高强亚稳β钛合金变形机制及其组织调控方法
Deformation Mechanism and Microstructure Control of High Strength Metastable β Titanium Alloy
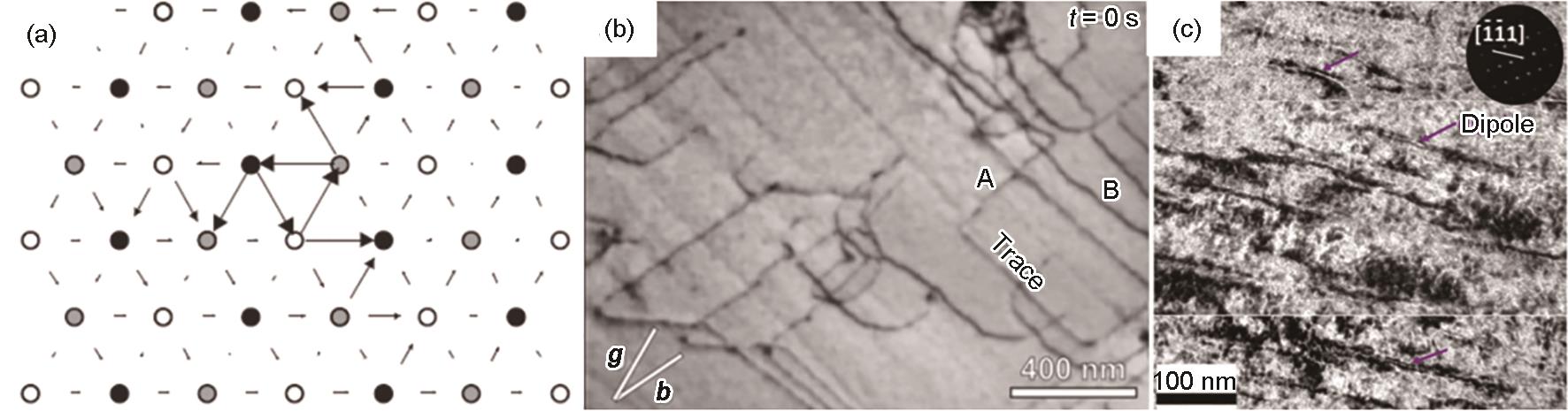
(a) differential displacement map illustrating the core structure of screw dislocations in bcc metals[
(b) in-situ TEM observation of the screw dislocations during the straining of Ti-23Nb-0.7Ta-2Zr-0.4Si alloy (t—framing time. The imaging condition was indicated by the g vector and Burgers vector b, of dislocations. Dislocations with different morphological features were highlighted by A and B, respectively)[
(c) dislocation dipoles in deformed microstructure of Ti-11.4Al-11.7Mo-1.9VSi alloy (A diffraction pattern along<