为了强调表面状态的重要性,Field和Kahles[4]早在1964年就明确提出表面完整性的概念;经过近60年的发展,不同的表面完整性概念陆续被提出[5~7]。表面完整性主要包含下述内容:表面形貌、表面缺陷、微观组织和表面层的冶金化学性能、表面层物理力学性能及表面层的其他工程技术特征。研究表明,吹砂处理使铝合金表面形成了100 MPa左右的压应力,但表面粗糙度Ra提高到接近15 μm,从而造成疲劳寿命降低[8];表面处理导致了IN738LC高温合金的性能下降[9]。在喷丸表面强化方面,高玉魁等[10]研究了GH909高温合金喷丸强化残余应力场,钟丽琼等[11]研究了喷丸强化对FGH4097粉末高温合金室温高周疲劳性能的影响。
DD6合金是我国自主研制的第二代单晶高温合金,其性能优于或达到欧美第二代单晶高温合金的水平,且含有2% (质量分数)的Re,成本较低,已在我国获得广泛应用[3,12,13]。单晶涡轮叶片精铸件研制过程中有多种工序,吹砂是单晶涡轮叶片精铸件研制过程中不可缺少的工序之一,可用于表面清理和粗糙度改善等;喷丸有时用于强化单晶涡轮叶片的榫齿;但吹砂、喷丸均会破坏单晶涡轮叶片的表面完整性,降低叶片的强度,因此研究吹砂、喷丸等对单晶高温合金表面完整性和疲劳强度的影响具有重要意义。高玉魁[14]研究了喷丸强化对DD6单晶高温合金高温旋转弯曲疲劳性能的影响;王欣等[15]研究了陶瓷弹丸喷丸强化对DD6单晶高温合金表面完整性的影响;熊继春等[16]将DD6合金表面吹砂并热暴露,研究了再结晶组织对持久性能的影响。综上所述,吹砂对单晶高温合金的表面形貌、硬度、粗糙度、微观组织的影响和由吹砂导致的不同温度疲劳性能的变化及机理分析等未见公开报道。本工作主要研究了吹砂对DD6单晶高温合金表面完整性和高周疲劳强度的影响。
1 实验方法
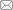
实验选用第二代单晶高温合金DD6,其化学成分(质量分数,%)为:Cr 4.3,Co 9.0,Mo 2.0,W 8.0,Re 2.0,Ta 7.5,Nb 0.5,Al 5.6,Hf 0.1,C 0.006,Ni余量[13]。采用螺旋选晶法在真空定向凝固炉中制备[001]取向的DD6单晶试棒,应用X射线衍射(XRD)极图法测定单晶试棒的晶体取向,选取[001]取向偏离主应力轴6°以内的单晶试棒。DD6合金的热处理制度为:1290℃、1 h + 1300℃、2 h + 1315℃、4 h、空冷(AC)固溶处理,1120℃、4 h、AC一级时效处理,870℃、32 h、AC二级时效处理。将热处理后的单晶试棒按图1所示的要求加工成旋转弯曲高周疲劳性能试样,试样表面粗糙度为0.4 μm。
图1
图1
高周疲劳试样的形状和尺寸示意图
Fig.1
Schematic of shape and size of specimen for high cycle fatigue test (unit: mm)
分别选用粒径为150、124和100 μm的白刚玉砂,吹砂压力0.5 MPa,对高周疲劳性能试样进行吹砂处理。使用MARSURF PS1粗糙度仪测量表面粗糙度,采用BCPCAS4800型场发射扫描电镜(FESEM)和DCM8共聚焦显微镜观察表面形貌。将吹砂后试样剖切,采用FM-700型Vickers硬度计沿深度分布测量硬度。测试150 μm、0.5 MPa吹砂试样的疲劳性能,实验条件为:测试温度分别为760和980℃,大气环境,旋转弯曲加载方式,应力比R = -1,应力集中系数Kt = 1,频率为83.3 Hz。
采用FESEM观察组织,使用LEO1450型扫描电镜(SEM)观察疲劳断口组织形貌。吹砂后采用2种方法制备透射电镜(TEM)试样,一种为聚焦离子束(FIB)技术制样;另一种为在试样表层切2个小片,对粘在一起,切成直径3 mm圆片,用Gatan691型离子减薄仪减出薄区。疲劳性能测试后,在疲劳断口下1 mm处用线切割机沿垂直轴向切取厚度0.4 mm的薄片,双面砂纸研磨至30 μm,用减薄仪减出薄区,采用TECNAI-20型TEM观察并分析位错形态。
2 实验结果
2.1 吹砂对表面粗糙度的影响
经测量,采用粒径100、124和150 μm白刚玉砂0.5 MPa吹砂后试样表面粗糙度分别为1.23、1.63和2.41 μm。可以看出,砂粒粒径增加,表面粗糙度增大。Mellali等[17]对铝合金和高强度钢的研究表明,砂粒粒径是决定表面粗糙度的最主要因素。本研究结果与其一致。
2.2 吹砂对表面形貌的影响
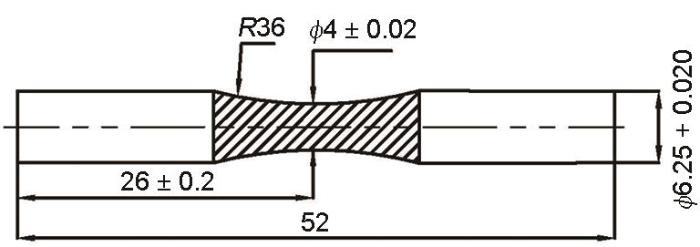
不同粒径白刚玉砂0.5 MPa吹砂后试样表面三维(3D)和二维(2D)形貌如图2所示。可以看出,随砂粒粒径增加,砂粒切削的深度增大,峰谷起伏范围增加。这是由于随砂粒粒径增加,单个砂粒质量增大,相应的动能增大,对试样表面的切削作用增强。
图2
图2
不同粒径砂粒吹砂后DD6高温合金试样表面的三维和二维形貌
Fig.2
3D (a, c, e) and 2D (b, d, f) morphologies of DD6 superalloy specimens after sand blasting with granularities of 150 μm (a, b), 124 μm (c, d), and 100 μm (e, f)
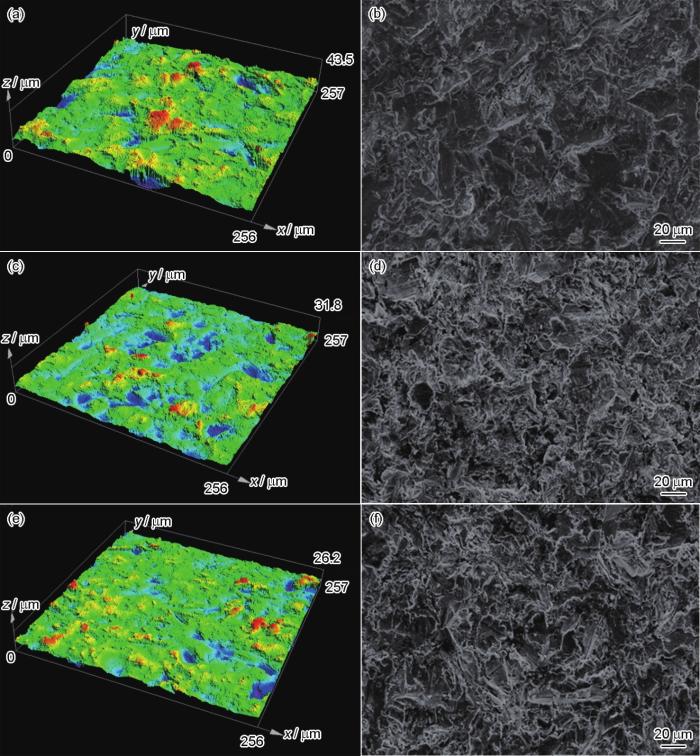
2.3 吹砂对硬度的影响
图3
图3
不同粒径砂粒吹砂后试样硬度随距离表面深度的变化
Fig.3
Variations of specimen hardness with distance from surface after sand blasting with different granularities
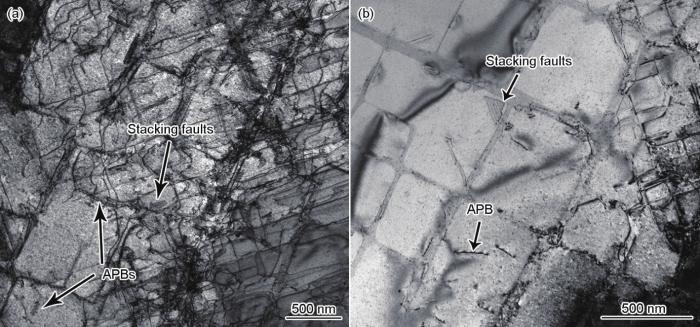
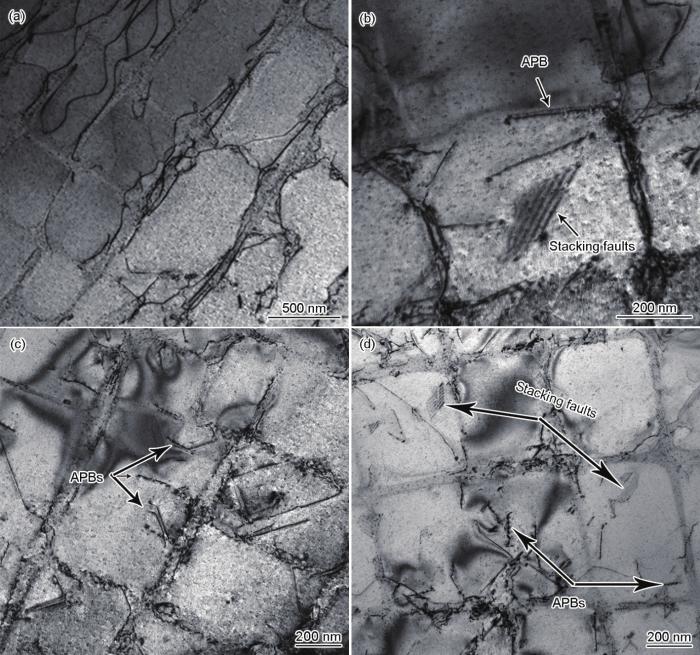
2.4 吹砂对位错形态的影响
图4
图4
150 μm白刚玉砂0.5 MPa吹砂后DD6高温合金试样的位错形态
Fig.4
Dislocation morphologies of DD6 superalloy specimen after sand blasting with 150 μm and 0.5 MPa sand (APB—antiphase domain boundary)
(a) near surface (b) slightly away from surface
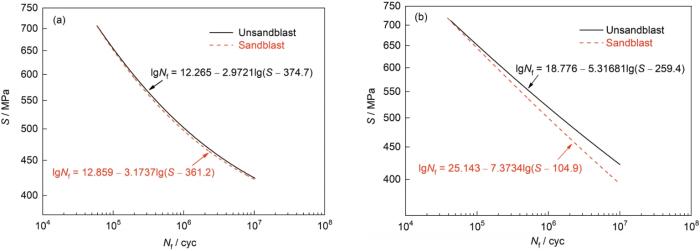
2.5 吹砂对疲劳性能的影响
图5
图5
未吹砂和粒径150 μm砂粒吹砂后DD6高温合金试样760和980℃的应力-寿命曲线
Fig.5
Stress-fatigue life curves of DD6 superalloy specimens at 760oC (a) and 980oC (b) before and after sand blasting with 150 μm granularity (S—stress, Nf—fatigue life)
式中,m和C是与材料、应力比、加载方式等有关的参数,Nf为试样断裂时的循环周次,S为应力,Sf为材料的疲劳强度。依据本研究的实验数据拟合获得方程如图5a所示。
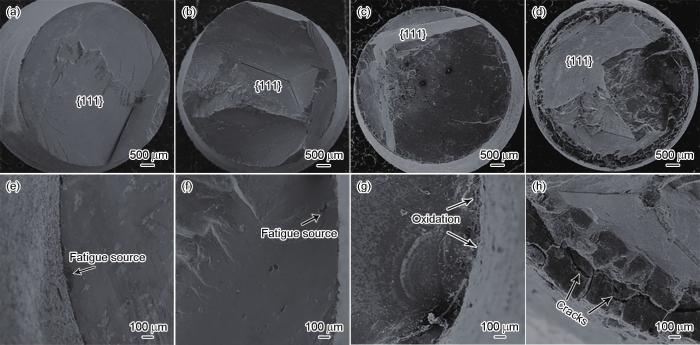
2.6 疲劳断口
图6
图6
未吹砂和粒径150 μm吹砂DD6高温合金试样在760和980℃旋转弯曲高周疲劳断口和疲劳源区形貌
Fig.6
High cycle fatigue fracture (a-d) and source zone (e-h) morphologies of DD6 superalloy specimens before (a, e, c, g) and after (b, f, d, h) sand blasting with 150 μm granularity under rotational bending at 760oC (a, e, b, f) and 980oC (c, g, d, h) (a, e) S = 460 MPa, Nf = 1.10 × 106 cyc (b, f) S = 500 MPa, Nf = 1.97 × 105 cyc (c, g) S = 440 MPa, Nf = 7.46 × 106 cyc (d, h) S = 500 MPa, Nf = 1.44 × 105 cyc
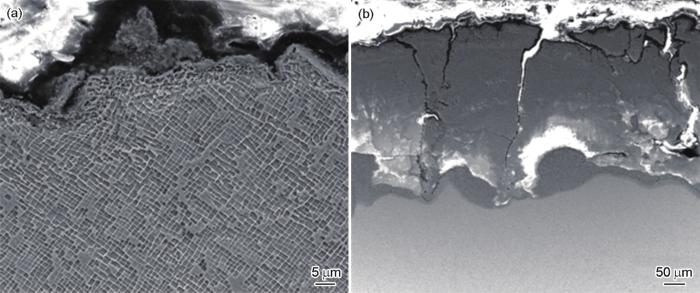
2.7 疲劳断口附近显微组织与位错
粒径150 μm吹砂试样760和980℃旋转弯曲高周疲劳断裂后的显微组织如图7所示。可以看出,760℃时,表面氧化层很薄;980℃时,表面氧化层较厚,氧化层存在很多横向及纵向裂纹。
图7
图7
粒径150 μm吹砂试样760和980℃旋转弯曲高周疲劳断裂后的横截面组织
Fig.7
Cross sectional microstructures of DD6 superalloy specimens after sand blasting with 150 μm granularity under rotational bending at 760oC (a) and 980oC (b)
图8为疲劳断口附近位错形态。可以看出,760和980℃时,合金断裂后γ'相仍保持较好的立方化形态。760℃低应力幅时(图8a),a / 2<011>位错主要集中在γ相通道中运动,未发现位错对剪切γ'相,且未见层错产生。760℃高应力幅时(图8b),2个基体a / 2<101>位错在γ'/γ相界面反应形成a / 2<112>位错,a / 2<112>位错通过分解成层错和分位错的方式切入γ'相,而a / 3<
图8
图8
150 μm吹砂后DD6高温合金试样760和980℃旋转弯曲高周疲劳断口附近的位错形态
Fig.8
Dislocation morphologies near high cycle fatigue fracture of DD6 superalloy specimens under rotational bending at different temperatures after sand blasting with 150 μm granularity
(a) 760oC, S = 430 MPa, Nf = 7.54 × 106 cyc (b) 760oC, S = 600 MPa, Nf = 8.07 × 104 cyc
(c) 980oC, S = 370 MPa, Nf = 8.71 × 106 cyc (d) 980oC, S = 700 MPa, Nf = 2.78 × 104 cyc
3 分析讨论
760℃时,表面氧化损伤较小,吹砂引入的形变强化和残余压应力层有利于提高疲劳性能。但是吹砂造成的表面粗糙度增加,使表面出现大量被砂粒尖角切削后不规则的凹坑,而凹坑的存在会带来缺口效应,这对疲劳性能产生不良影响。研究[27,29,30]表明,表面粗糙度增加会引起疲劳性能下降。Remes等[31]对一种高强钢的研究表明,残余压应力和低的表面粗糙度会提高疲劳性能。形变强化和残余压应力对疲劳性能有增益作用,但粗糙度增加带来的缺口效应会引起疲劳性能下降,抵消了形变强化和残余压应力的增益作用。本工作中,吹砂后试样与未吹砂试样疲劳性能相当,这是吹砂引入的形变强化和压应力层的增益作用与缺口效应负面影响的耦合作用所导致。
980℃时,吹砂后试样疲劳性能变化受下述因素的影响:(1) 吹砂后试样表面凹坑带来的缺口效应,降低疲劳性能;(2) 随应力幅降低,高温旋转弯曲高周疲劳寿命增加,表面氧化程度逐渐加大,氧化损伤对疲劳断裂的影响增加,降低疲劳性能;(3) 吹砂后试样表面形变强化层具有脆性特征,在高温和循环应力作用下会形成裂纹,并促进亚表面发生氧化,使试样表面层承载能力下降;已有研究[31~33]表明,形变强化会导致高温条件下试件的疲劳强度大幅降低,表面冷作硬化因素会引起GH49合金900℃高周疲劳寿命降低35%以上;(4) 虽然吹砂引入的残余压应力对疲劳寿命有增益作用,但在高温条件下,位错运动加剧,残余应力快速释放,残余压应力增益作用显著降低;研究[33]表明,随环境温度提高,喷丸处理后的AISI4140试件表面残余应力的释放速度随之加快,且随应力幅降低,测试时间增加,残余应力释放更加充分。综上所述,吹砂后980℃疲劳寿命低于未吹砂疲劳寿命,2者之差随应力幅的减小而增大,这是缺口效应、氧化损伤与形变强化层的负面影响及残余压应力快速释放使性能增益减小等因素耦合作用所导致的。
4 结论
(1) 吹砂后靠近表面区域位错大量增殖,且大量位错剪切γ'相,形成反相畴界和层错。吹砂造成形变强化、引入残余应力,使表面出现砂粒切削凹坑、表面粗糙度增加,破坏了单晶高温合金表面完整性。
(2) 未吹砂与粒径150 μm吹砂DD6单晶高温合金试样760℃旋转弯曲高周疲劳强度分别为434和431 MPa,980℃旋转弯曲高周疲劳强度分别为425和394 MPa。
(3) 吹砂引入形变强化和压应力层的增益作用与缺口效应负面影响的耦合作用导致吹砂后760℃疲劳寿命与未吹砂疲劳寿命相当。
(4) 缺口效应、氧化损伤与形变强化层的负面影响及残余压应力快速释放使性能增益减小等因素耦合导致吹砂后980℃疲劳寿命低于未吹砂疲劳寿命,2者之差随应力幅的减小而增大。
参考文献
Combined high and low cycle fatigue life prediction model based on damage mechanics and its application in determining the aluminized location of turbine blade
[J].
Thermomechanical fatigue experiment and failure analysis on a nickel-based superalloy turbine blade
[J].Thermomechanical fatigue (TMF) experiment with dwell times on a nickel-based superalloy turbine blade was conducted. The strain field and temperature field of the test section were simulated well through adjusting gripping fixture and induction coil. In addition to the loading, heating, cooling and control subsystems, high temperature strain measurement subsystem was introduced into the experiment to ensure the accuracy of the simulation results of service condition for the test section. In the whole experiment, the service condition of the test section was reproduced. The experiment result showed that TMF crack initiated at the trailing edge of the test section and propagated along the leading edge direction. Using the scanning electron microscope (SEM), multiple crack sources at the surface of turbine blade were observed and the crack surface was oxidized seriously. In addition, based on the fractographic and metallographic observation, the mixed features of intergranular fracture and transgranular fracture were found. The interaction of oxidation, creep damage and fatigue damage is an important reason for the TMF failure of the turbine blade.
High cycle fatigue behavior of second generation single crystal superalloy
[J].
第二代单晶高温合金高周疲劳行为研究
[J].
The surface integrity of machined-and-ground high strength steels
[J].
Application of high strength alloy and technonolgy of anti-fatigue manufacturing
[J].
高强度合金应用与抗疲劳制造技术
[J].
Surface integrity and fracture resistance of engineering metallic materials and components
[J].
工程金属材料/零件的表面完整性及其断裂抗力
[J].
Research status and development trend of surface integrity
[J].
表面完整性研究现状及发展趋势
[J].
Effect of surface treatment on mechanical properties of 7B05 aluminum alloy MIG butt welded joints
[J].
表面处理对7系铝合金MIG焊对接接头力学性能的影响
[J].
TLP repaired IN738LC superalloy with uneven surface defect gap width after post heat treatment: Microstructure and mechanical properties
[J].
Research on residual stress field of GH909 alloy by shot peening
[J].
GH909合金喷丸强化残余应力场的研究
[J].
Effect of shot peening on high cycle fatigue limit of FGH4097 P/M superalloys at room temperature
[J].
喷丸强化对FGH4097粉末高温合金室温高周疲劳极限的影响
[J].
A low-cost second generation single crystal superalloy DD6
[A].
Effects of low angle boundaries on the mechanical properties of single crystal superalloy DD6
[A].
Influence of shot peening on high temperature rotating bending fatigue property of DD6 single crystal superalloy
[J].
喷丸强化对DD6单晶高温合金高温旋转弯曲疲劳性能的影响
[J].
Influence of ceramic-shot-peening on surface integrity of DD6 single crystal superalloy
[J].
陶瓷弹丸喷丸强化对DD6单晶高温合金表面完整性的影响
[J].
Microstructure of recrystallization and their effects on stress rupture property of single crystal superalloy DD6
[J].The specimens of single crystal superalloy DD6 were grit blasted and heat treated at 1100, 1200, and 1300 ℃ for 4 h at vacuum atmosphere respectively, then the microstructure of recrystallized DD6 alloy and their effects on the stress rupture performance were investigated. The results showed that cellular recrystallization nucleated in grit blasted samples heat treated at 1100 ℃ for 4 h, the dislocation tangles were found in the front of cellular recrystallization grain boundary in DD6 alloy, equiaxed recrystallization grains nucleated in grit blasted samples heat treated at 1300 ℃ for 4 h, and the carbides precipitate at the equiaxed recrystallization grain boundary, while the coexistence of equiaxed recrystallization grains and cellular recrystallization, defined as mixed recrystallization, occurred in the grit blasted samples heat treated at 1200 ℃ for 4 h. The cellular recrystallization reduced the stress rupture lives of DD6 alloy slightly, and the equiaxed recrystallization reduced stress rupture lives seriously, while the reduction degree of the stress rupture lives of the mixed recrystallization was between cellular recrystallization and equiaxed recrystallization. Besides this, with increase of depth of recrystallization and stress, the stresses rupture life decreased. It was also found that the fracture surface configuration was belonging to intergranular fracture with equiaxed recrystallization samples. The characteristic of the fracture surface changed to dimple fracture with cellular recrystallization samples, at all these condition the crack nucleated on the recrystallization grain boundaries of specimens during stress rupture process.
单晶高温合金DD6再结晶组织及其对持久性能的影响
[J].对单晶高温合金DD6进行表面吹砂处理, 然后分别在1100, 1200和1300 ℃保温4 h, 研究了不同加热条件下DD6合金的再结晶组织及其对持久性能的影响. 结果表明, DD6合金吹砂试样1100 ℃加热4 h形成胞状再结晶组织, 胞状再结晶晶界前沿的基体中存在大量的位错缠结, 合金的持久寿命略微降低; 1200 ℃加热4 h形成胞状再结晶与等轴再结晶同时存在的混合型再结晶组织, 合金的持久寿命降低; 1300 ℃加热4 h形成等轴再结晶组织, 等轴再结晶晶界上发现碳化物析出, 合金的持久寿命严重降低. 带有等轴再结晶组织的持久试样的断口形貌为沿晶断口, 带有胞状再结晶组织的持久试样的断口形貌为韧窝断口, 带有再结晶组织的试样裂纹起源于再结晶晶界.
Alumina grit blasting parameters for surface preparation in the plasma spraying operation
[J].
Effect of over-temperature on microstructure and high cycle fatigue properties of DD6 single crystal superalloy
[J].
超温对DD6单晶高温合金组织及高周疲劳性能影响
[J].
Effect of recrystallization on axial high cycle fatigue properties of DD6 single crystal superalloy
[J].
再结晶对DD6单晶高温合金轴向高周疲劳性能的影响
[J].
High-temperature ultra-high cycle fatigue damage of notched single crystal superalloys at high mean stresses
[J].
High cycle fatigue behavior of a single crystal superalloy at elevated temperatures
[J].
The effect of casting conditions on the high-cycle fatigue properties of the single-crystal nickel-base superalloy PWA 1483
[J].
Effects of microstructure and temperature on fatigue behavior of E319-T7 cast aluminum alloy in very long life cycles
[J].
Primary creep in single crystal superalloys: Some comments on effects of composition and microstructure
[J].
Review on the pretreatment of substrate for thermal spray process
[J].
热喷涂基体表面前处理技术的研究进展
[J].
The effect on fatigue life of residual stress and surface hardness resulting from different cutting conditions of 0.45%C steel
[J].
Effect of near-surface residual stress and microstructure modification from machining on the fatigue endurance of a tool steel
[J].
The fatigue behavior and mechanism of FV520B-I with large surface roughness in a very high cycle regime
[J].
Effect of toe grinding on fatigue strength of ship structure
[J].
Influence of surface integrity on the fatigue strength of high-strength steels
[J].