : ...
... ε -Cu在铁素体上形核的自由能Δ G C u m Δ G C u d i s Δ G C u m a t r i x ε -Cu的自由能变化为[30 ] : ...
... ε -Cu在铁素体基体上形核时的自由能变化(Δ G C u m a t r i x ) 为[30 ] : ...
... 式中,d Cu 为ε -Cu新相沿位错线形成的核胚直径,L Cu 为单位长度的位错能量,G Cu 、b Cu 、v Cu 分别为Cu的切变模量、Burgers矢量模和Poisson比.由于刃型位错比螺型位错更适合析出物形核[30 ] ,所以只考虑形核位置为刃型位错的情况. ...
... (Ti, Mo)C临界形核功(Δ G M C * ) 为[30 ] : ...
... ε -Cu均匀析出和在位错线上析出的临界形核功Δ G C u m a t r i x * Δ G C u d i s * [30 ] : ...
... (Ti, Mo)C和ε -Cu析出的相对开始时间分别为[30 ] : ...
... 表1 [29 ,30 ,35 ~41 ] 为动力学计算中所使用的参数及其取值,析出动力学计算结果如图4 所示.复合碳化物(Ti, Mo)C在550~700℃保温区间,随温度的升高,化学式系数x 单调增加,如图4 a所示,即TiC在(Ti, Mo)C的占比由0.65增加到0.84,由此可得(Ti, Mo)C中Ti/Mo比由1.8增加到5.4.当温度为550~700℃时,随温度的升高,由于固溶度的增大,(Ti, Mo)C与ε -Cu的形核驱动力均单调减小,如图4 b所示,(Ti, Mo)C的驱动力的范围为4.88 × 109 ~4.41 × 109 J/m3 ,而ε -Cu的驱动力的范围为1.67 × 109 ~4.96 × 108 J/m3 ,2者之比由2.45扩大至8.88,可以看出,温度升高大幅降低了ε -Cu析出的驱动力,而(Ti, Mo)C的驱动力变化较小.(Ti, Mo)C与ε -Cu的析出相对开始时间即析出-温度-时间(PTT)曲线如图4 c所示,在550~700℃范围内,ε -Cu的PTT曲线呈典型C形状,鼻尖温度为586℃,当温度范围为550~586℃时,随温度的升高,ε -Cu的相对开始析出时间会越来越短,即孕育期越短;而温度范围为586~700℃时,随温度的升高,ε -Cu的相对开始析出时间会越来越长,即孕育期越长.而在550~700℃范围内,(Ti, Mo)C则呈单调下降趋势,即随温度的降低,(Ti, Mo)C的相对开始析出时间会越来越长,即孕育期越长. ...
... 计算中使用的参数[29 ,30 ,35 ~41 ] ...
... Parameters used in calculations[29 ,30 ,35 -41 ] ...
... [
30 ]
G Cu Shear modulus of Cu 44689 - 15.936T GPa [30 ] k Boltzmann constant 1.38 × 10-23 J·K-1 图4 不同温度下(Ti, Mo)C与<i>ε</i>-Cu在铁素体中析出热/动力学的计算结果 (a) Ti/Mo atomic ratio and x (b) driving force (c) PTT curves (d) solid solution content ...
... [
30 ]
k Boltzmann constant 1.38 × 10-23 J·K-1 图4 不同温度下(Ti, Mo)C与<i>ε</i>-Cu在铁素体中析出热/动力学的计算结果 (a) Ti/Mo atomic ratio and x (b) driving force (c) PTT curves (d) solid solution content ...
17
2006
... 根据复合析出相的固溶析出模型计算二元复合型碳化物(Ti, Mo)C析出动力学[30 ] ,假设条件如下:① 均热温度为1200℃,析出物完全溶解;② NaCl型TiC和MoC相互溶解,碳化物无间隙缺位,满足化学计量比,在复合碳化物中TiC的化学式系数x ,MoC的化学式系数为1- x ,复合碳化物记为Tix 1 - x
... 由于复合析出相在铁素体中满足平衡固溶的热力学平衡,同时处于析出态的Ti、Mo和C元素比满足化学计量比,可得到[30 ~32 ] : ...
... Cu在铁素体中的固溶量需要满足固溶度积公式为[30 ] : ...
... 首先计算(Ti, Mo)C和ε -Cu的形核驱动力,即(Ti, Mo)C和ε -Cu在铁素体中析出的体积自由能(Δ G V ) 由其Gibbs摩尔自由能(Δ G m ) 和摩尔体积(V m )表示[30 ] : ...
... 已知TiC、MoC和ε -Cu与铁素体之间半共格界面比界面能随温度变化的计算公式[30 ] : ...
... 球形(Ti, Mo)C在铁素体基体上形核时的自由能变化(Δ G M C ) 为[30 ] : ...
... ε -Cu在铁素体上形核的自由能Δ G C u m Δ G C u d i s Δ G C u m a t r i x ε -Cu的自由能变化为[30 ] : ...
... ε -Cu在铁素体基体上形核时的自由能变化(Δ G C u m a t r i x ) 为[30 ] : ...
... 式中,d Cu 为ε -Cu新相沿位错线形成的核胚直径,L Cu 为单位长度的位错能量,G Cu 、b Cu 、v Cu 分别为Cu的切变模量、Burgers矢量模和Poisson比.由于刃型位错比螺型位错更适合析出物形核[30 ] ,所以只考虑形核位置为刃型位错的情况. ...
... (Ti, Mo)C临界形核功(Δ G M C * ) 为[30 ] : ...
... ε -Cu均匀析出和在位错线上析出的临界形核功Δ G C u m a t r i x * Δ G C u d i s * [30 ] : ...
... (Ti, Mo)C和ε -Cu析出的相对开始时间分别为[30 ] : ...
... 表1 [29 ,30 ,35 ~41 ] 为动力学计算中所使用的参数及其取值,析出动力学计算结果如图4 所示.复合碳化物(Ti, Mo)C在550~700℃保温区间,随温度的升高,化学式系数x 单调增加,如图4 a所示,即TiC在(Ti, Mo)C的占比由0.65增加到0.84,由此可得(Ti, Mo)C中Ti/Mo比由1.8增加到5.4.当温度为550~700℃时,随温度的升高,由于固溶度的增大,(Ti, Mo)C与ε -Cu的形核驱动力均单调减小,如图4 b所示,(Ti, Mo)C的驱动力的范围为4.88 × 109 ~4.41 × 109 J/m3 ,而ε -Cu的驱动力的范围为1.67 × 109 ~4.96 × 108 J/m3 ,2者之比由2.45扩大至8.88,可以看出,温度升高大幅降低了ε -Cu析出的驱动力,而(Ti, Mo)C的驱动力变化较小.(Ti, Mo)C与ε -Cu的析出相对开始时间即析出-温度-时间(PTT)曲线如图4 c所示,在550~700℃范围内,ε -Cu的PTT曲线呈典型C形状,鼻尖温度为586℃,当温度范围为550~586℃时,随温度的升高,ε -Cu的相对开始析出时间会越来越短,即孕育期越短;而温度范围为586~700℃时,随温度的升高,ε -Cu的相对开始析出时间会越来越长,即孕育期越长.而在550~700℃范围内,(Ti, Mo)C则呈单调下降趋势,即随温度的降低,(Ti, Mo)C的相对开始析出时间会越来越长,即孕育期越长. ...
... 计算中使用的参数[29 ,30 ,35 ~41 ] ...
... Parameters used in calculations[29 ,30 ,35 -41 ] ...
... [
30 ]
G Cu Shear modulus of Cu 44689 - 15.936T GPa [30 ] k Boltzmann constant 1.38 × 10-23 J·K-1 图4 不同温度下(Ti, Mo)C与<i>ε</i>-Cu在铁素体中析出热/动力学的计算结果 (a) Ti/Mo atomic ratio and x (b) driving force (c) PTT curves (d) solid solution content ...
... [
30 ]
k Boltzmann constant 1.38 × 10-23 J·K-1 图4 不同温度下(Ti, Mo)C与<i>ε</i>-Cu在铁素体中析出热/动力学的计算结果 (a) Ti/Mo atomic ratio and x (b) driving force (c) PTT curves (d) solid solution content ...
Solubility products for titanium-, vanadium-, and niobium-carbide in ferrite
0
1995
Equilibrium solubility products of molybdenum carbide and tungsten carbide in iron
1
2012
... 由于复合析出相在铁素体中满足平衡固溶的热力学平衡,同时处于析出态的Ti、Mo和C元素比满足化学计量比,可得到[30 ~32 ] : ...
Nucleation on dislocations
1
1957
... 根据修正的Cahn位错形核理论[33 ,34 ] ,可得到球形ε -Cu在位错线上形核时的自由能变化Δ G C u d i s
Theory of nucleation on dislocations
1
1990
... 根据修正的Cahn位错形核理论[33 ,34 ] ,可得到球形ε -Cu在位错线上形核时的自由能变化Δ G C u d i s
Superconductivity of the transition-metal carbides
5
1967
... 式中,β 为Cahn理论中的位错线形核参量[35 ] ,其值在-1~0之间. ...
... 表1 [29 ,30 ,35 ~41 ] 为动力学计算中所使用的参数及其取值,析出动力学计算结果如图4 所示.复合碳化物(Ti, Mo)C在550~700℃保温区间,随温度的升高,化学式系数x 单调增加,如图4 a所示,即TiC在(Ti, Mo)C的占比由0.65增加到0.84,由此可得(Ti, Mo)C中Ti/Mo比由1.8增加到5.4.当温度为550~700℃时,随温度的升高,由于固溶度的增大,(Ti, Mo)C与ε -Cu的形核驱动力均单调减小,如图4 b所示,(Ti, Mo)C的驱动力的范围为4.88 × 109 ~4.41 × 109 J/m3 ,而ε -Cu的驱动力的范围为1.67 × 109 ~4.96 × 108 J/m3 ,2者之比由2.45扩大至8.88,可以看出,温度升高大幅降低了ε -Cu析出的驱动力,而(Ti, Mo)C的驱动力变化较小.(Ti, Mo)C与ε -Cu的析出相对开始时间即析出-温度-时间(PTT)曲线如图4 c所示,在550~700℃范围内,ε -Cu的PTT曲线呈典型C形状,鼻尖温度为586℃,当温度范围为550~586℃时,随温度的升高,ε -Cu的相对开始析出时间会越来越短,即孕育期越短;而温度范围为586~700℃时,随温度的升高,ε -Cu的相对开始析出时间会越来越长,即孕育期越长.而在550~700℃范围内,(Ti, Mo)C则呈单调下降趋势,即随温度的降低,(Ti, Mo)C的相对开始析出时间会越来越长,即孕育期越长. ...
... 计算中使用的参数[29 ,30 ,35 ~41 ] ...
... Parameters used in calculations[29 ,30 ,35 -41 ] ...
... [
35 ]
a Cu Lattice constant of ε -Cu at room temperature 0.362 nm [36 ] a Fe Lattice constant of α -Fe at room temperature 0.287 nm α TiC Linear expansion coefficient of TiC 7.86 × 10-6 K-1 [37 ] α MoC Linear expansion coefficient of MoC 6.88 × 10-6 K-1 [38 ] α Cu Linear expansion coefficient of Cu 16.5 × 10-6 K-1 [39 ] Q Ti Activation energy of Ti in α -Fe 248 kJ·mol-1 [40 ] Q Mo Activation energy of Mo in α -Fe 229 kJ·mol-1 [41 ] Q Cu Activation energy of Cu in α -Fe 284 kJ·mol-1 [41 ] v Fe Poisson ratio of Fe 0.291 [41 ] v Cu Poisson ratio of Cu 0.345 [41 ] G Fe Shear modulus of Fe 89334 - 29.688T GPa [30 ] G Cu Shear modulus of Cu 44689 - 15.936T GPa [30 ] k Boltzmann constant 1.38 × 10-23 J·K-1 图4 不同温度下(Ti, Mo)C与<i>ε</i>-Cu在铁素体中析出热/动力学的计算结果 (a) Ti/Mo atomic ratio and x (b) driving force (c) PTT curves (d) solid solution content ...
Lattice parameters, densities, expansion coefficients and perfection of structure of Cu and of Cu-In α phase
1
1969
... Parameters used in calculations
[29 ,30 ,35 -41 ] Table 1 Symbol Description Magnitude Unit Ref. a TiC Lattice constant of TiC at room temperature 0.433 nm [29 ] a MoC Lattice constant of MoC at room temperature 0.428 nm [35 ] a Cu Lattice constant of ε -Cu at room temperature 0.362 nm [36 ] a Fe Lattice constant of α -Fe at room temperature 0.287 nm α TiC Linear expansion coefficient of TiC 7.86 × 10-6 K-1 [37 ] α MoC Linear expansion coefficient of MoC 6.88 × 10-6 K-1 [38 ] α Cu Linear expansion coefficient of Cu 16.5 × 10-6 K-1 [39 ] Q Ti Activation energy of Ti in α -Fe 248 kJ·mol-1 [40 ] Q Mo Activation energy of Mo in α -Fe 229 kJ·mol-1 [41 ] Q Cu Activation energy of Cu in α -Fe 284 kJ·mol-1 [41 ] v Fe Poisson ratio of Fe 0.291 [41 ] v Cu Poisson ratio of Cu 0.345 [41 ] G Fe Shear modulus of Fe 89334 - 29.688T GPa [30 ] G Cu Shear modulus of Cu 44689 - 15.936T GPa [30 ] k Boltzmann constant 1.38 × 10-23 J·K-1
图4 不同温度下(Ti, Mo)C与<i>ε</i>-Cu在铁素体中析出热/动力学的计算结果 (a) Ti/Mo atomic ratio and x (b) driving force (c) PTT curves (d) solid solution content ...
Thermal expansion of some transition metal carbides
1
1958
... Parameters used in calculations
[29 ,30 ,35 -41 ] Table 1 Symbol Description Magnitude Unit Ref. a TiC Lattice constant of TiC at room temperature 0.433 nm [29 ] a MoC Lattice constant of MoC at room temperature 0.428 nm [35 ] a Cu Lattice constant of ε -Cu at room temperature 0.362 nm [36 ] a Fe Lattice constant of α -Fe at room temperature 0.287 nm α TiC Linear expansion coefficient of TiC 7.86 × 10-6 K-1 [37 ] α MoC Linear expansion coefficient of MoC 6.88 × 10-6 K-1 [38 ] α Cu Linear expansion coefficient of Cu 16.5 × 10-6 K-1 [39 ] Q Ti Activation energy of Ti in α -Fe 248 kJ·mol-1 [40 ] Q Mo Activation energy of Mo in α -Fe 229 kJ·mol-1 [41 ] Q Cu Activation energy of Cu in α -Fe 284 kJ·mol-1 [41 ] v Fe Poisson ratio of Fe 0.291 [41 ] v Cu Poisson ratio of Cu 0.345 [41 ] G Fe Shear modulus of Fe 89334 - 29.688T GPa [30 ] G Cu Shear modulus of Cu 44689 - 15.936T GPa [30 ] k Boltzmann constant 1.38 × 10-23 J·K-1
图4 不同温度下(Ti, Mo)C与<i>ε</i>-Cu在铁素体中析出热/动力学的计算结果 (a) Ti/Mo atomic ratio and x (b) driving force (c) PTT curves (d) solid solution content ...
First-principles calculations of hydrostatic pressure effects on the structural, elastic and thermodynamic properties of cubic monocarbides X C (X = Ti, V, Cr, Nb, Mo, Hf)
1
2012
... Parameters used in calculations
[29 ,30 ,35 -41 ] Table 1 Symbol Description Magnitude Unit Ref. a TiC Lattice constant of TiC at room temperature 0.433 nm [29 ] a MoC Lattice constant of MoC at room temperature 0.428 nm [35 ] a Cu Lattice constant of ε -Cu at room temperature 0.362 nm [36 ] a Fe Lattice constant of α -Fe at room temperature 0.287 nm α TiC Linear expansion coefficient of TiC 7.86 × 10-6 K-1 [37 ] α MoC Linear expansion coefficient of MoC 6.88 × 10-6 K-1 [38 ] α Cu Linear expansion coefficient of Cu 16.5 × 10-6 K-1 [39 ] Q Ti Activation energy of Ti in α -Fe 248 kJ·mol-1 [40 ] Q Mo Activation energy of Mo in α -Fe 229 kJ·mol-1 [41 ] Q Cu Activation energy of Cu in α -Fe 284 kJ·mol-1 [41 ] v Fe Poisson ratio of Fe 0.291 [41 ] v Cu Poisson ratio of Cu 0.345 [41 ] G Fe Shear modulus of Fe 89334 - 29.688T GPa [30 ] G Cu Shear modulus of Cu 44689 - 15.936T GPa [30 ] k Boltzmann constant 1.38 × 10-23 J·K-1
图4 不同温度下(Ti, Mo)C与<i>ε</i>-Cu在铁素体中析出热/动力学的计算结果 (a) Ti/Mo atomic ratio and x (b) driving force (c) PTT curves (d) solid solution content ...
Thermal expansion of reference materials: Copper, silica and silicon
1
1973
... Parameters used in calculations
[29 ,30 ,35 -41 ] Table 1 Symbol Description Magnitude Unit Ref. a TiC Lattice constant of TiC at room temperature 0.433 nm [29 ] a MoC Lattice constant of MoC at room temperature 0.428 nm [35 ] a Cu Lattice constant of ε -Cu at room temperature 0.362 nm [36 ] a Fe Lattice constant of α -Fe at room temperature 0.287 nm α TiC Linear expansion coefficient of TiC 7.86 × 10-6 K-1 [37 ] α MoC Linear expansion coefficient of MoC 6.88 × 10-6 K-1 [38 ] α Cu Linear expansion coefficient of Cu 16.5 × 10-6 K-1 [39 ] Q Ti Activation energy of Ti in α -Fe 248 kJ·mol-1 [40 ] Q Mo Activation energy of Mo in α -Fe 229 kJ·mol-1 [41 ] Q Cu Activation energy of Cu in α -Fe 284 kJ·mol-1 [41 ] v Fe Poisson ratio of Fe 0.291 [41 ] v Cu Poisson ratio of Cu 0.345 [41 ] G Fe Shear modulus of Fe 89334 - 29.688T GPa [30 ] G Cu Shear modulus of Cu 44689 - 15.936T GPa [30 ] k Boltzmann constant 1.38 × 10-23 J·K-1
图4 不同温度下(Ti, Mo)C与<i>ε</i>-Cu在铁素体中析出热/动力学的计算结果 (a) Ti/Mo atomic ratio and x (b) driving force (c) PTT curves (d) solid solution content ...
Solubility and diffusion of titanium in iron
1
1959
... Parameters used in calculations
[29 ,30 ,35 -41 ] Table 1 Symbol Description Magnitude Unit Ref. a TiC Lattice constant of TiC at room temperature 0.433 nm [29 ] a MoC Lattice constant of MoC at room temperature 0.428 nm [35 ] a Cu Lattice constant of ε -Cu at room temperature 0.362 nm [36 ] a Fe Lattice constant of α -Fe at room temperature 0.287 nm α TiC Linear expansion coefficient of TiC 7.86 × 10-6 K-1 [37 ] α MoC Linear expansion coefficient of MoC 6.88 × 10-6 K-1 [38 ] α Cu Linear expansion coefficient of Cu 16.5 × 10-6 K-1 [39 ] Q Ti Activation energy of Ti in α -Fe 248 kJ·mol-1 [40 ] Q Mo Activation energy of Mo in α -Fe 229 kJ·mol-1 [41 ] Q Cu Activation energy of Cu in α -Fe 284 kJ·mol-1 [41 ] v Fe Poisson ratio of Fe 0.291 [41 ] v Cu Poisson ratio of Cu 0.345 [41 ] G Fe Shear modulus of Fe 89334 - 29.688T GPa [30 ] G Cu Shear modulus of Cu 44689 - 15.936T GPa [30 ] k Boltzmann constant 1.38 × 10-23 J·K-1
图4 不同温度下(Ti, Mo)C与<i>ε</i>-Cu在铁素体中析出热/动力学的计算结果 (a) Ti/Mo atomic ratio and x (b) driving force (c) PTT curves (d) solid solution content ...
7
1992
... 表1 [29 ,30 ,35 ~41 ] 为动力学计算中所使用的参数及其取值,析出动力学计算结果如图4 所示.复合碳化物(Ti, Mo)C在550~700℃保温区间,随温度的升高,化学式系数x 单调增加,如图4 a所示,即TiC在(Ti, Mo)C的占比由0.65增加到0.84,由此可得(Ti, Mo)C中Ti/Mo比由1.8增加到5.4.当温度为550~700℃时,随温度的升高,由于固溶度的增大,(Ti, Mo)C与ε -Cu的形核驱动力均单调减小,如图4 b所示,(Ti, Mo)C的驱动力的范围为4.88 × 109 ~4.41 × 109 J/m3 ,而ε -Cu的驱动力的范围为1.67 × 109 ~4.96 × 108 J/m3 ,2者之比由2.45扩大至8.88,可以看出,温度升高大幅降低了ε -Cu析出的驱动力,而(Ti, Mo)C的驱动力变化较小.(Ti, Mo)C与ε -Cu的析出相对开始时间即析出-温度-时间(PTT)曲线如图4 c所示,在550~700℃范围内,ε -Cu的PTT曲线呈典型C形状,鼻尖温度为586℃,当温度范围为550~586℃时,随温度的升高,ε -Cu的相对开始析出时间会越来越短,即孕育期越短;而温度范围为586~700℃时,随温度的升高,ε -Cu的相对开始析出时间会越来越长,即孕育期越长.而在550~700℃范围内,(Ti, Mo)C则呈单调下降趋势,即随温度的降低,(Ti, Mo)C的相对开始析出时间会越来越长,即孕育期越长. ...
... 计算中使用的参数[29 ,30 ,35 ~41 ] ...
... Parameters used in calculations[29 ,30 ,35 -41 ] ...
... [
41 ]
Q Cu Activation energy of Cu in α -Fe 284 kJ·mol-1 [41 ] v Fe Poisson ratio of Fe 0.291 [41 ] v Cu Poisson ratio of Cu 0.345 [41 ] G Fe Shear modulus of Fe 89334 - 29.688T GPa [30 ] G Cu Shear modulus of Cu 44689 - 15.936T GPa [30 ] k Boltzmann constant 1.38 × 10-23 J·K-1 图4 不同温度下(Ti, Mo)C与<i>ε</i>-Cu在铁素体中析出热/动力学的计算结果 (a) Ti/Mo atomic ratio and x (b) driving force (c) PTT curves (d) solid solution content ...
... [
41 ]
v Fe Poisson ratio of Fe 0.291 [41 ] v Cu Poisson ratio of Cu 0.345 [41 ] G Fe Shear modulus of Fe 89334 - 29.688T GPa [30 ] G Cu Shear modulus of Cu 44689 - 15.936T GPa [30 ] k Boltzmann constant 1.38 × 10-23 J·K-1 图4 不同温度下(Ti, Mo)C与<i>ε</i>-Cu在铁素体中析出热/动力学的计算结果 (a) Ti/Mo atomic ratio and x (b) driving force (c) PTT curves (d) solid solution content ...
... [
41 ]
v Cu Poisson ratio of Cu 0.345 [41 ] G Fe Shear modulus of Fe 89334 - 29.688T GPa [30 ] G Cu Shear modulus of Cu 44689 - 15.936T GPa [30 ] k Boltzmann constant 1.38 × 10-23 J·K-1 图4 不同温度下(Ti, Mo)C与<i>ε</i>-Cu在铁素体中析出热/动力学的计算结果 (a) Ti/Mo atomic ratio and x (b) driving force (c) PTT curves (d) solid solution content ...
... [
41 ]
G Fe Shear modulus of Fe 89334 - 29.688T GPa [30 ] G Cu Shear modulus of Cu 44689 - 15.936T GPa [30 ] k Boltzmann constant 1.38 × 10-23 J·K-1 图4 不同温度下(Ti, Mo)C与<i>ε</i>-Cu在铁素体中析出热/动力学的计算结果 (a) Ti/Mo atomic ratio and x (b) driving force (c) PTT curves (d) solid solution content ...
Effects of hot-deformation on grain boundary precipitation and segregation in Ti-Mo microalloyed steels
1
2018
... (Ti, Mo)C中Ti/Mo原子比是探究Mo在复合碳化物作用的重要内容,也是化学成分设计的关键环节.Jang等[13 ] 对含Ti-Mo钢在630℃等温时效析出实验研究发现,碳化物中Ti/Mo比随析出物尺寸的增大而增加,当碳化物尺寸在5~14 nm内,(Ti, Mo)C析出物中Ti/Mo比为2.0~4.3.Wang等[42 ] 通过三维原子探针(APT)研究了Ti-Mo微合金钢在890℃进行热变形和不进行热变形时(Ti, Mo)C化学组分的演变规律,结果表明热变形对(Ti, Mo)C中的化学组分影响不大,热变形后并在650℃等温时Ti/Mo比为2.7,而不变形时为2.6.Dhara等[43 ] 采用APT和小角度中子散射(SANS)研究(Ti, Mo)C的组分变化,结果表明650℃形成的(Ti, Mo)C,当析出粒子尺寸的Guinier半径> 3 nm时,碳化物中的Ti/Mo比接近于平衡态的2.5,而Timokhina等[44 ] 研究发现,650℃保温1700 s后,(Ti, Mo)C的Ti/Mo比为3.3.综上可知,(Ti, Mo)C碳化物在630~650℃保温期间,Ti/Mo比基本在2.5~4.3范围内,在本实验600~660℃温度范围内,如图4 a所示,Ti/Mo比为2.5~4.5,基本与实验结果相近.当温度由600℃提高到660℃时,化学式系数x 单调增加,Ti/Mo比为由2.5增大到4.5,碳化物组成由Ti0.71 Mo0.29 C演变为Ti0.79 Mo0.21 C,也就是说MoC在低温时析出分数占比较高,而在高温时占比降低.这与组成复合碳化物的TiC和MoC的固溶度积有关,TiC的固溶度积比较小,为难固溶相,而MoC的固溶度积较大,为易固溶相.随着温度升高,2者的固溶度积均增大,固溶[Ti]和[Mo]均增大,但固溶[Mo]增加幅度更大,如图4 d所示,导致复合碳化物中MoC比例下降,Ti/Mo比增大. ...
Precipitation and clustering in a Ti-Mo steel investigated using atom probe tomography and small-angle neutron scattering
1
2018
... (Ti, Mo)C中Ti/Mo原子比是探究Mo在复合碳化物作用的重要内容,也是化学成分设计的关键环节.Jang等[13 ] 对含Ti-Mo钢在630℃等温时效析出实验研究发现,碳化物中Ti/Mo比随析出物尺寸的增大而增加,当碳化物尺寸在5~14 nm内,(Ti, Mo)C析出物中Ti/Mo比为2.0~4.3.Wang等[42 ] 通过三维原子探针(APT)研究了Ti-Mo微合金钢在890℃进行热变形和不进行热变形时(Ti, Mo)C化学组分的演变规律,结果表明热变形对(Ti, Mo)C中的化学组分影响不大,热变形后并在650℃等温时Ti/Mo比为2.7,而不变形时为2.6.Dhara等[43 ] 采用APT和小角度中子散射(SANS)研究(Ti, Mo)C的组分变化,结果表明650℃形成的(Ti, Mo)C,当析出粒子尺寸的Guinier半径> 3 nm时,碳化物中的Ti/Mo比接近于平衡态的2.5,而Timokhina等[44 ] 研究发现,650℃保温1700 s后,(Ti, Mo)C的Ti/Mo比为3.3.综上可知,(Ti, Mo)C碳化物在630~650℃保温期间,Ti/Mo比基本在2.5~4.3范围内,在本实验600~660℃温度范围内,如图4 a所示,Ti/Mo比为2.5~4.5,基本与实验结果相近.当温度由600℃提高到660℃时,化学式系数x 单调增加,Ti/Mo比为由2.5增大到4.5,碳化物组成由Ti0.71 Mo0.29 C演变为Ti0.79 Mo0.21 C,也就是说MoC在低温时析出分数占比较高,而在高温时占比降低.这与组成复合碳化物的TiC和MoC的固溶度积有关,TiC的固溶度积比较小,为难固溶相,而MoC的固溶度积较大,为易固溶相.随着温度升高,2者的固溶度积均增大,固溶[Ti]和[Mo]均增大,但固溶[Mo]增加幅度更大,如图4 d所示,导致复合碳化物中MoC比例下降,Ti/Mo比增大. ...
On the Ti-Mo-Fe-C atomic clustering during interphase precipitation in the Ti-Mo steel studied by advanced microscopic techniques
1
2016
... (Ti, Mo)C中Ti/Mo原子比是探究Mo在复合碳化物作用的重要内容,也是化学成分设计的关键环节.Jang等[13 ] 对含Ti-Mo钢在630℃等温时效析出实验研究发现,碳化物中Ti/Mo比随析出物尺寸的增大而增加,当碳化物尺寸在5~14 nm内,(Ti, Mo)C析出物中Ti/Mo比为2.0~4.3.Wang等[42 ] 通过三维原子探针(APT)研究了Ti-Mo微合金钢在890℃进行热变形和不进行热变形时(Ti, Mo)C化学组分的演变规律,结果表明热变形对(Ti, Mo)C中的化学组分影响不大,热变形后并在650℃等温时Ti/Mo比为2.7,而不变形时为2.6.Dhara等[43 ] 采用APT和小角度中子散射(SANS)研究(Ti, Mo)C的组分变化,结果表明650℃形成的(Ti, Mo)C,当析出粒子尺寸的Guinier半径> 3 nm时,碳化物中的Ti/Mo比接近于平衡态的2.5,而Timokhina等[44 ] 研究发现,650℃保温1700 s后,(Ti, Mo)C的Ti/Mo比为3.3.综上可知,(Ti, Mo)C碳化物在630~650℃保温期间,Ti/Mo比基本在2.5~4.3范围内,在本实验600~660℃温度范围内,如图4 a所示,Ti/Mo比为2.5~4.5,基本与实验结果相近.当温度由600℃提高到660℃时,化学式系数x 单调增加,Ti/Mo比为由2.5增大到4.5,碳化物组成由Ti0.71 Mo0.29 C演变为Ti0.79 Mo0.21 C,也就是说MoC在低温时析出分数占比较高,而在高温时占比降低.这与组成复合碳化物的TiC和MoC的固溶度积有关,TiC的固溶度积比较小,为难固溶相,而MoC的固溶度积较大,为易固溶相.随着温度升高,2者的固溶度积均增大,固溶[Ti]和[Mo]均增大,但固溶[Mo]增加幅度更大,如图4 d所示,导致复合碳化物中MoC比例下降,Ti/Mo比增大. ...