耐热铝合金:组织设计与合金制备
Heat-Resistant Al Alloys: Microstructural Design and Preparation
耐热铝合金:组织设计与合金制备 |
| 孙军, 刘刚, 杨冲, 张鹏, 薛航 |
|
Heat-Resistant Al Alloys: Microstructural Design and Preparation |
| SUN Jun, LIU Gang, YANG Chong, ZHANG Peng, XUE Hang |
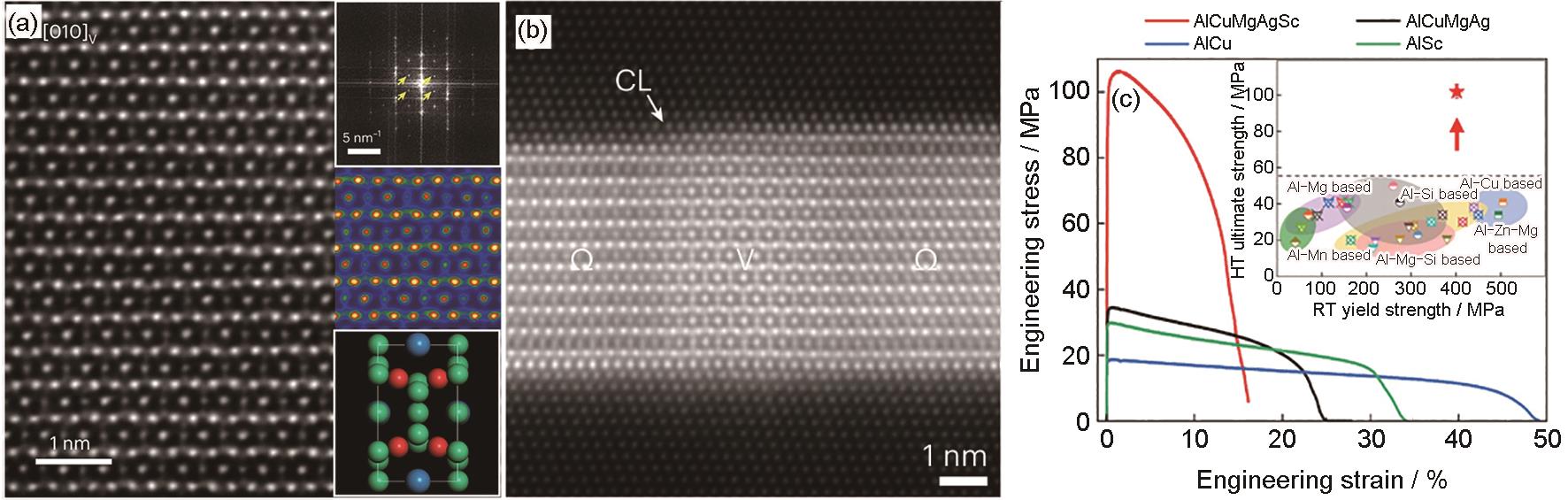
| 图3 V相HAADF像及其对应的结构分析和结构模型(观察方向[010]),Sc在共格台阶(CL)处浸入并诱发Ω→V原位相变的HAADF像,及400 ℃下拉伸应力-应变曲线对比以及拉伸强度与其他铝合金对比[ |
| Fig.3 Representative HAADF image to show the crystal structure of V phase, viewed along [010] (Insets show the corresponding fast Fourier transform image (top right) and colorized Z-contrast image (middle right). In top right image, an additional set of patterns is clearly detected (marked by yellow arrows) that indicate a substructure. Green, red, and blue colors in the structural sketch (bottom right) represent Al, Cu, and Sc atoms, respectively) (a), representative HAADF image showing the Ω→V in situ phase transformation induced by the Sc intake at the coherent ledge (CL) (b), and tensile stress-strain curves at 400 oC, showing the tensile strength > 100 MPa achieved in Al-Cu-Mg-Ag-Sc alloy much greater than that in other comparing alloys (The inset figure demonstrates that the tensile strength > 100 MPa at 400 oC is over one time of all the reported Al alloys. HT—high temperature of 400 oC, RT—room temperature) (c)[ |

|