金属玻璃结构及其失稳的原子层次研究
Atomic-Level Study in the Structure and Its Instability of Metallic Glasses
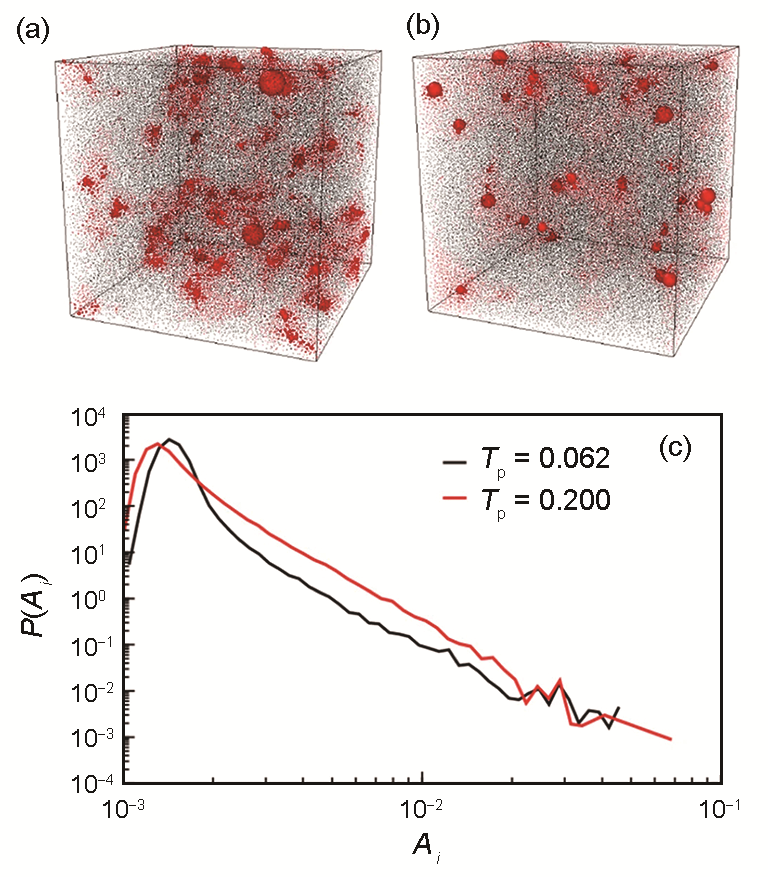
(a, b) snapshots obtained for glassy samples with high stability (a) and poor stability (b). The particles are shown with their radius given by the “atomic softness” A(i) calculated from the lowest quasi-localized modes
(c) the probability distribution of A(i) (P(Ai)) for glassy samples with high stability (a) and poor stability (b). For sample with high stability (a), there is a smaller fraction of the particles with larger A(i), and thus the modes are more localized (Tp—parent temperature)