一种第四代镍基单晶高温合金的同相位热机械疲劳行为及损伤机制
In-Phase Thermal-Mechanical Fatigue Behavior and Damage Mechanism of a Fourth-Generation Ni-Based Single-Crystal Superalloy
一种第四代镍基单晶高温合金的同相位热机械疲劳行为及损伤机制 |
| 谭子昊, 李永梅, 王新广, 赵浩川, 谭海兵, 王标, 李金国, 周亦胄, 孙晓峰 |
|
In-Phase Thermal-Mechanical Fatigue Behavior and Damage Mechanism of a Fourth-Generation Ni-Based Single-Crystal Superalloy |
| TAN Zihao, LI Yongmei, WANG Xinguang, ZHAO Haochuan, TAN Haibing, WANG Biao, LI Jinguo, ZHOU Yizhou, SUN Xiaofeng |
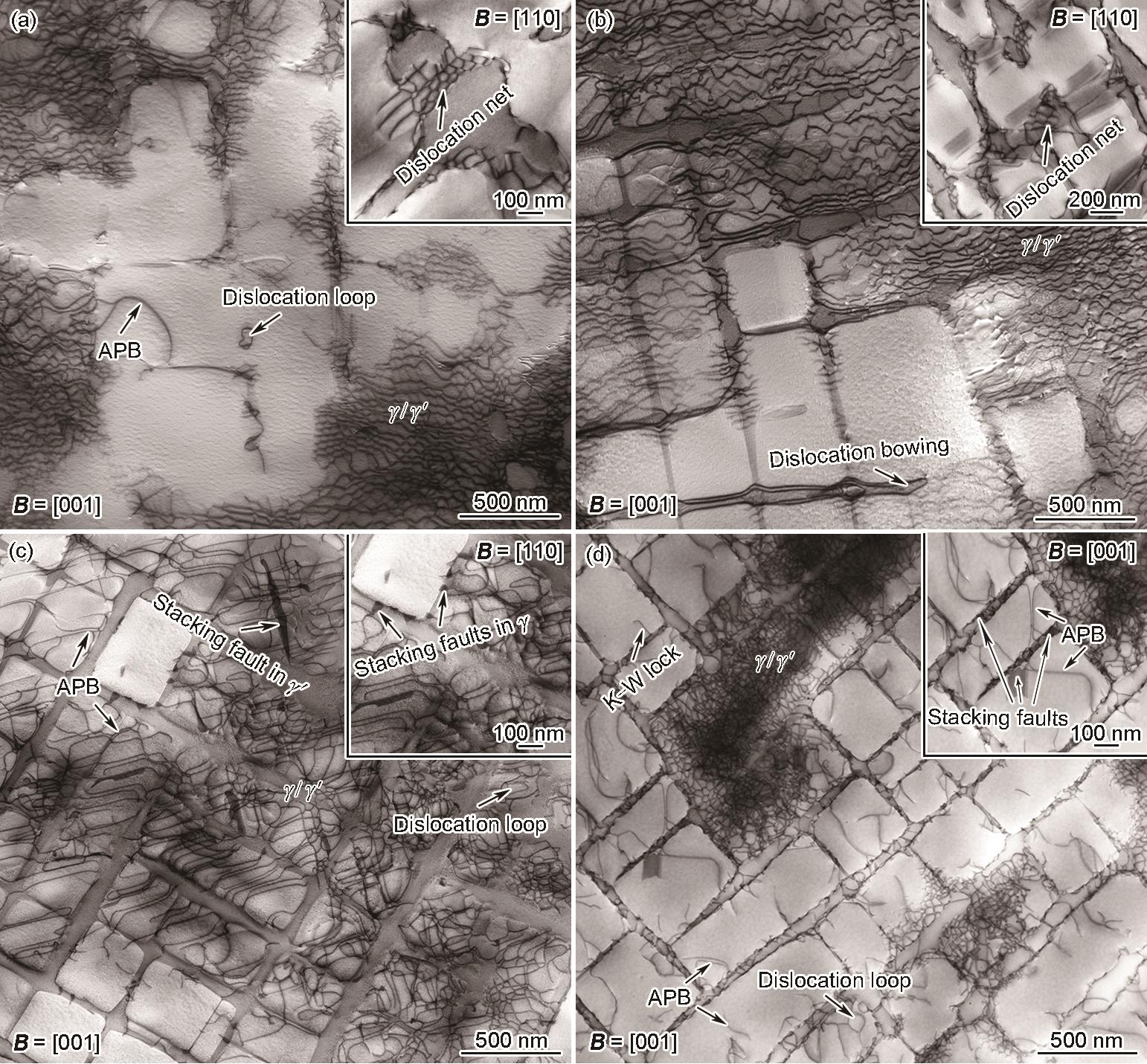
| 图11 DD91合金在不同应变幅下IP-TMF断裂后的特征位错组态 |
| Fig.11 Typical dislocation configurations of the DD91 alloy after IP-TMF fracture at strain amplitudes of 0.5% (a), 0.6% (b), 0.8% (c), and 0.9% (d) (Insets show magnified images of special configurations. APB—anti-phase boundary, K-W—Kear-Wilsdorf) |

|