异构金属材料及其塑性变形与应变硬化
Heterostructured Metallic Materials: Plastic Deformation and Strain Hardening
异构金属材料及其塑性变形与应变硬化 |
| 武晓雷, 朱运田 |
|
Heterostructured Metallic Materials: Plastic Deformation and Strain Hardening |
| WU Xiaolei, ZHU Yuntian |
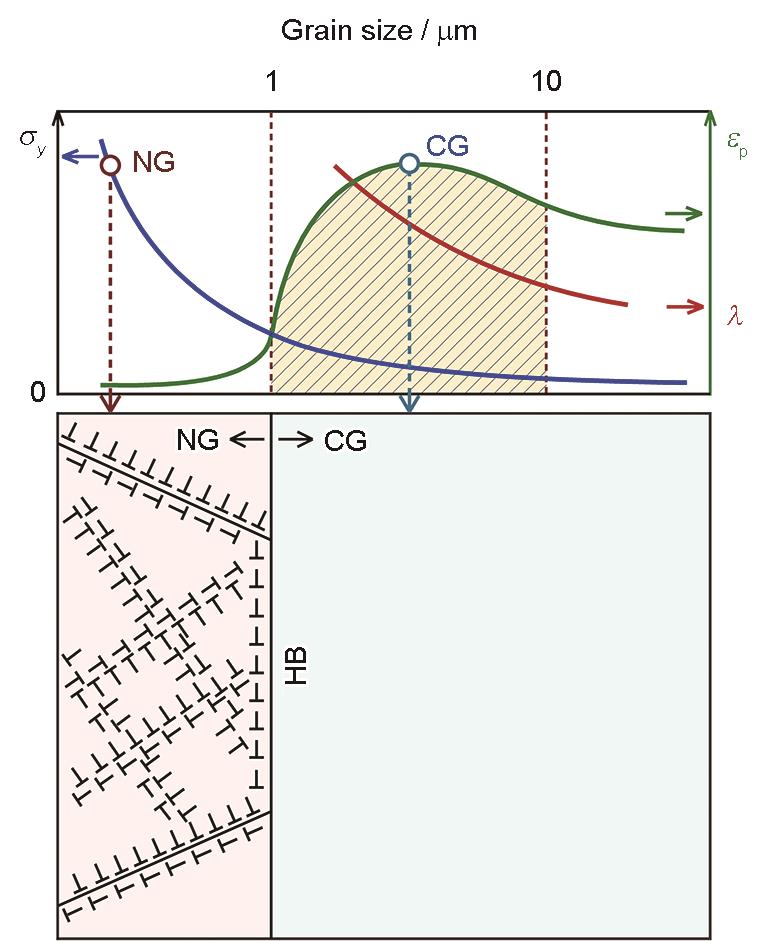
| 图2 异构基元及其微观设计 |
| Fig.2 Schematic of characteristic zones in a heterostructure (Upper panel: yield strength (σy), plastic strain (εp), and strain gradient (λ), all as a function of grain size. Thereinto, σy obeys the Hall-Petch relationship, while both εp and λ are of the plasticity-related size effect[ |

|