异构金属材料及其塑性变形与应变硬化
Heterostructured Metallic Materials: Plastic Deformation and Strain Hardening
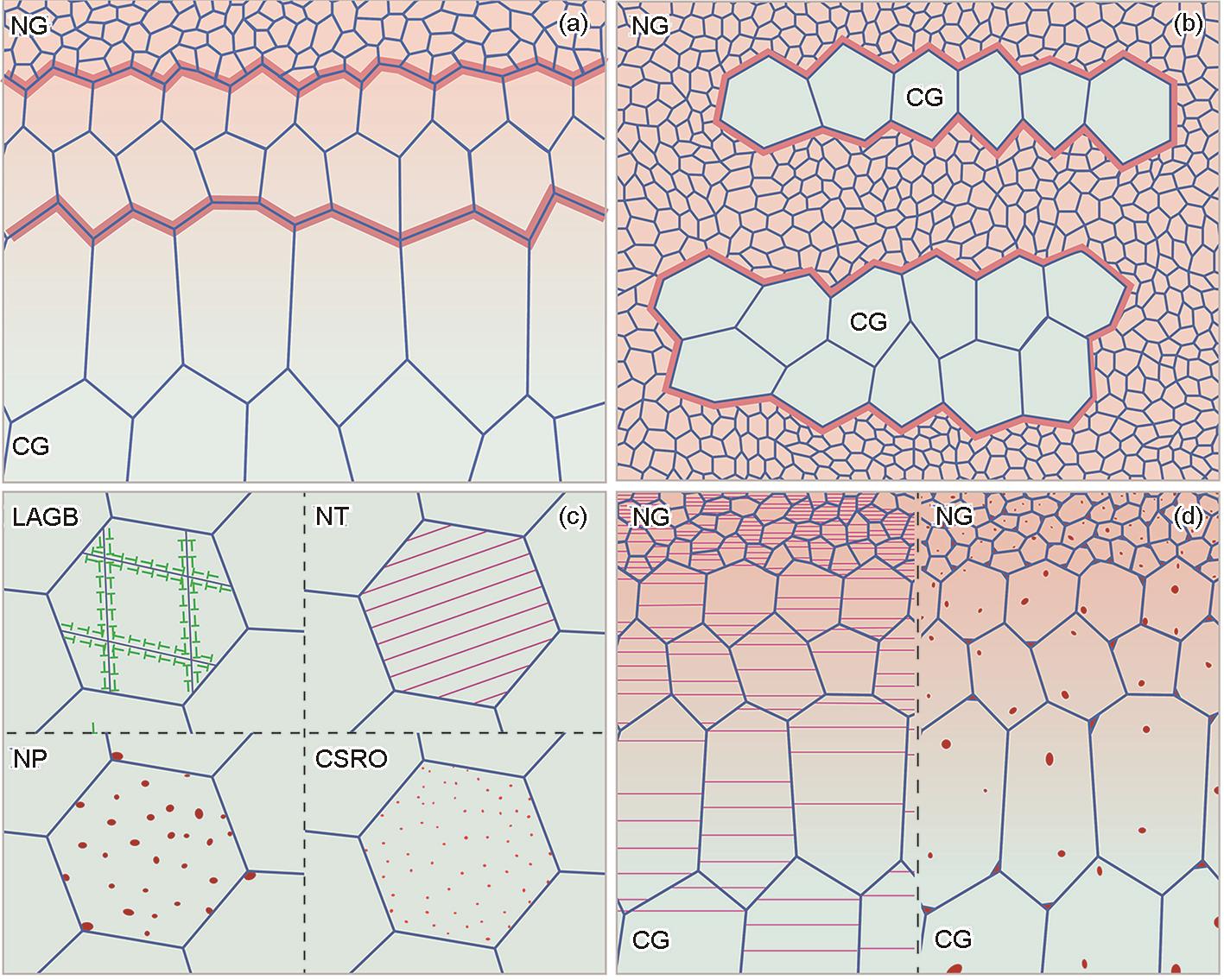
(a, b) zone HSs. Typical examples are gradient structure (a) and lamellar structure (b) (Thick dull-red lines: hetero-zone boundaries; NG: nano-grain; CG: coarse grain)
(c) sub-zone HSs of four kinds, respectively, with the low-angle grain boundary (LAGB), nano-twin (NT), nano-precipitate (NP), and chemical short-range order (CSRO) inside the grain interior, all independently as the sub-constituent of HSs
(d) composite-like HSs, usually with dual-gradients in both grain size and nano-twin (left)/nano-precipitate (right)