异质纳米结构金属强化韧化机理研究进展
Progress in Strengthening and Toughening Mechanisms of Heterogeneous Nanostructured Metals
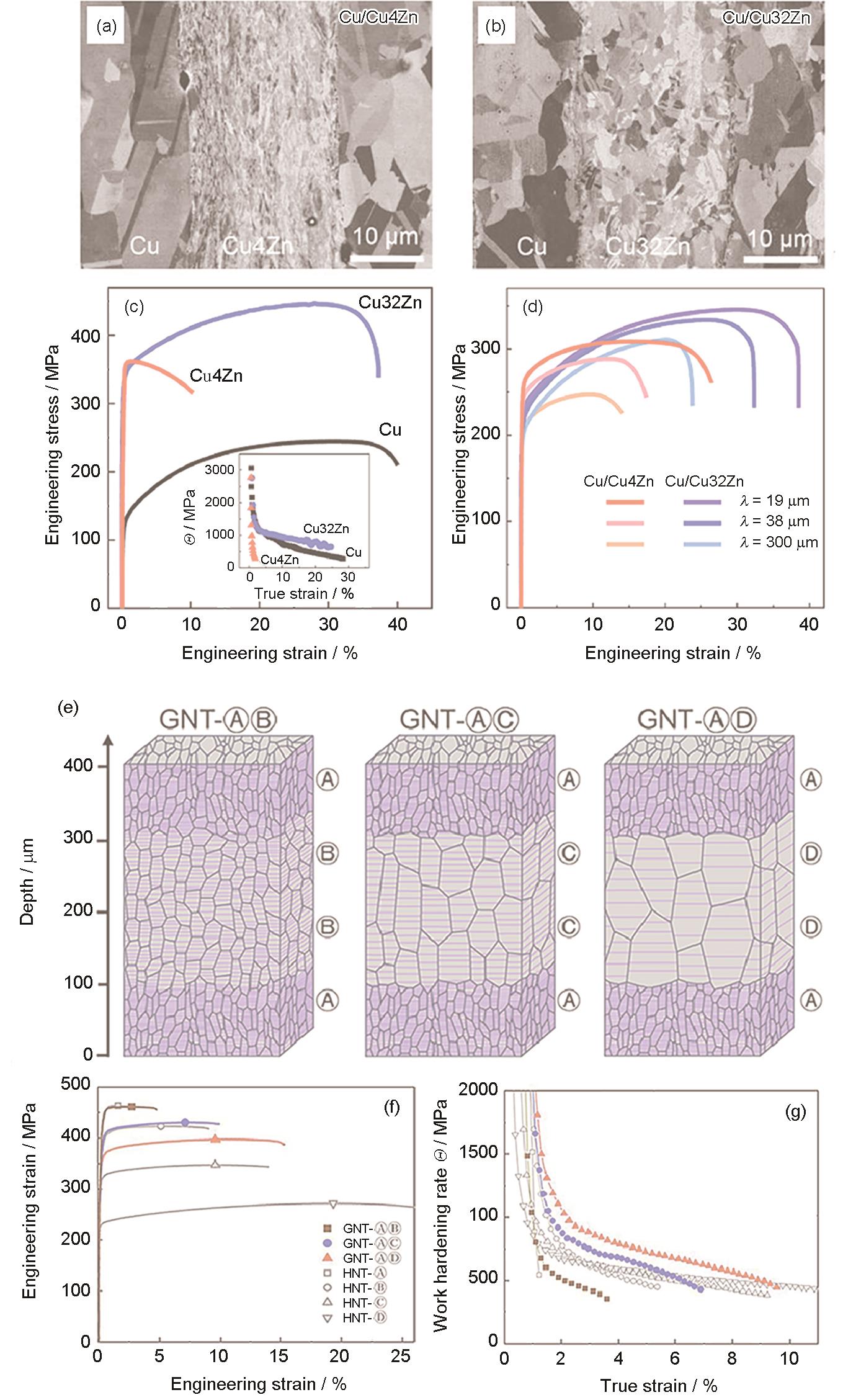
(a, b) microstructures of laminated Cu/Cu4Zn (a) and Cu/Cu32Zn (b) with layer thickness (λ) of 19 μm[
异质纳米结构金属强化韧化机理研究进展 |
| 卢磊, 赵怀智 |
|
Progress in Strengthening and Toughening Mechanisms of Heterogeneous Nanostructured Metals |
| LU Lei, ZHAO Huaizhi |
| 图1 层状结构Cu/Cu4Zn和Cu/Cu32Zn的局部微观结构(层间距λ = 19 μm)与相应的工程应力-应变曲线,以及3种层状纳米孪晶Cu样品的微观结构示意图与相应的工程应力-应变曲线和加工硬化率曲线,并与相应的单组分进行对照[ |
| Fig.1 Microstructures and engineering stress-strain curves of laminated Cu/Cu4Zn and Cu/Cu32Zn, or nanotwinned Cu samples (GNT—gradient nanotwinned, HNT—homogeneous nanotwinned) (a, b) microstructures of laminated Cu/Cu4Zn (a) and Cu/Cu32Zn (b) with layer thickness (λ) of 19 μm[ |

|