增材制造可降解金属医用植入物
|
|
郑玉峰, 夏丹丹, 谌雨农, 刘云松, 徐钰倩, 温鹏, 田耘, 赖毓霄
|
Additively Manufactured Biodegrabable Metal Implants
|
|
ZHENG Yufeng, XIA Dandan, SHEN Yunong, LIU Yunsong, XU Yuqian, WEN Peng, TIAN Yun, LAI Yuxiao
|
|
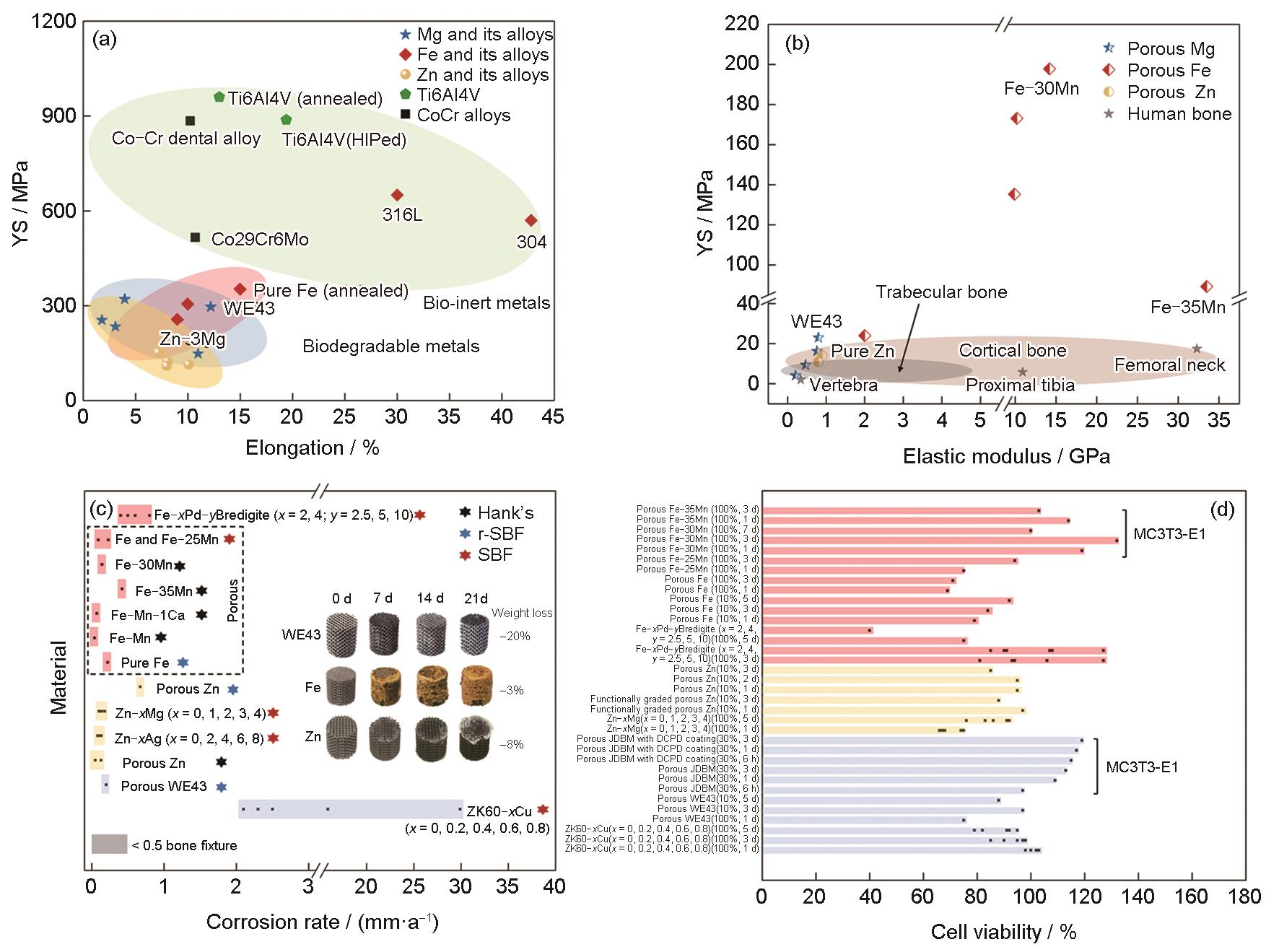
图7 L-PBF成形块体医用金属材料的拉伸性能[59,112,115,116,119,123,125,127~136],L-PBF成形多孔可降解金属的压缩屈服强度与弹性模量之间的关系[58,78~81,118,121,142],L-PBF成形可降解金属的降解速率[78~80,118,119,121,128,137,144,145],及MG63及MC3T3-E1细胞在L-PBF成形可降解金属浸提液中的细胞成活率(未标出部分为MG63细胞的结果)[58,78~81,118,121,128,137,151,152]
|
Fig.7 Tensile properties of bulk medical metallic materials manufactured by L-PBF (a)[59,112,115,116,119,123,125,127-136], elastic modulus-compressive yield strength relationship of biodegradable scaffolds manufactured by L-PBF (b)[58,78-81,118,121,142], biodegradation rates of L-PBF biodegradable metals (c)[78-80,118,119,121,128,137,144,145], and cell viability of MG63 and MC3T3-E1 cell lines in L-PBF biodegradable metals' extractions (The unmarked parts are the cell viabilities of MG63) (d)[58,78-81,118,121,128,137,151,152]
|
|
|
|
|

