金属玻璃中的非晶多形态转变
Polyamorphic Transitions in Metallic Glasses
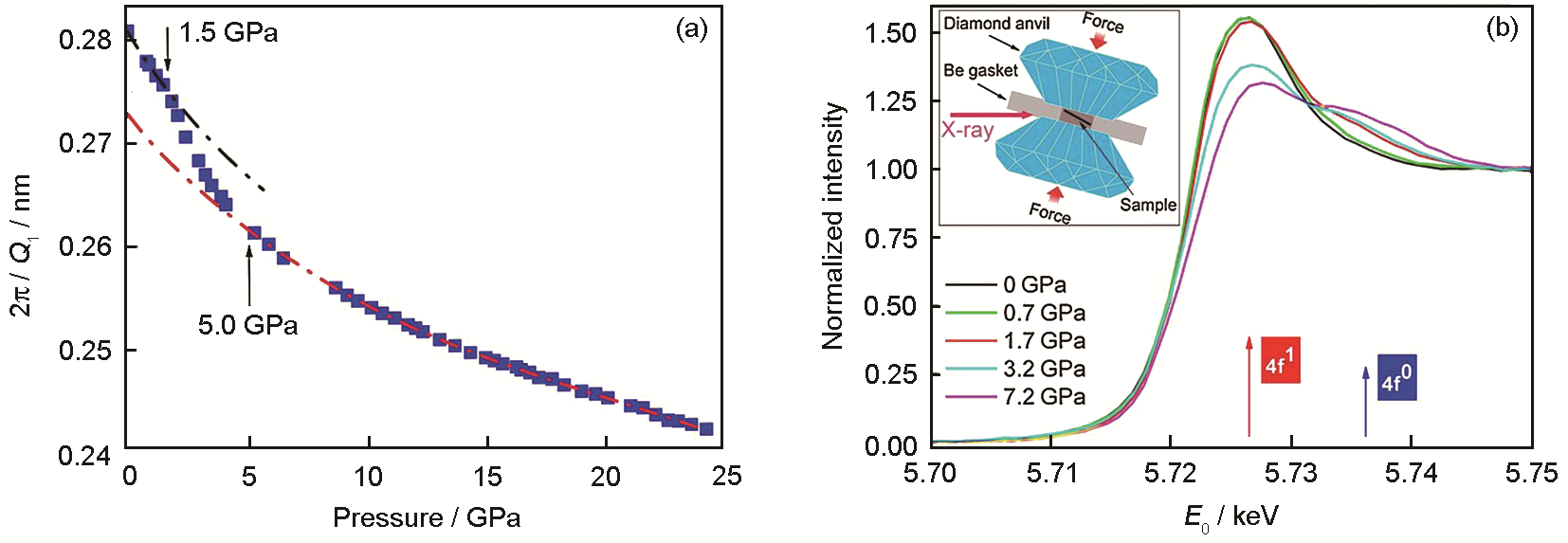
(a) inverse main diffraction peak positions 2π/Q1 of Ce75Al25 metallic glass as a function of pressure (Two different states, low density amorphous (dashed black line) and high density amorphous (dashed red line) along with a transition region from about 1.5 to 5.0 GPa can be identified. The data are smooth owing to the hydrostatic pressure conditions, and the error for experimental data are smaller than the symbol size. Q1—peak position of the first sharp diffraction peak)
(b) in situ high-pressure Ce L3-edge X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) spectra of Ce75Al25 metallic glass (The arrows point to the 4f0 and 4f1 components. The appearance of the 4f0 feature indicates the delocalization of 4f electron, and coincides with the volume collapse in XRD results. 4f0—itinerant 4f electron state, 4f1—localized 4f electron state, E0— incident energy)