可充电镁电池负极材料及界面化学的研究进展
Research Progress on Anode Materials and Interfacial Chemistry for Rechargeable Magnesium Batteries
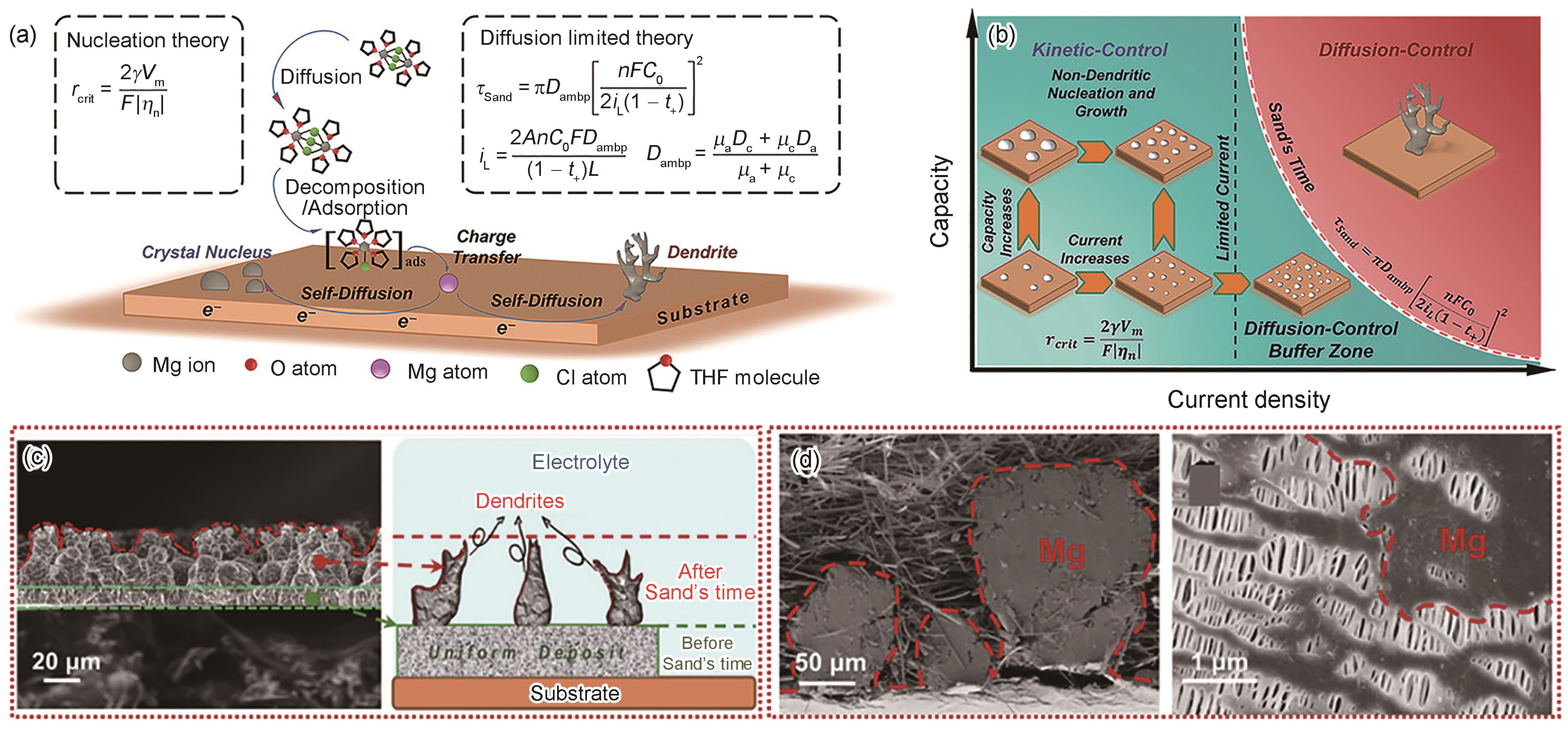
(a) schematic of Mg electroplating progress and the standard parameters to guide the diffusion limited theory and the nucleation theory (take the all phenyl complex (APC) electrolyte as an example) (rcrit—critical radius, ηn—overpotential, γ—surface energy, F—Faraday's constant, Vm—molar volume, τSand—Sand's time, iL—limited current, C0—salt concentration in bulk electrolyte, Dambp—ambipolar diffusion coefficient, n—electron transfer number, A—electrode area, L—thickness, μa—anion transference number, μc—cationic transference number, Dc—self-diffusion coefficient of individual cation, Da—self-diffusion coefficient of individual anion, t+—cationic transference number. THF—tetrahydrofuran)
(b) diagram of diffusion-control buffer zone
(c) cross sectional SEM image and schematic of Mg deposit at 10 mA/cm2 in APC electrolyte
(d) Mg plating in glass fiber separator at 5 mA/cm2