零热膨胀金属材料研究进展
Research Progress on Zero Thermal Expansion Metallic Materials
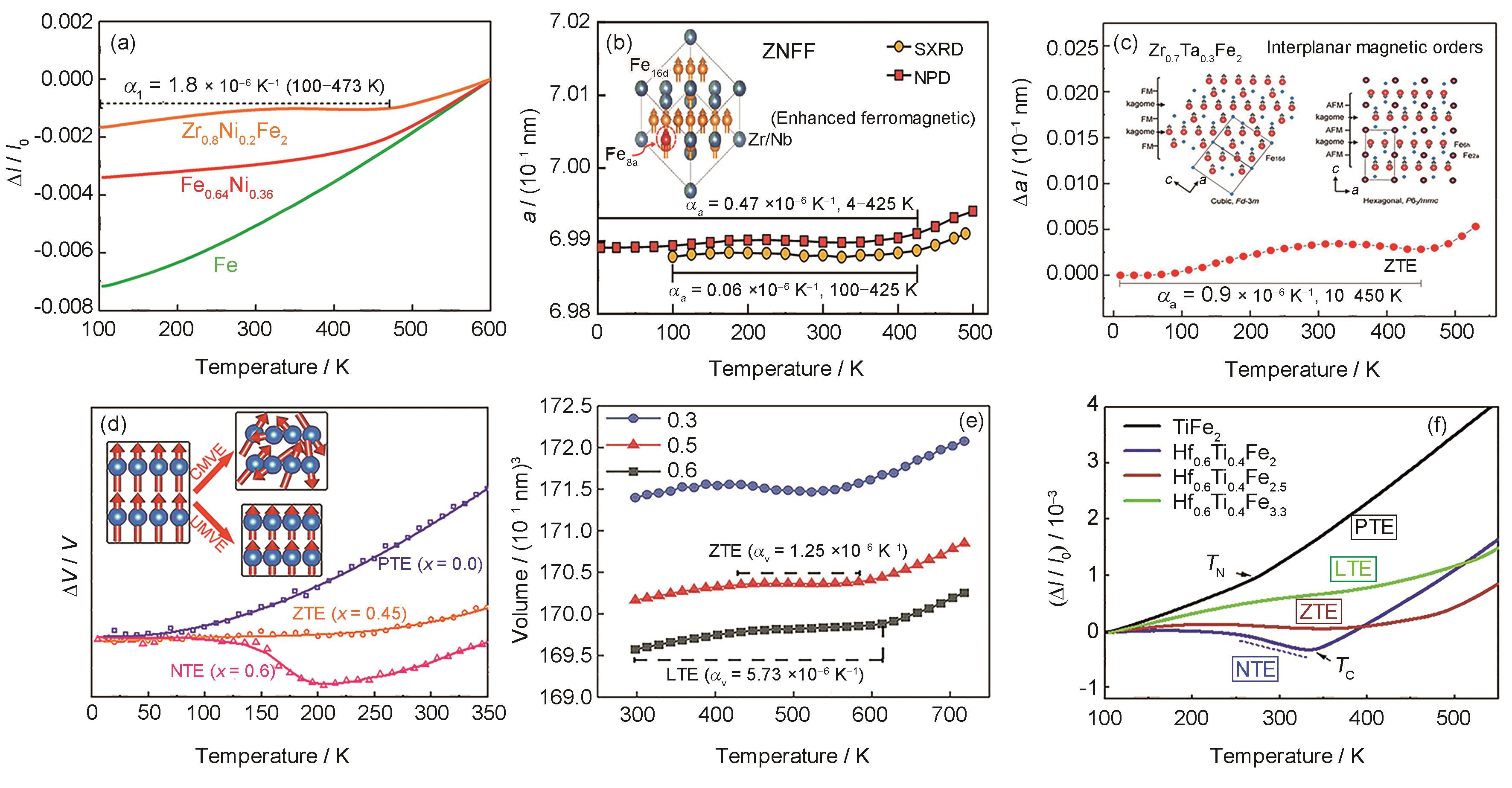
(a) comparison of macroscopic linear expansion of Zr0.8Nb0.2Fe2, Fe0.64Ni0.36, and Fe[
(b) temperature dependence of cell parameters for neutron diffraction and synchrotron radiation analysis of (Zr0.65Nb0.35)0.95Fe0.05Fe2 (ZNFF)[
(c) variation of cell parameters of Zr0.7Ta0.3Fe2 with temperature (Δa—change of a,ZTE—zero thermal expansion, FM—ferromagnetic, AFM—antiferromagnetic)[
(d) relative cell volume of (Sc, Ti)Fe2 varies with temperature when x = 0 (PTE—positive thermal expansion), x = 0.45 (ZTE), and x = 0.6 (NTE—negative thermal expansion)[
(e) temperature dependence of unit cell volumes for HfFe2 + δ (δ = 0.3, 0.5, and 0.6)[
(f) dilatometer thermal expansion of TiFe2 and Hf0.6Ti0.4Fe2 + x (x = 0, 0.5, and 1.3)[