增材制造可降解金属医用植入物
Additively Manufactured Biodegrabable Metal Implants
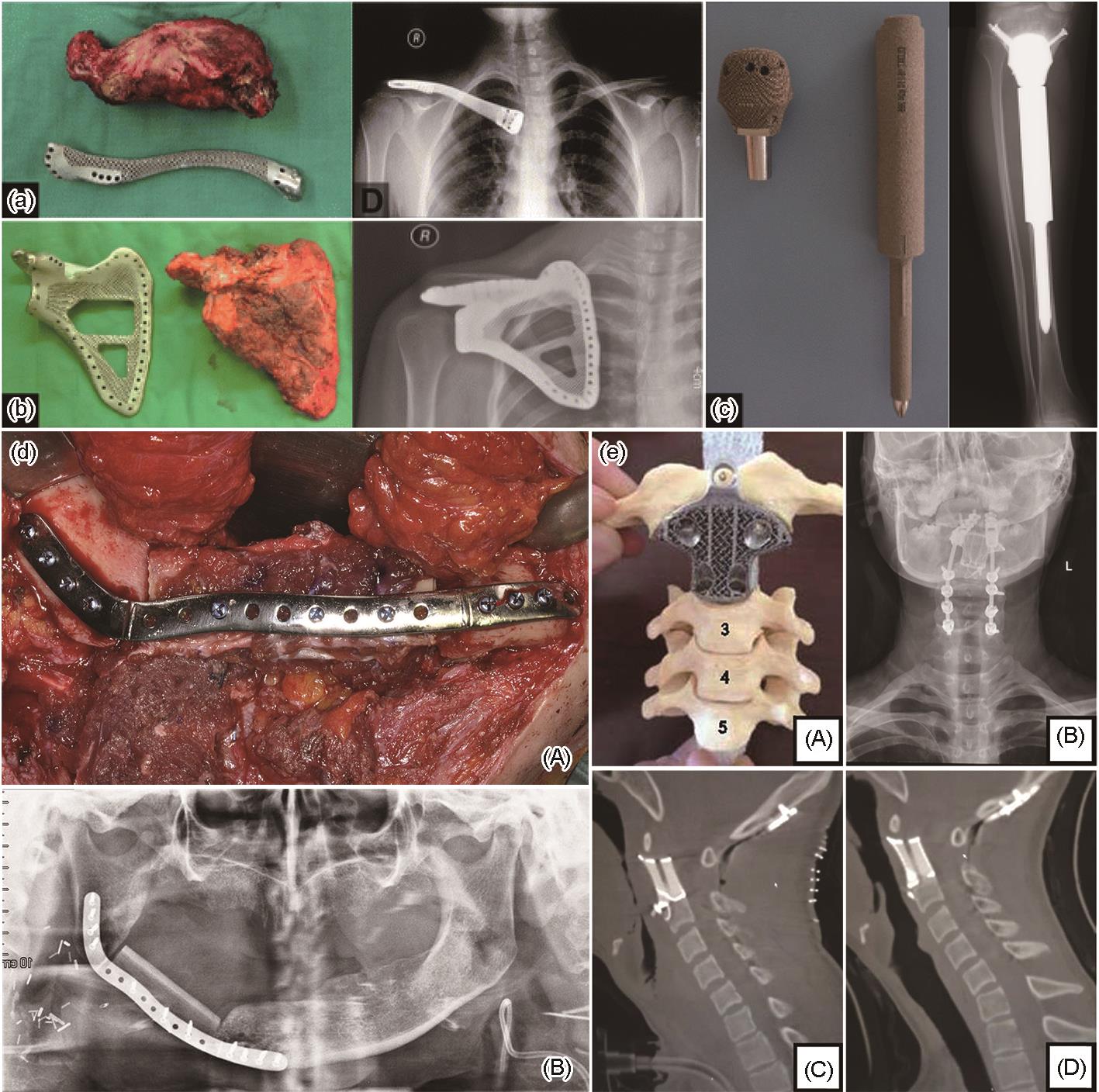
(a-c) clavicle (a), scapula (b), and uncemented proximal tibial reconstruction (c), respectively [
(d) additively manufactured Ti alloy bone plate[
(A) reconstruction of unilateral mandible with AM Ti bone plate
(B) 12 months postoperative radiologic examination
(e) replacement using AM Ti alloy vertebral body[
(A) model
(B) postoperative X-ray demonstrating how the self-stabilizing artificial vertebral body was inserted C2
(C) sagittal reconstruction immediately postoperatively
(D) at the 1-year follow-up showing evidence of implant osseointegration, no subsidence or displacement of the construct, and no local recurrence of the tumor