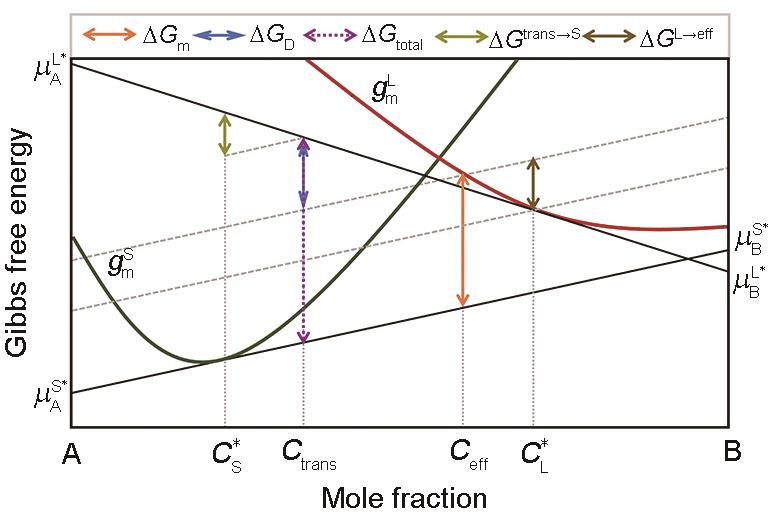
Fig.6 Mole Gibbs free energy diagram for the solid/liquid interface kinetic processes with a partial solute-drag effect under a non-steady-state condition (The total Gibbs free energy dissipated by the interface after solidification of 1 mol liquid is = . By translating the tangent of Gibbs free energy curve of solid at to the Gibbs free energy curve of liquid at Ceff, Gtotal is divided into two parts. The upper one for trans-interface diffusion is = and latter part for interface migration is Gm = . The difference in GD between the steady-state condition and the non-steady-state condition is = , which is the Gibbs free energy dissipated to adjust the actual composition transferred across the interface from to Ctrans for trans-interface diffusion. The difference in Gm between the two cases with a full solute-drag effect and with a partial solute-drag effect is = , which is the Gibbs free energy dissipated to adjust the liquid composition ahead of the solid/liquid interface from to Ceff for interface migration. It should be pointed out that Hareland et al. [30] confused the concepts of Ctrans under non-steady-state and Ceff. Furthermore, it is also queried that the definition of Ceff can be stilled be used for a non-steady state condition. For example, there will be a problem when < Ceff < Ctrans (Ceff—effective concentration)
|