材料研究中的可解释机器学习
Explainable Machine Learning in the Research of Materials Science
材料研究中的可解释机器学习 |
| 王冠杰, 刘盛咸, 周健, 孙志梅 |
|
Explainable Machine Learning in the Research of Materials Science |
| WANG Guanjie, LIU Shengxian, ZHOU Jian, SUN Zhimei |
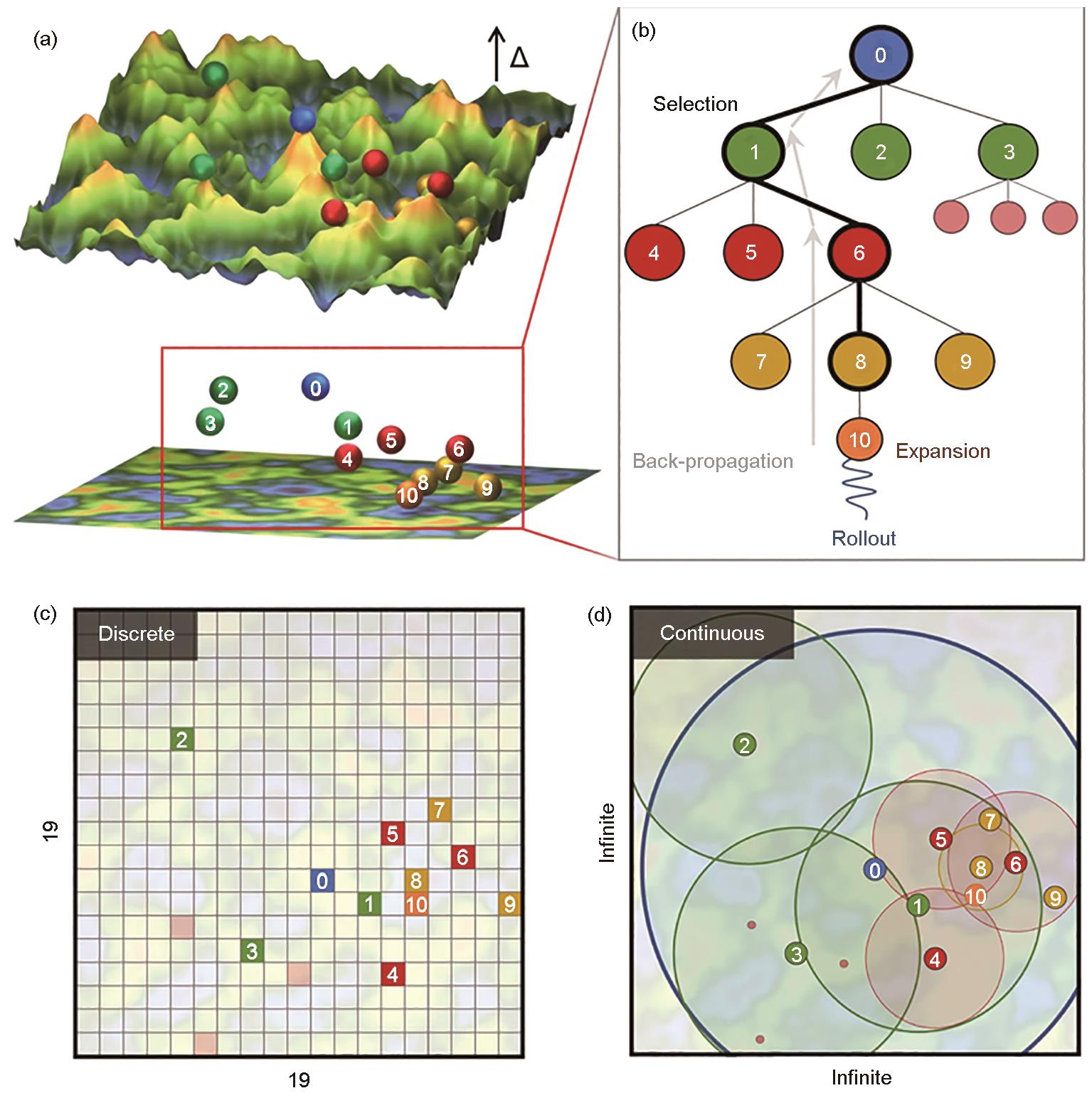
| 图4 连续决策树搜索算法流程,Monte Carlo树搜索(MCTS)决策树结构中根节点、父节点、子节点及其关系的示意图,传统MCTS算法的搜索空间的离散数据点,及本文中的参数搜索问题[ |
| Fig.4 Continuous decision tree search algorithm flow (The spheres represent candidates for different model parameters in the MCTS run, and the numbers on the spheres correspond to their node positions in the Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) tree shown in Fig.4b. These numbers roughly correspond to the exploration order of the candidates, Δ represents the difference between predicted values and objective values) (a); schematic of the root node, parent node, child nodes and their relationships in the MCTS decision tree structure (b); discrete data points in the search space of the traditional MCTS algorithm (c); and parameter search problem in this paper so that the algorithm can converge to the optimal solution (d)[ |

|